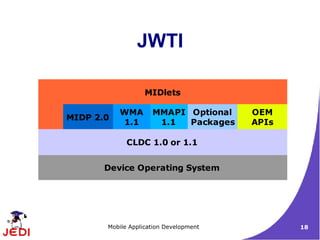
This document provides an introduction to mobile application development. It describes the characteristics of mobile devices and outlines the Java 2 Micro Edition (J2ME) architecture, including the Connected Limited Device Configuration (CLDC) and Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP). CLDC defines core Java APIs for limited devices, while MIDP provides user interface and networking APIs for mobile phones. A MIDP application called a MIDlet follows a lifecycle of being created, started, paused, and destroyed by the device's Application Management System (AMS).












![MIDlet
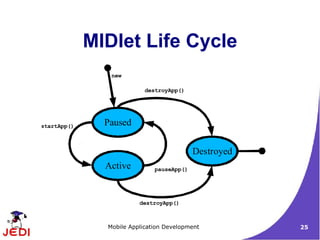
●
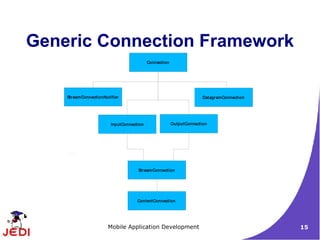
A MIDP application is called a MIDlet. The device's
application management software (AMS) interacts directly
with the MIDlet with the MIDlet's create, start, pause, and
destroy methods.
●
The MIDlet is part of the javax.microedition.midlet package.
A MIDlet must extend the MIDlet class. It can request
parameters from the AMS as defined in the application
descriptor (JAD).
●
A MIDlet does not have (and MUST NOT have) a public
static void main(String[] argv) method. It will not be
recognized by the AMS as the program's starting point.
Mobile Application Development 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-1-121207174418-phpapp02/85/Mobile-Application-Development-JEDI-24-320.jpg)