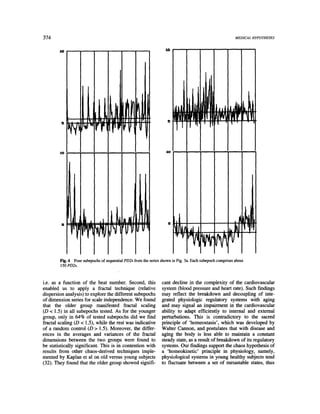
This document describes a study that analyzed the fractal organization of heart rate variability in 10 healthy subjects. The researchers calculated pointwise correlation dimensions from subjects' heart rate data and analyzed the dispersion of these dimensions over time. They found evidence that heart rate complexity is modulated by a non-random fractal mechanism and is reduced with aging, supporting the "chaos hypothesis". The relative dispersion index they introduced may help quantify cardiovascular dynamics in clinical settings.


![FRACTAL ORGANIZATION IN HEART RATE 369
20 rain. All recordings were done between 10 and series were time-delayed for successive embedding
12 a.m., and each subject was allowed to adjust dimensions (from m = 1 to m = 16). Within a given
comfortably for 10 min in a supine position before the embedding dimension, the distance (r) of each point
data were collected. They all gave informed consent to every other point was calculated. Their absolute
to the protocol. values were rank-ordered from the smallest to the
largest, and the range from the smallest to the largest
Data aquisition value was broken up into discrete intervals. Then, the
number of times a distance fell within an interval was
The ECG signals were continuously recorded using a counted. A cumulative histogram was then formed
laptop-based HIPEC ANALIZER HA-200/AH system by summing the number of instances for which a
(Aerotel - - computerized systems, Israel) with a distance was less than or equal to the upper boundary
sampling rate of 1000 Hz, and 16 bit signal resolu- of the interval. This is the correlation integral C(r).
tion. The ECG records were transferred to a personal C(r) was then plotted as a function of r on a log-log
computer for off-line analysis which started with a representation, resulting in a sigmoid-shaped curve
quality control procedure: visual inspection, baseline (in this case implying chaotic dynamics). The slope
shift evaluation and a 'moving average' (four points over the largest linear range (if there is one) was
averaging in succession along the record) for signal to measured, using linear regression (with a regression
noise ratio improvement. Then the interbeat intervals coefficient R 2 > 0.98). In this scaling range the local
(R-R) were computed using an algorithm developed exponent is constant and ~ d InC(r)/d In(r). Then, the
in our laboratory, with which an R wave threshold embedding dimension was advanced and its corre-
detection was combined with first derivative and QRS sponding slope was calculated. These slopes were
width considerations, for an accurate R wave detection. then plotted versus the embedding dimension, looking
for a saturation region, i.e. a region in which the
Attractor reconstruction slopes no longer grow. This plateau region was then
Usually the experimentalist is confronted with in- considered as the correlation dimension (D2), and its
ability to gain access to m simultaneous recordings value was calculated with a weighted average tech-
necessary to describe the system's trajectory in nique (each value in the plateau region was weighted
m-dimensional phase space. Thus, only one scalar by the variance of its underlying slope calculation).
observable can be monitored as a function of time. This process was also performed for randomized
Fortunately, it has been shown that certain properties versions of the R - R series (with similar mean and
of the dynamics are feasible through the method of variance) in order to provide confidence limits for our
time delays using Taken's theorem, as follows (23). calculations.
Consider a single time series regularly spaced in
time: xi = x%), i = 1..... N. Then a time lag "~is intro- Pointwise dimension of R-R intervals
duced, such that m-dimensional vectors are created:
xi= [x(ti), x(ti + "c)..... x(ti+ (m-1)x)]. This process is The 'point' estimate of the correlation dimension
termed embedding, and m is called the embedding (PD2) begins with the time lag calculation, followed
dimension. Through this reconstruction a phase by the embedding procedure, as described before.
