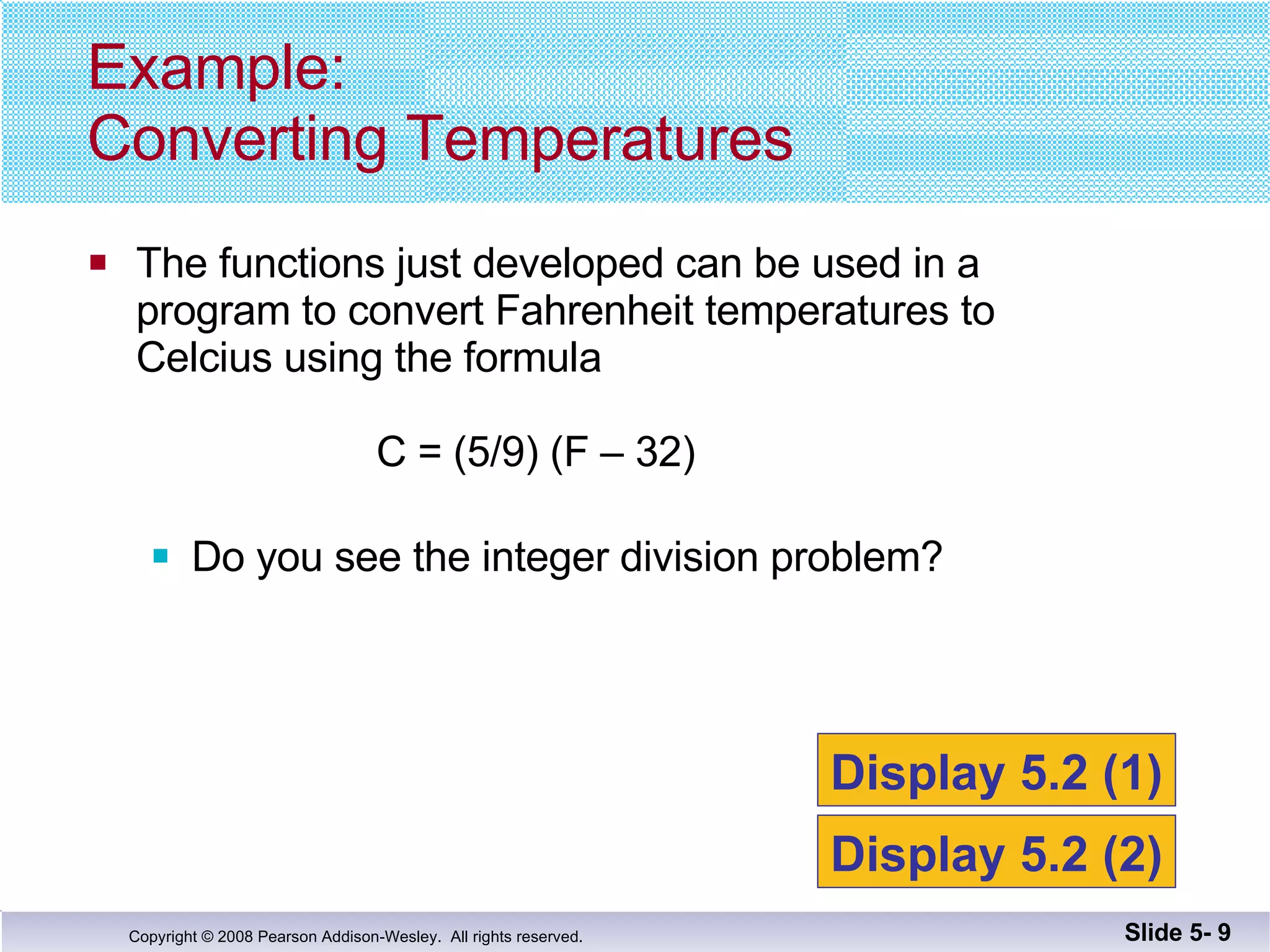
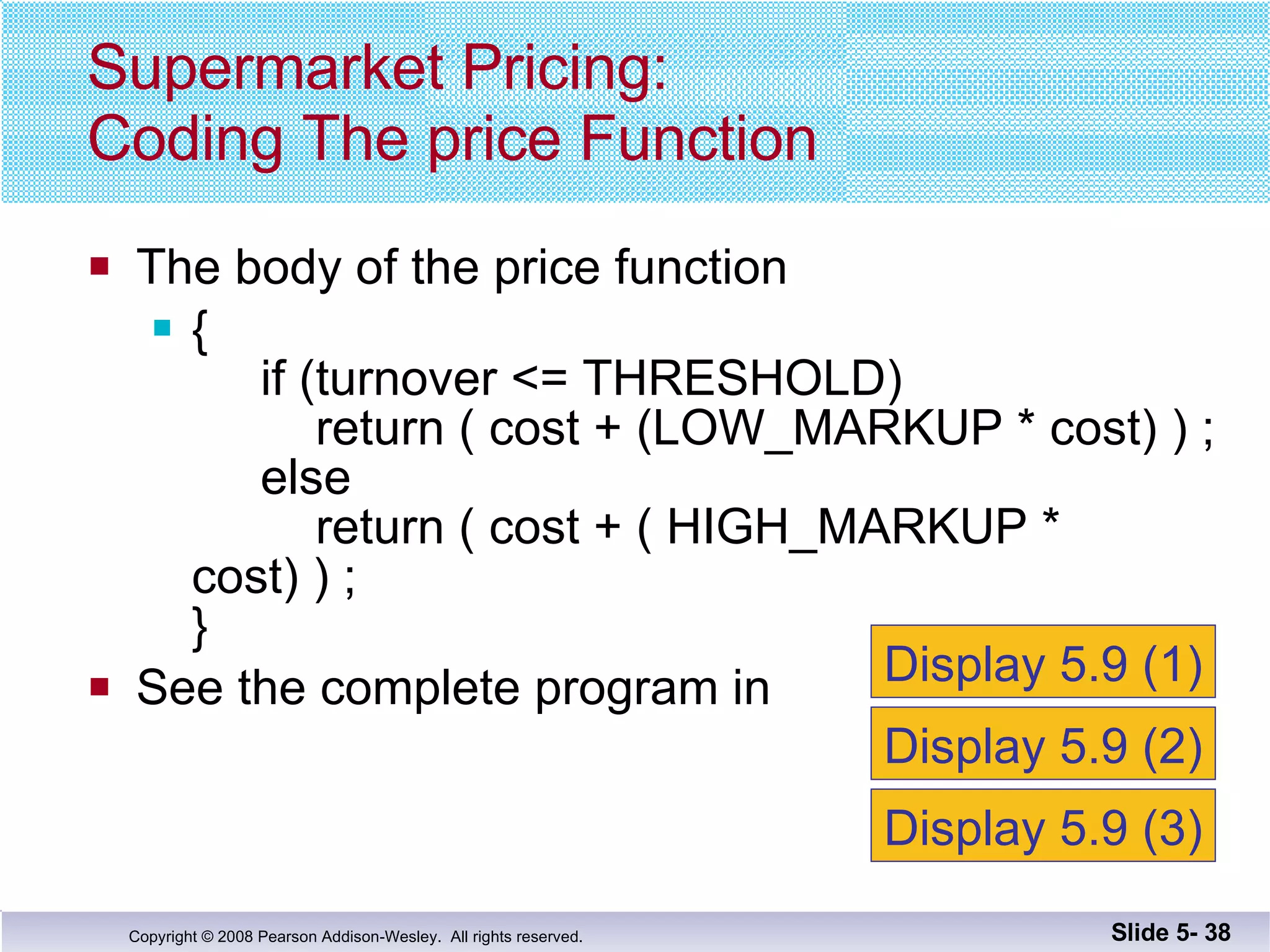
