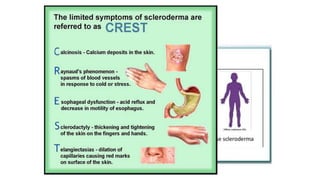
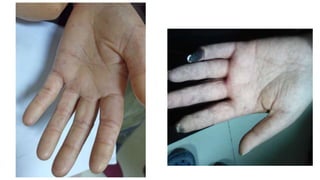
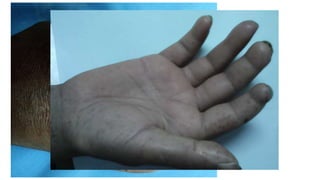
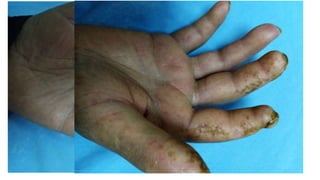
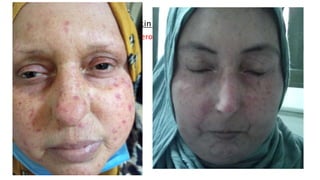
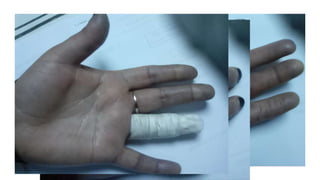
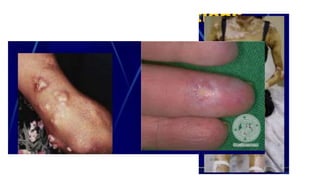
- The patient presents with dyspnea, fatigue and Raynaud's phenomenon. Physical exam shows thickened skin on fingers and telangiectasias on face and palms.
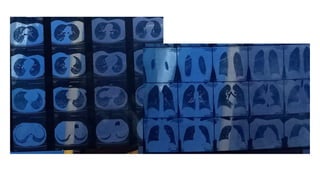
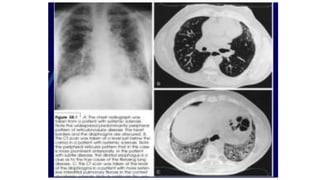
- Additional tests would include pulmonary function tests and echocardiogram to evaluate for possible interstitial lung disease and pulmonary hypertension given her symptoms and history of scleroderma.
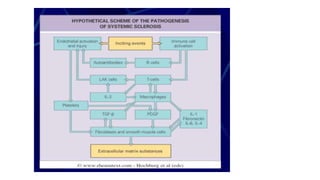
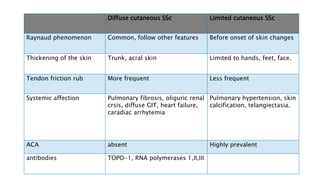
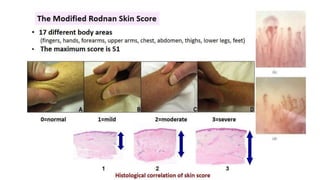
- The diagnosis is likely systemic sclerosis or scleroderma given her history of Raynaud's phenomenon for 10 years and characteristic skin findings on exam.