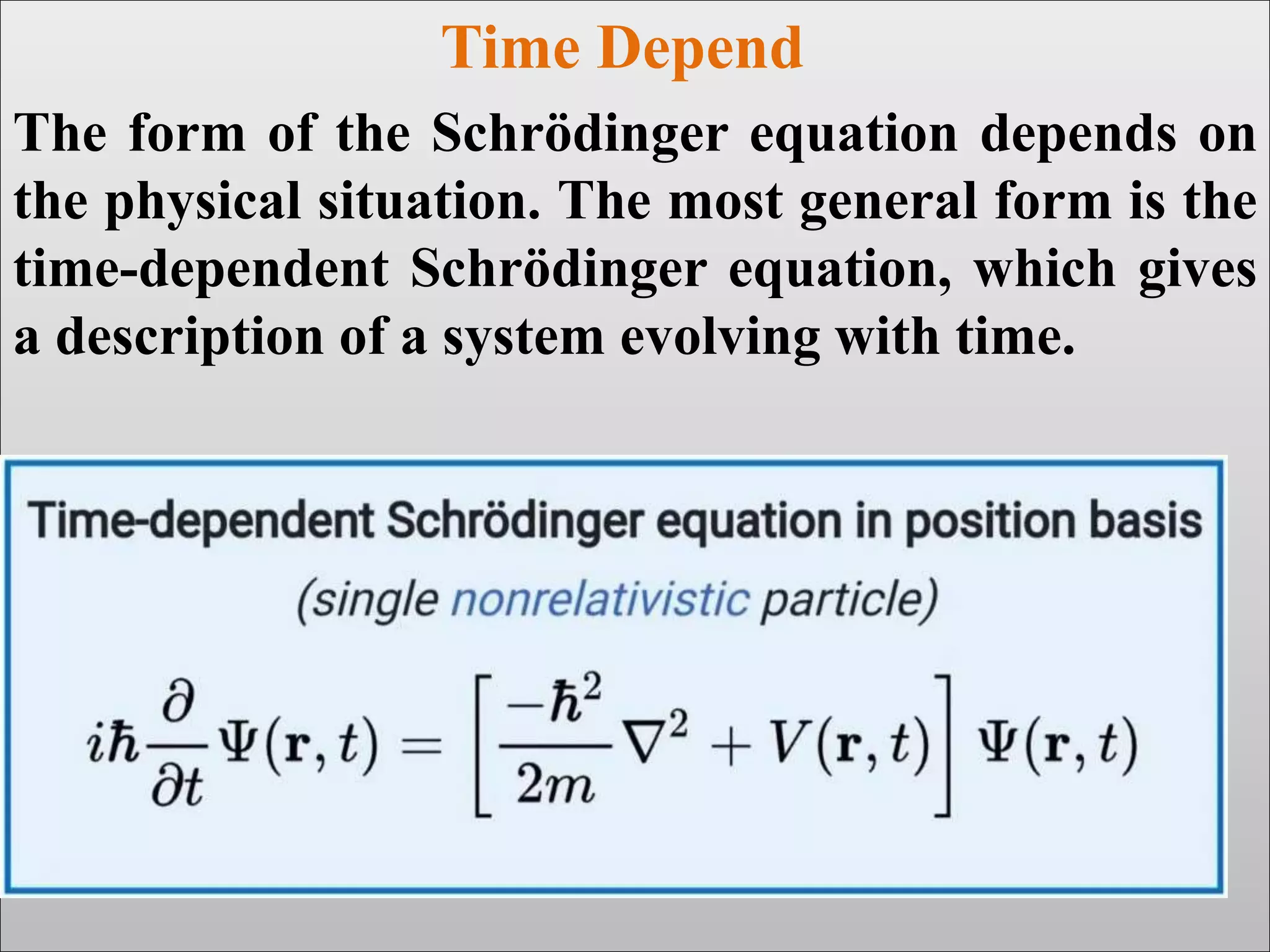
The document discusses the Schrodinger equation, which is a partial differential equation that uses the concepts of energy conservation and kinetic and potential energy to describe the behavior of electrons bound to an atom's nucleus. It has both time-dependent and time-independent forms. The time-dependent equation describes how a quantum system evolves over time, while the time-independent equation predicts stationary states. The Schrodinger equation is widely used in physics and chemistry to study atomic structure and find allowed energy levels of quantum systems.
![University of Halabja
College Of Science
Department Of Physics
3rd Stage
[Schrodinger equation]
Prepared by : Supervised :
Shene Aziz Mr.Yousif Hussein
Gyabnd qubad](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shoedengerequation-230219113704-74610d84/75/Schrodinger-equation-pptx-1-2048.jpg)