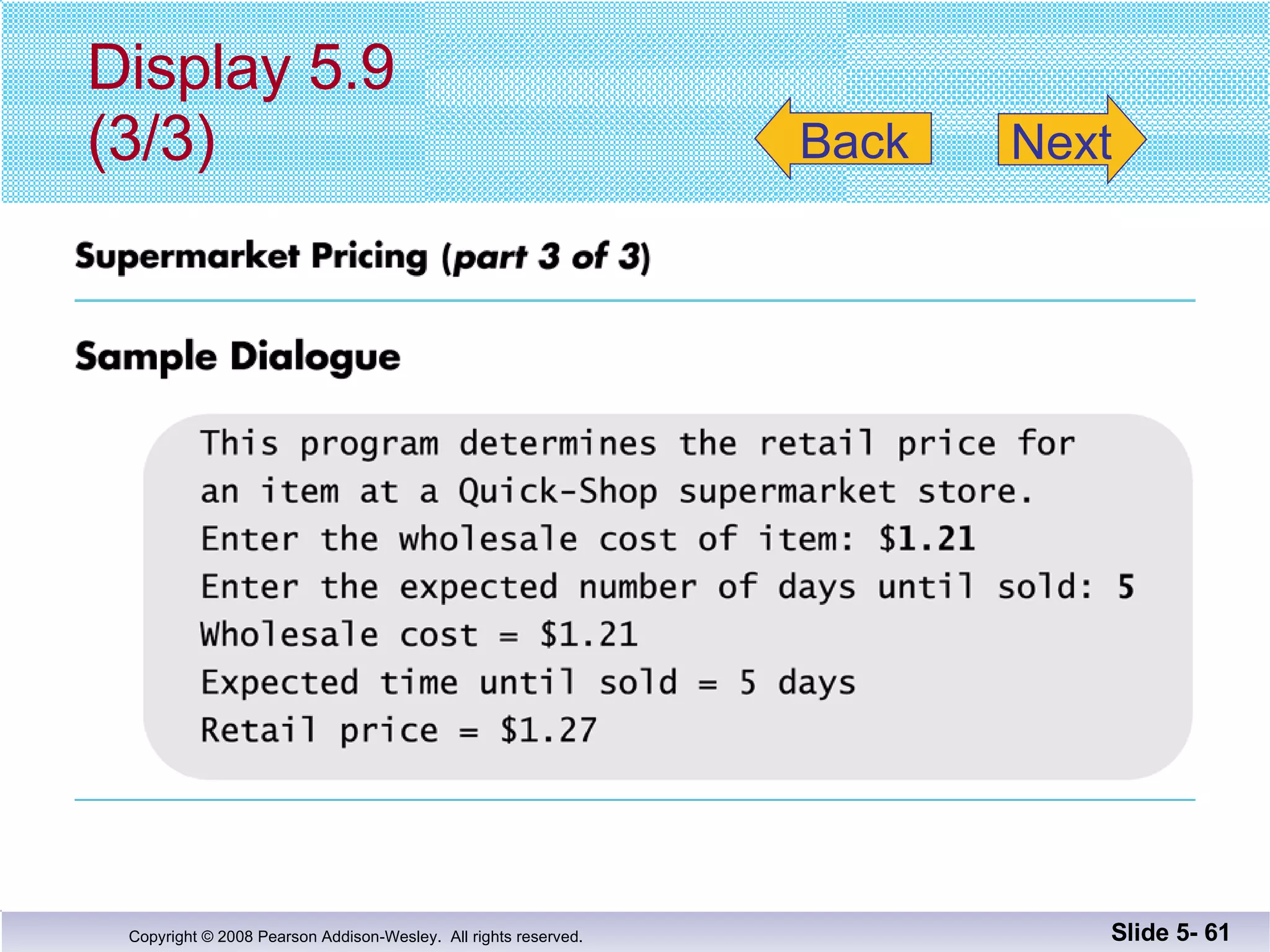
This document summarizes key points about functions from Chapter 5:
