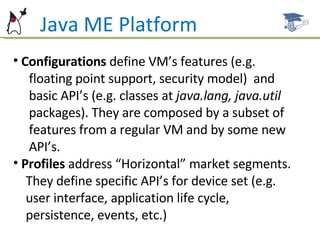
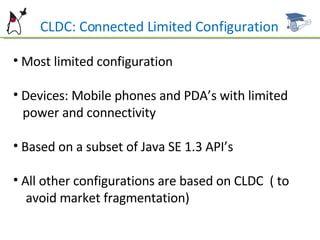
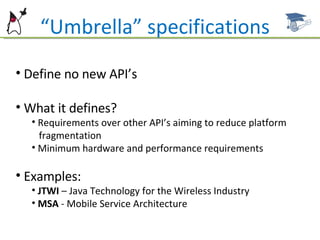
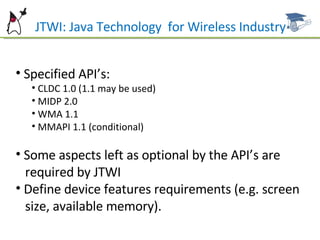
The document introduces the Java ME platform and the SCMAD certification, detailing its configurations, profiles, and specifications for resource-constrained devices such as mobile phones and PDAs. It outlines the requirements and features of the Java ME platform, including CLDC and MIDP specifications, as well as the certification exam structure and objectives. Additionally, it provides resources for further study and certification requirements for aspiring mobile application developers.











![References ALVES F. Eduardo. SCMAD Study Guide, 27/04/2008. JAKL Andreas, Java Platform, Micro Edition Part 01 slides, 12/2007. Sun Certification Mobile Application Developer Website: [http://www.sun.com/training/certification/java/scmad.xml].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter01-1226363712726224-9/85/Scmad-Chapter-01-24-320.jpg)