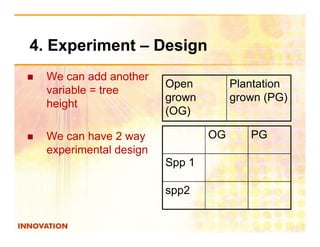
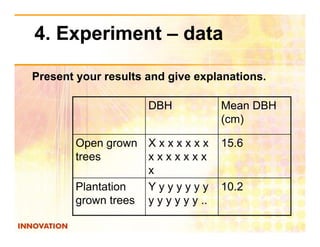
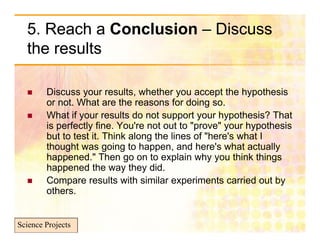
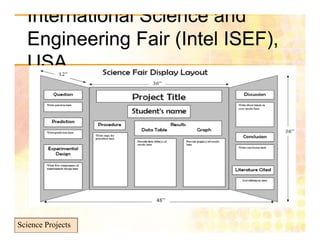
The document is a guide on how to effectively conduct science projects, especially for students, highlighting the steps involved from topic selection to experimentation and conclusion formation. It emphasizes the importance of original ideas, well-defined objectives, and proper data presentation, while also mentioning notable science fairs and competitions. Additionally, it discusses challenges faced by students in environments with examination-based education systems, particularly in accessing resources and conducting experiments.