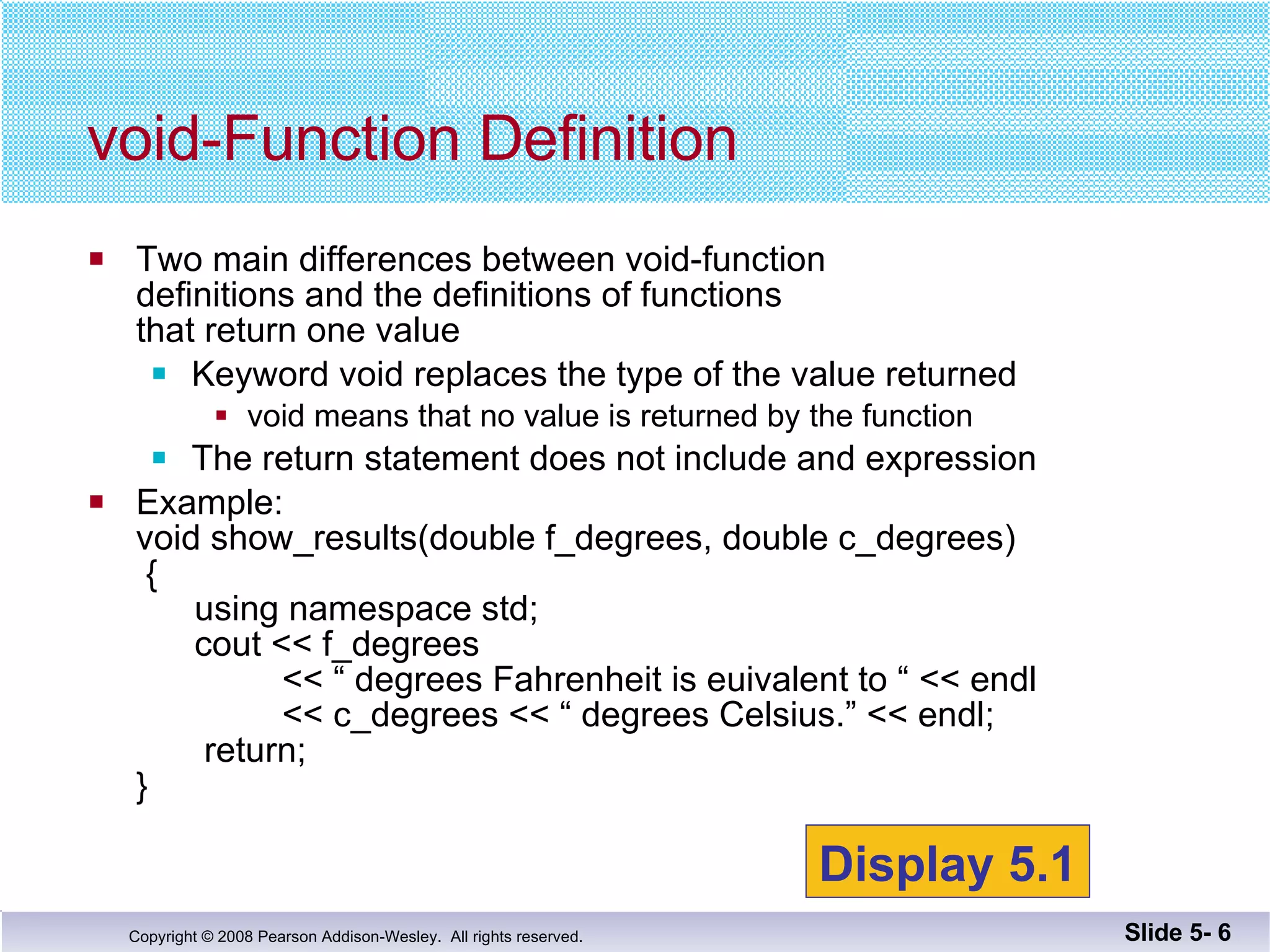
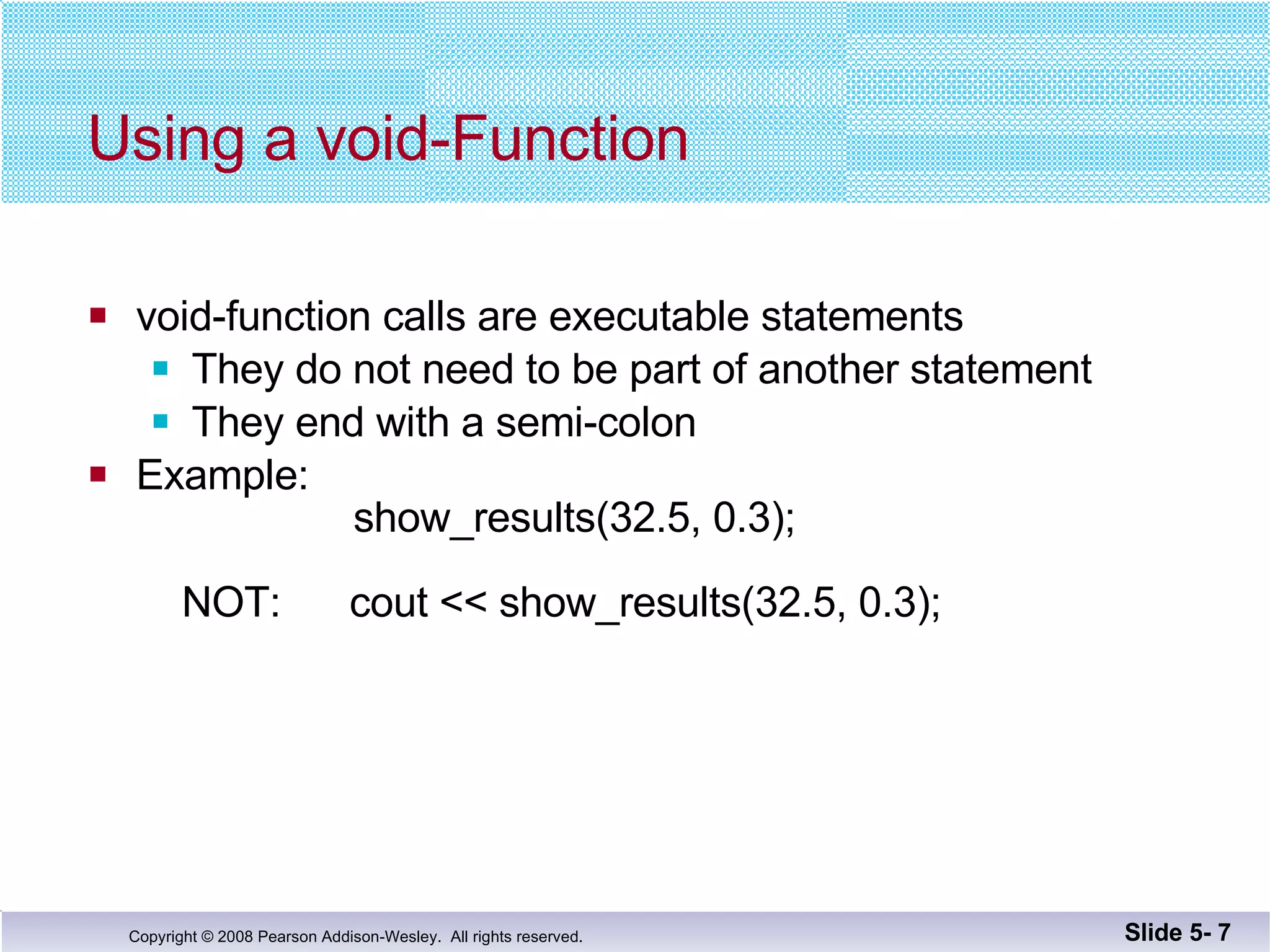
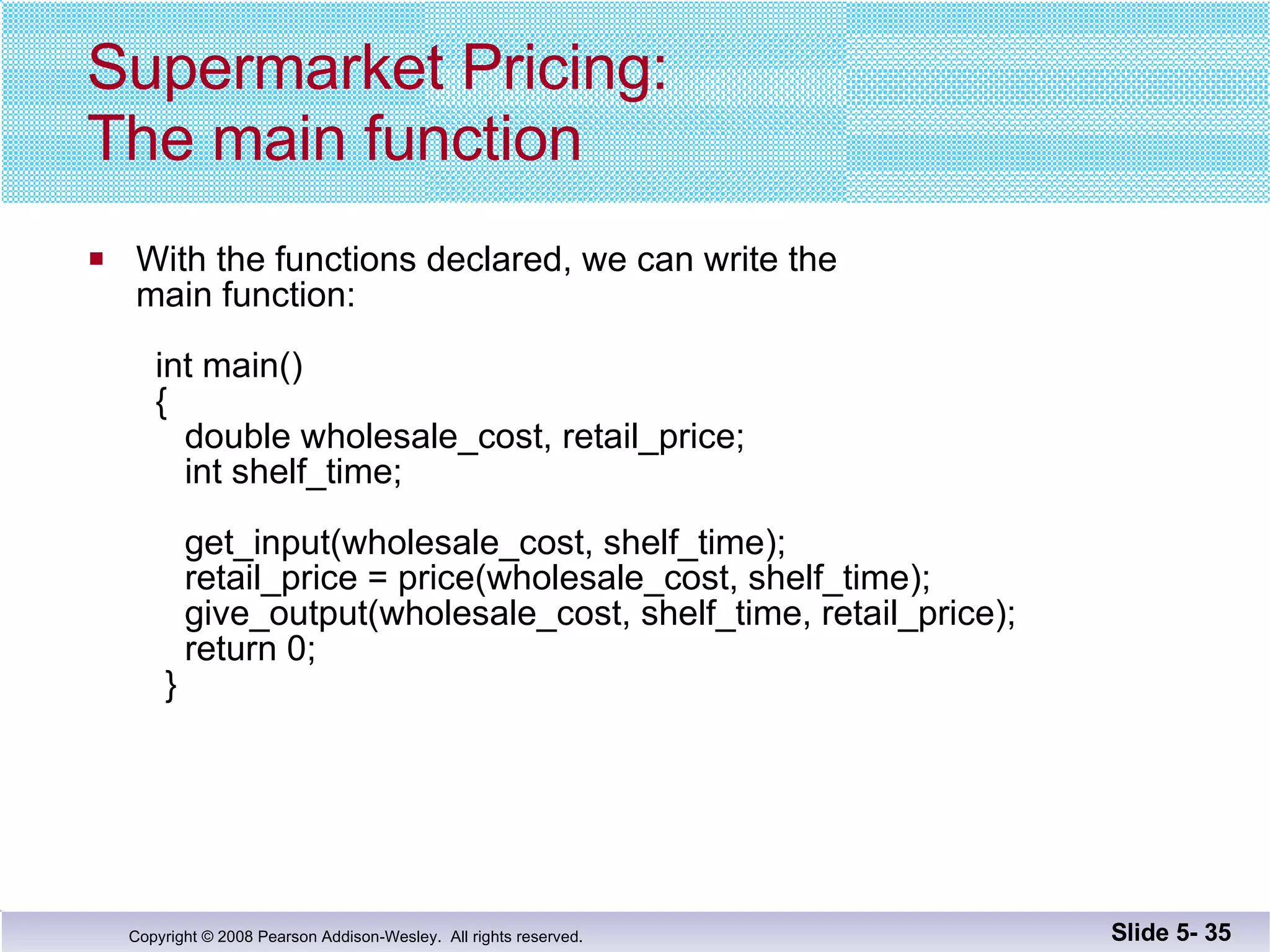
