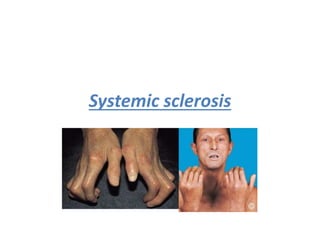
Systemic sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. It is more common in females and there are three subtypes: limited cutaneous, diffuse cutaneous, and morphea. Complications can include pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, gastrointestinal issues, and renal crisis. Treatment involves managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and treating complications aggressively. Scleroderma renal crisis, in particular, requires strict blood pressure control using ACE inhibitors.