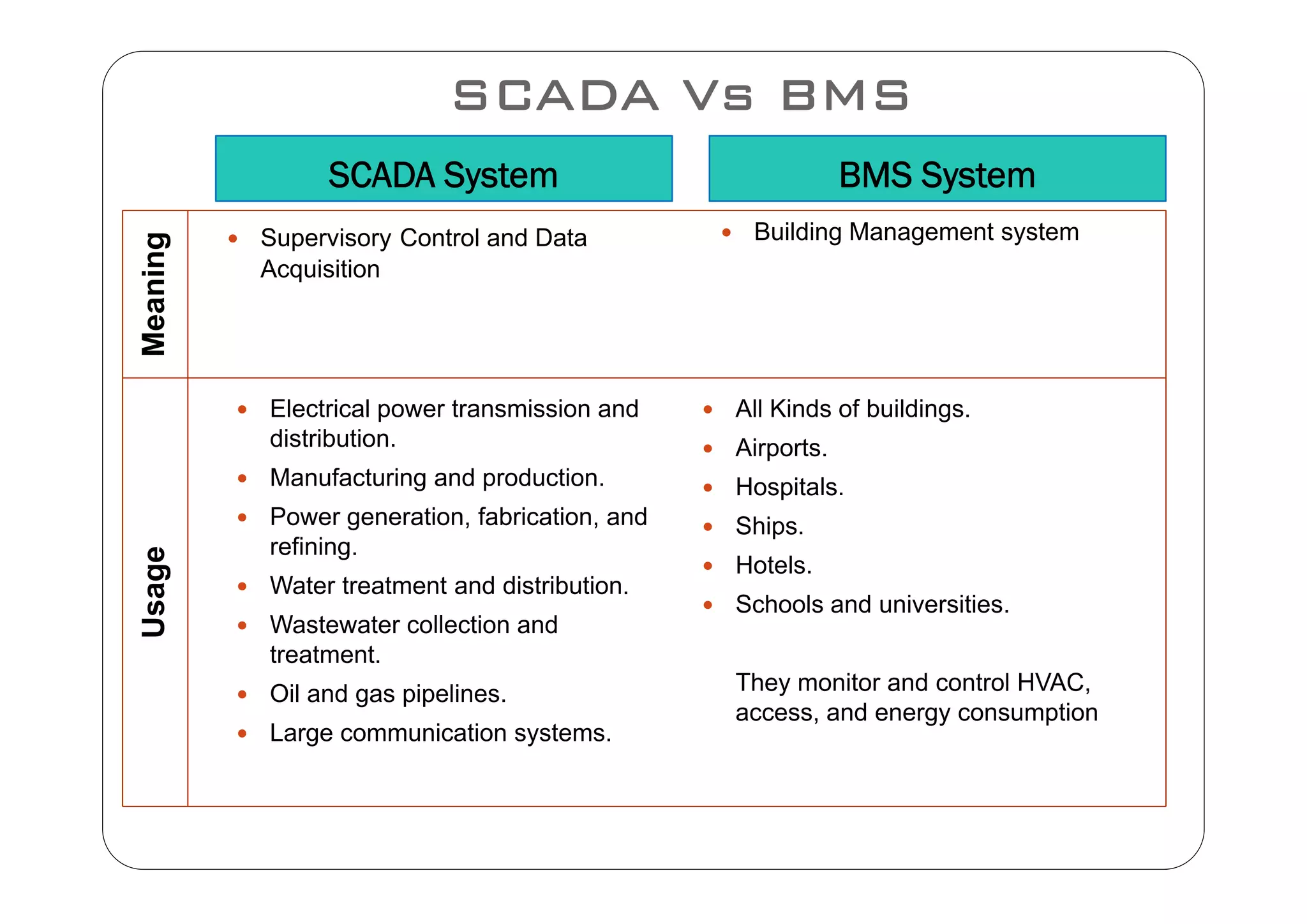
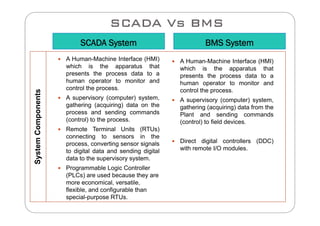
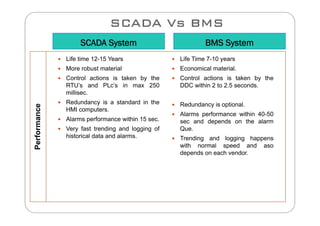
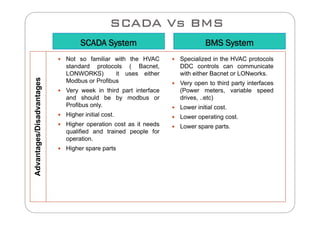
This document compares SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and BMS (Building Management System) in terms of their meaning, usage, components, systems, performance, protocols, advantages, and disadvantages. SCADA is used for electrical power transmission and large industrial processes, while BMS is used for managing all aspects of buildings. Key differences include SCADA having a longer lifetime, faster response times, and higher costs, while BMS integrates more easily with HVAC systems and has lower operation and spare parts costs.