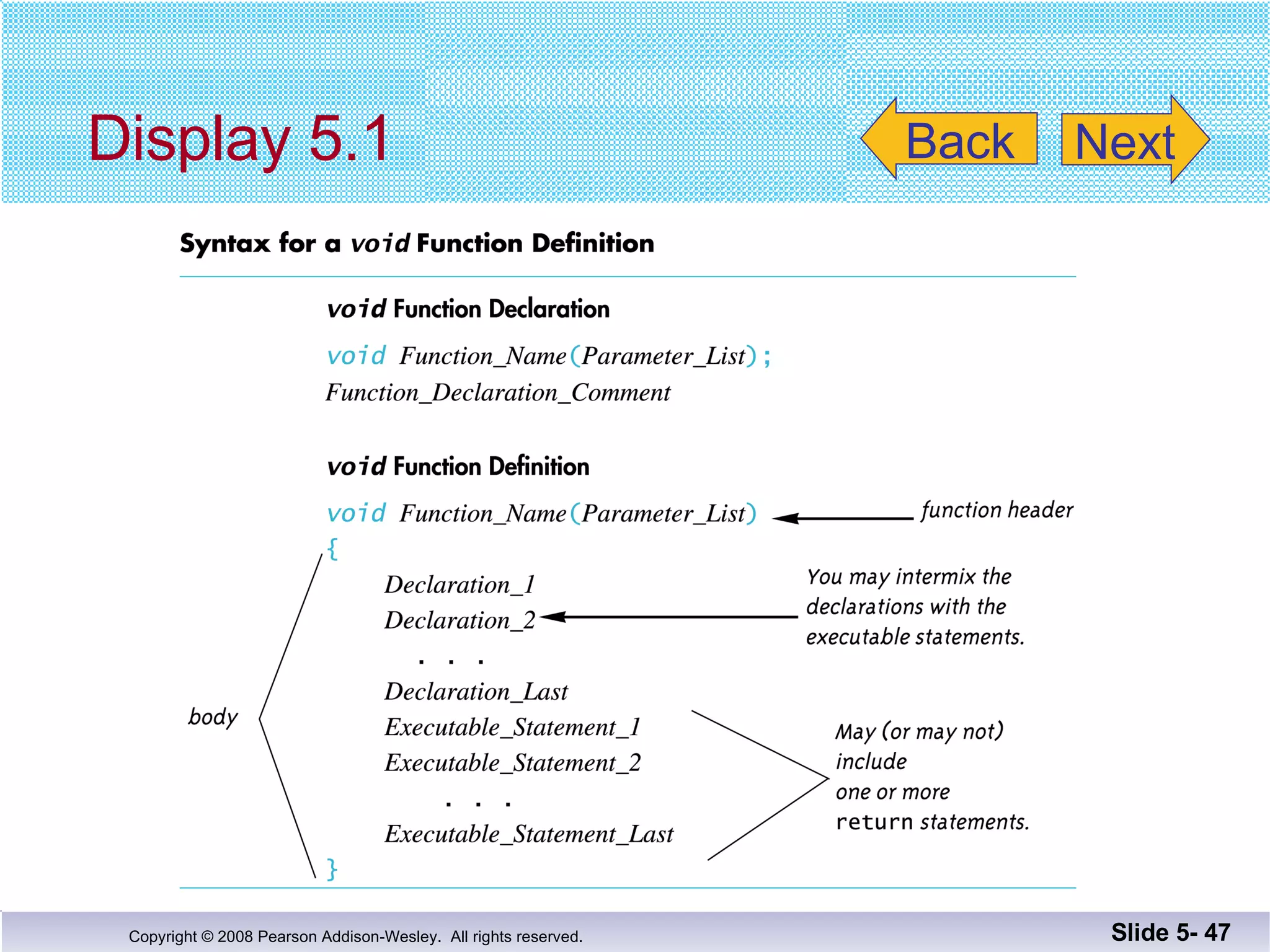
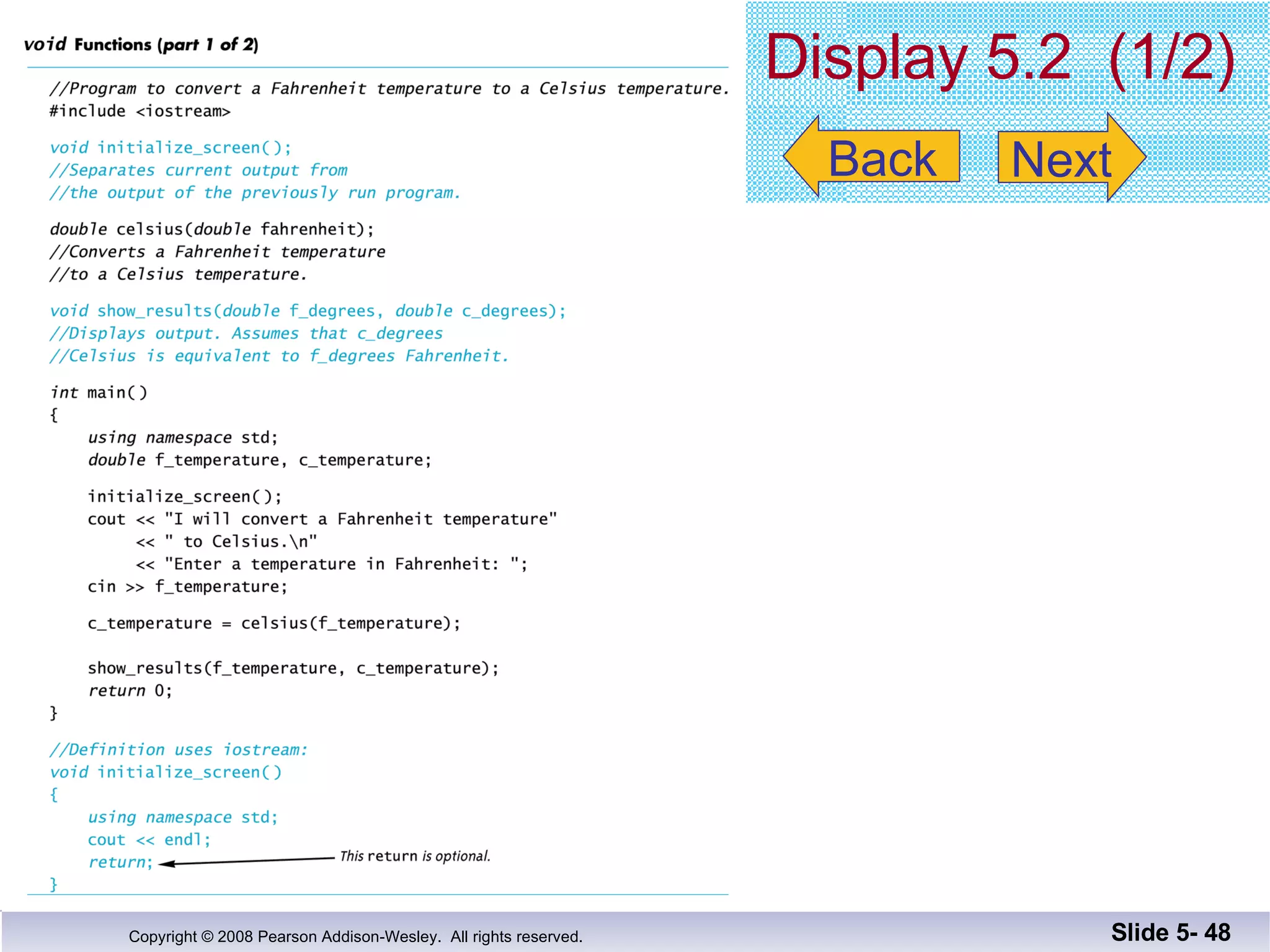