space is spanned and dynamical and metric measures Then, starting with the initial point in the series, its
(Lyapunov exponents, dimensions) may be accessible. local correlation integral is calculated, i.e. the dis-
tances are taken with respect to this point and ranked-
ordered as usual, for each embedding dimension
Correlation dimension of R-R intervals
(m = 1..... 16). The slopes for each m were evaluated
The correlation dimension was calculated using the using a linear regression (R2> 0.98), and a slope
method of Grassberger and Procaccia (G-P) as follows values, corresponding to m = 8 ..... 16 were stored in
(24). First, for each R - R interval series, the normal- a file. The algorithm steps to the next point in the
ized autocorrelation function given by: series, and the whole procedure is repeated until the
whole file is exhausted. Then comes the procedure
~g('~) = {(I/N) £[R-R)i - < (R-R) >][(R-R)i+x -
that we call slope convergence, which calculates the
< (R-R) >] }/{(I/N) Z[R-R)i - < (R-R) >]2}
slope of the 9 slopes versus the embedding dimensions
where (m = 8 ..... 16) using linear regression. Our innova-
tion was to subject this to the imposition of three
< (R-R) > = (l/N) Z (R-R)/
conditions as follows: Ill if the slope was less than
was constructed, and its first zero crossing was calcu- 0.5 and larger than -0.23, we considered this as good
lated to provide the time lag (x) in beats. Then, the convergence and the PD2 could be estimated using](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/science-111115101920-phpapp02/85/Science-3-320.jpg)

![FRACTAL ORGANIZATION IN HEART RATE 373
10
I N of points
round(D2)-
alp-)0.50
0 N o! p-
4z m
0
| round(O2)- I N of p- 0
i
I round(D2}-
round(D2)-
2 H o f p-
3 H of
rouncl(D2)m 4 N o f
roun4(D2)- S N of
roarl4(D2)- 6 N o f
p-
pm 246
p- Se2
pm 146
0
"k
roun4(D2)- 7 X o f p - 64
round(D2)- 8 g of p,, ].
round(D2)- 9 N o f p- 0
round(D2)-20 N of p- 0
i
roun4(D2)-22 N of p- 0
round(D2)-12 N of p- 0
round(D2)-13 N of p- 0
round(D2)-14 N of p- 0
round(D2)-25 N of p- 0
round(D2)-26 H of p" 0
round(D2)-17 N of p,, 0
round(D2)-28 N of p- 0
round(D2)-lg N Of p- 0
round(D2)-20 N of p- @
H of exclu sip<-0.23 2v •
a
0 250 500 750 1000 1250
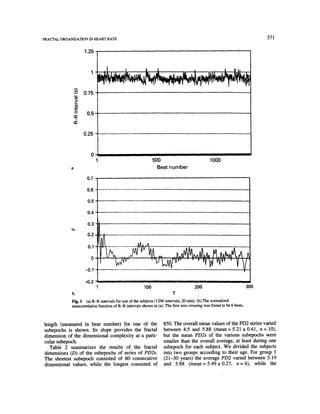
Fig. 3 (a) Serial pointwise dimensions (PD2s) as a function of the beat number (nref) for one of the subjects. The zero-valued PD2s are
only 'sign' of the instances for which a dimensional estimate could not be derived. (b) A histogram showing the distribution of the beat
number as a function of the rounded dimensional estimates. At the two extremes of the diagram we note the number of points for which a
random fluctuation is supposed to take place (slope > 0.5), and on the other side the number of point for which an estimate could not be
found (slope < -0.23).
chaotic attractor. Later, other groups provided sup- periodic behavior was seen in normal subjects, with
portive evidence to this hypothesis (18,28), although an increase in complexity during sleep (21). Recent
recently Kanters et al found weak evidence in favor studies found the dimensional complexity during
(19). Thus, the existence of low dimensional chaos in experimental myocardial infarction in pigs to decline
cardiac activity, at least at the whole organ level of significantly prior to the occurrence of ventricular
activity, is still an open question. Most of the estima- fibrillation (31). This has motivated Skinner et al
tions were based on dimensional estimations of the to evaluate lethal arryhythmias in various groups of
widely used Grassbeger-Procaccia algorithm. Imple- high-risk patients. It was found (with high specificity
mentation of this algorithm needs several precondi- and sensitivity) that the dimensional complexity
tions to be observed (29,30): an adequate choice of is reduced hours before the occurrence of lethal
embedding dimension, a suitable choice of the time arrhythmias (22).
delay needed to span the attractor, low level of noise Our results support the contention of low-
present in the system, stationarity, and the data set dimensional chaos, as proposed by others. The corre-
should not be too short. Some of these requirements lation dimension was found to vary between 3.29
are not attainable in biology and in physiology in and 5.16, with a mean of 4.01 + 0.54 (n = 10). The
particular. Moreover, the G-P algorithm provides a average pointwise dimension ranged between 4.58
dimensional estimate which averages out possible and 5.88, with a mean of 5.21 + 0.41 (n = 10). Further-
relevant dynamical features. Recently, the intro- more, we noticed that our subjects could be divided
duction of the pointwise dimension algorithm, which into two groups according to age as follows: group 1
provides series of 'point' dimensions, has provided (21-30) years, n = 6) had a higher average, 5.49 + 0.27,
some solutions to the limitations of the G-P algo- than group 2 (47-56 years, n = 4 ) at 4.79+ 0.17.
rithm, namely, non-stationarity and record length. Our innovation in this study was twofold. First, we
This method was implemented for heart transplant included in the dimensional complexity algorithm
recipients and the dimensional complexity was found means to include both instances of low-dimensional
to oscillate almost periodically (20). Also, a roughly chaos and stochastic bursts in a sequential manner,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/science-111115101920-phpapp02/85/Science-7-320.jpg)