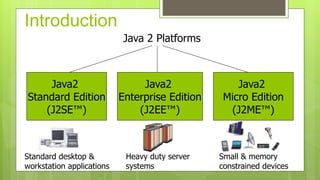
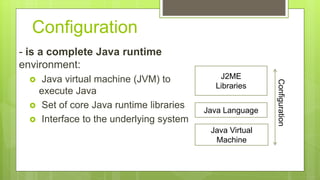
The document provides an overview of Java's various editions, with a focus on Java 2 Micro Edition (J2ME) and its key components such as configurations, profiles, and optional packages. It details the history and evolution of J2ME, highlighting its adaptations for low-end and high-end consumer devices through Connected Limited Device Configuration (CLDC) and Connected Device Configuration (CDC). Additionally, it explains the Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP) and the lifecycle of midlets, which are applications designed for mobile devices.