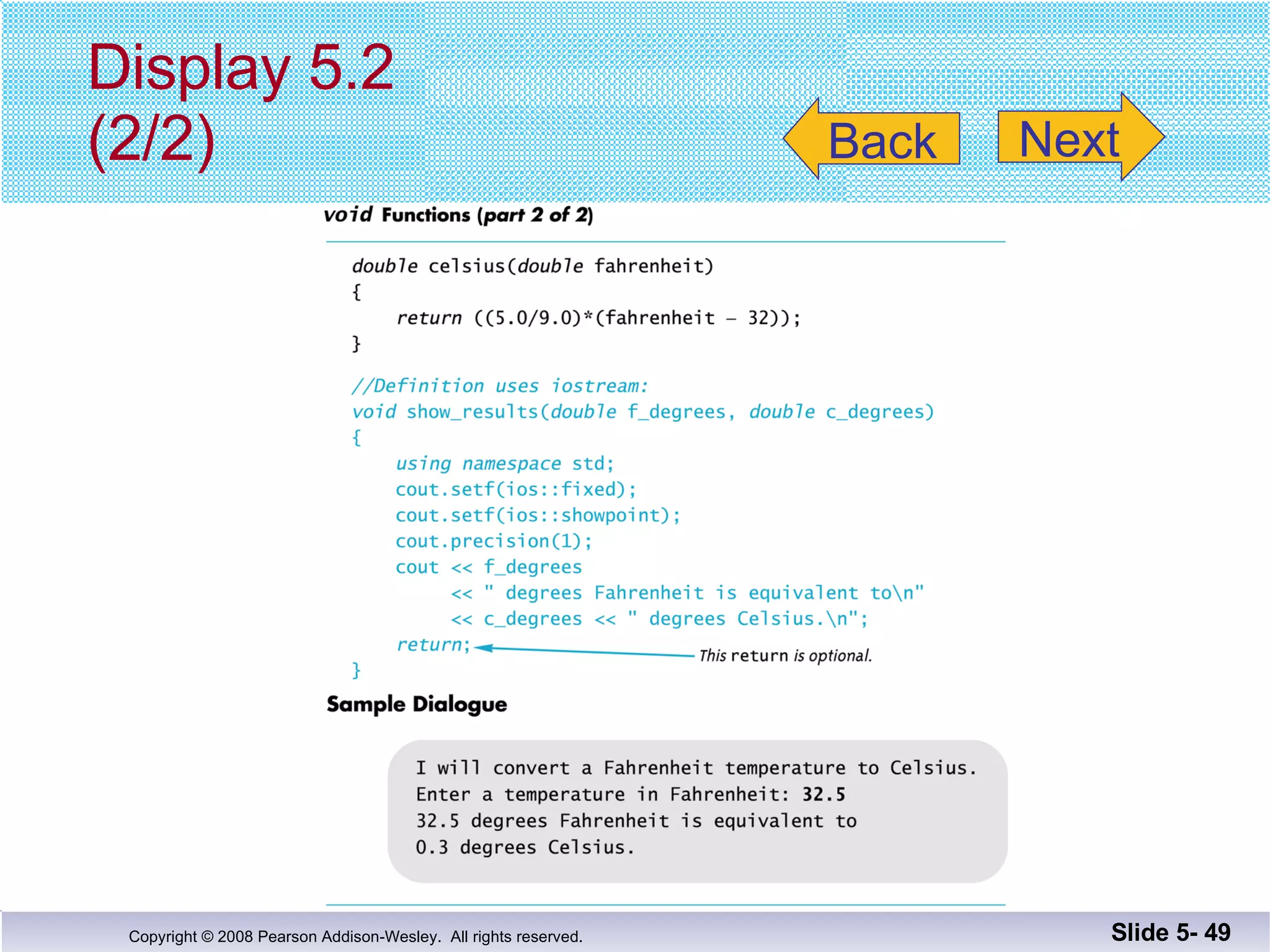
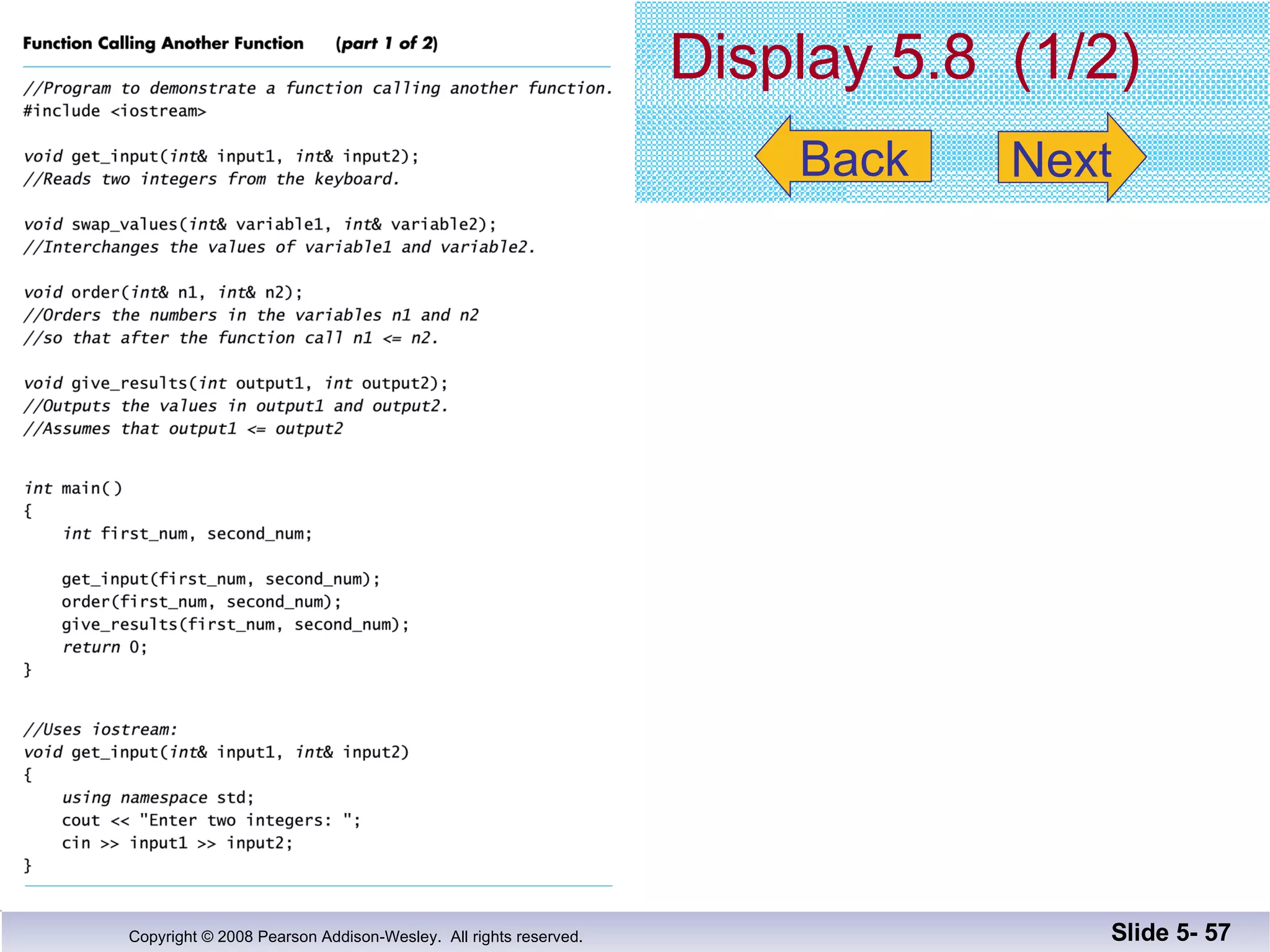
