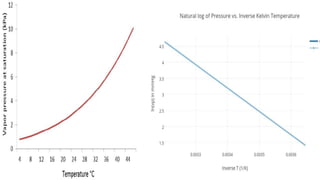
The document is a lab report on measuring the vapor pressure curve of water. It includes an introduction to vapor pressure, how it increases with temperature. The history discusses Raoul's discovery about vapor pressure of solutions. The aim is to determine the vapor pressure curve of water at 200C and 50 bar and calculate the heat of vaporization. The lab used a high pressure steam boiler, beakers, burner and measured vapor pressure at various temperatures, recording the data in a table. Calculations included converting between Celsius and Kelvin and plotting vapor pressure against the inverse of temperature on a graph. Vapor pressure is important in applications like frying foods.





![Apparatuses:
1]High-pressure steam boiler
2]Beaker DURAN
3]Stand base V-shape
4]Heat protective gloves
5]Safety goggles
6]butane gas burner
7]butane cartridge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shenegull-230218210331-abaa44dd/85/shene-6-320.jpg)

![Aim of vapor and pressure:
1]Determining the steam pressure curve of water
at 200c and pressure near50bar.
2]Determine heat of vaporization of water.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shenegull-230218210331-abaa44dd/85/shene-8-320.jpg)

![Calculation:
k=c+273
1]T=200c=473.15k
T=1/T K=1/K
1]T=473.15K=1/473.15=2.113*10^-3K^-1
P(bar)=ln(p)
1]19bar=ln19=2.94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shenegull-230218210331-abaa44dd/85/shene-10-320.jpg)