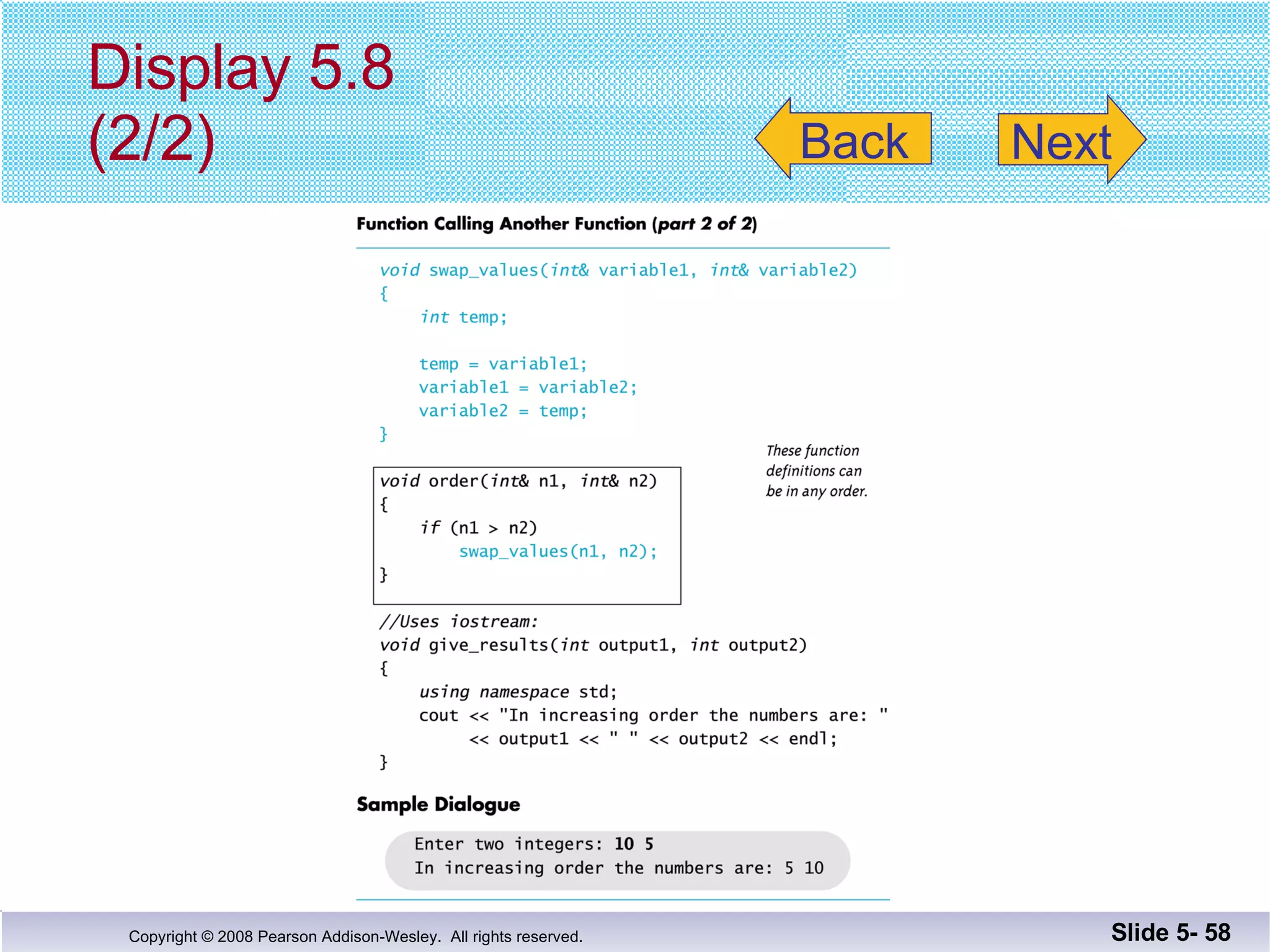
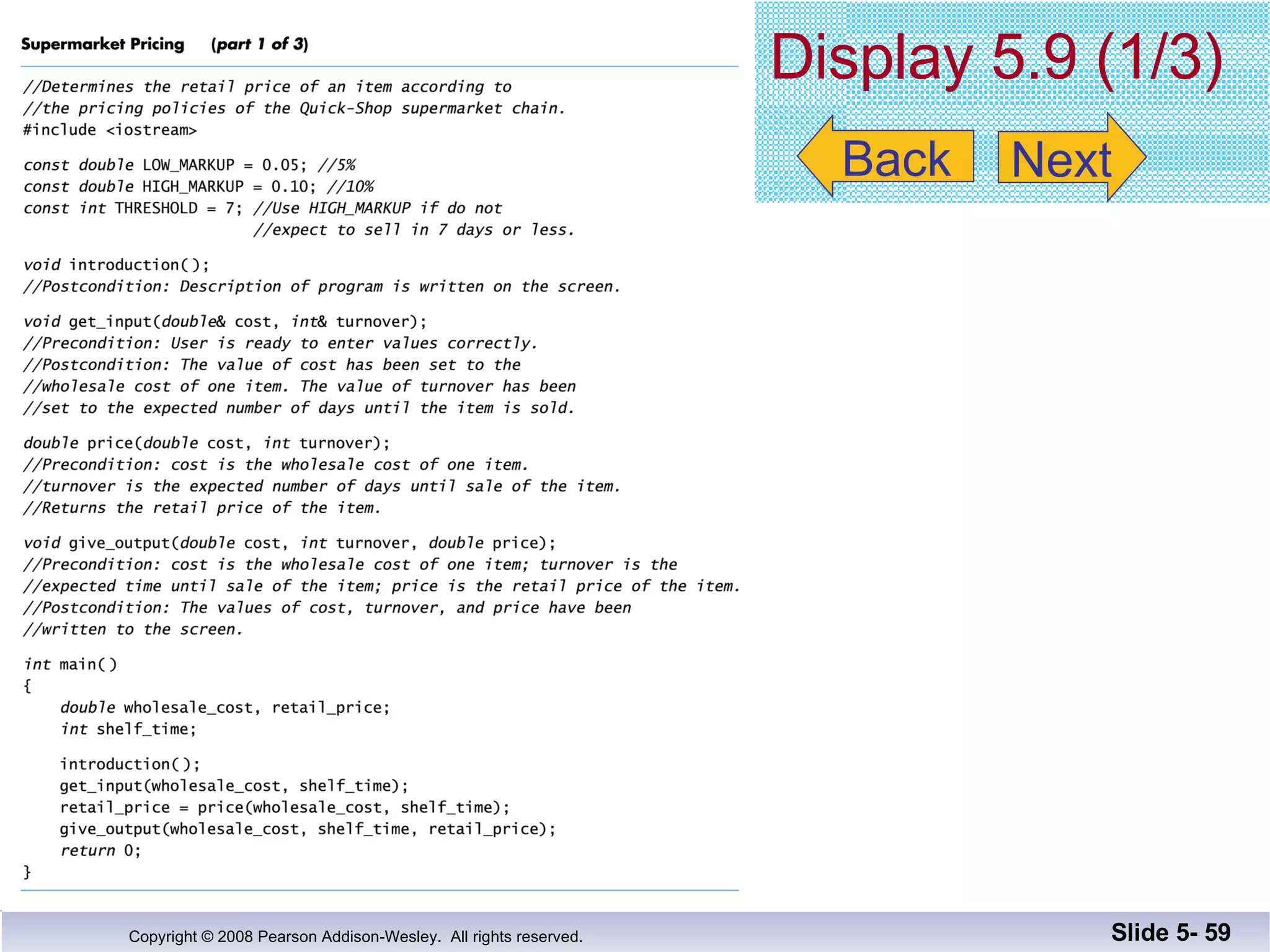
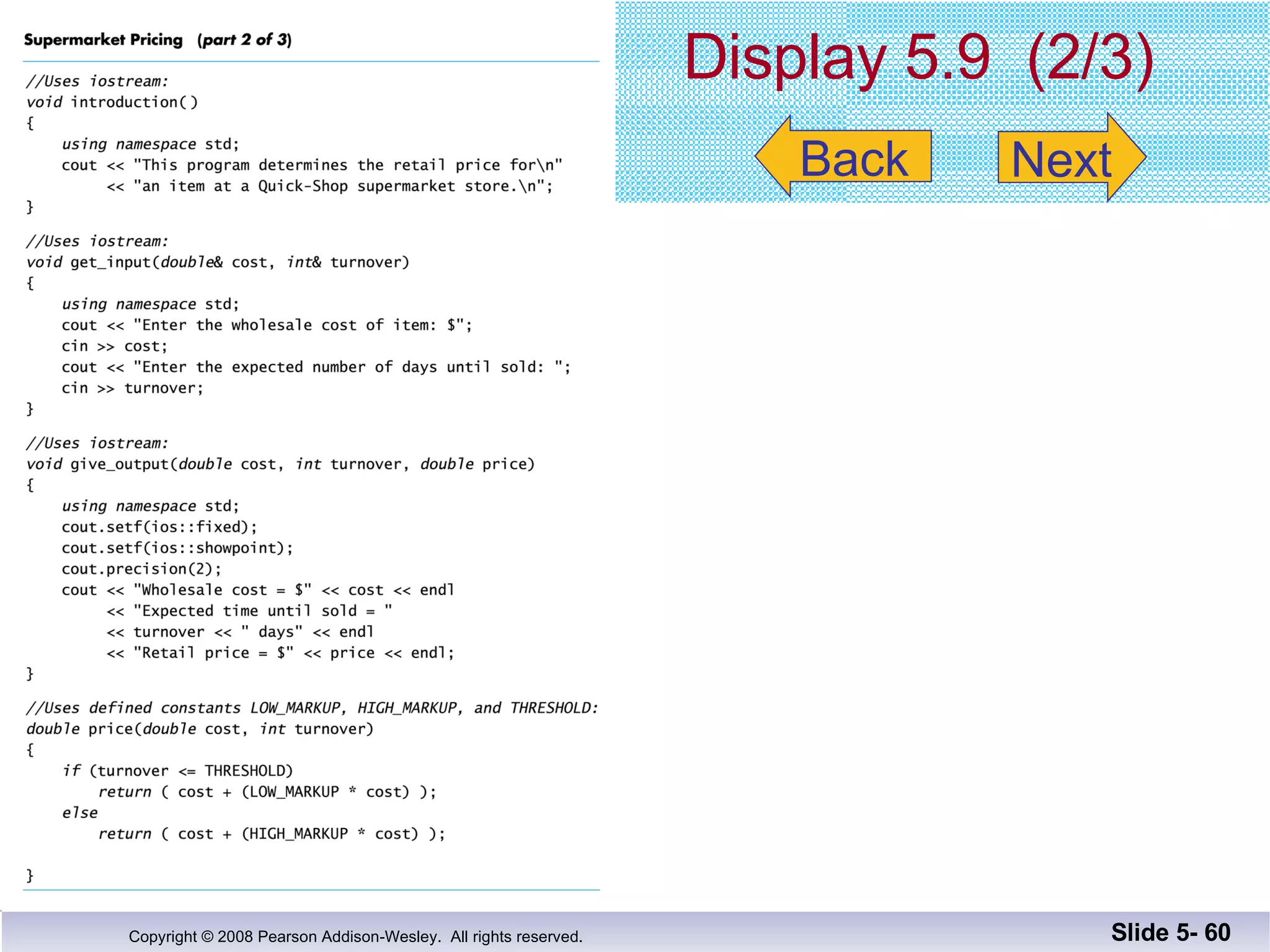
- Void functions can be used to implement subtasks that return no value or multiple values. They differ from value-returning functions in their return type and lack of return expression.
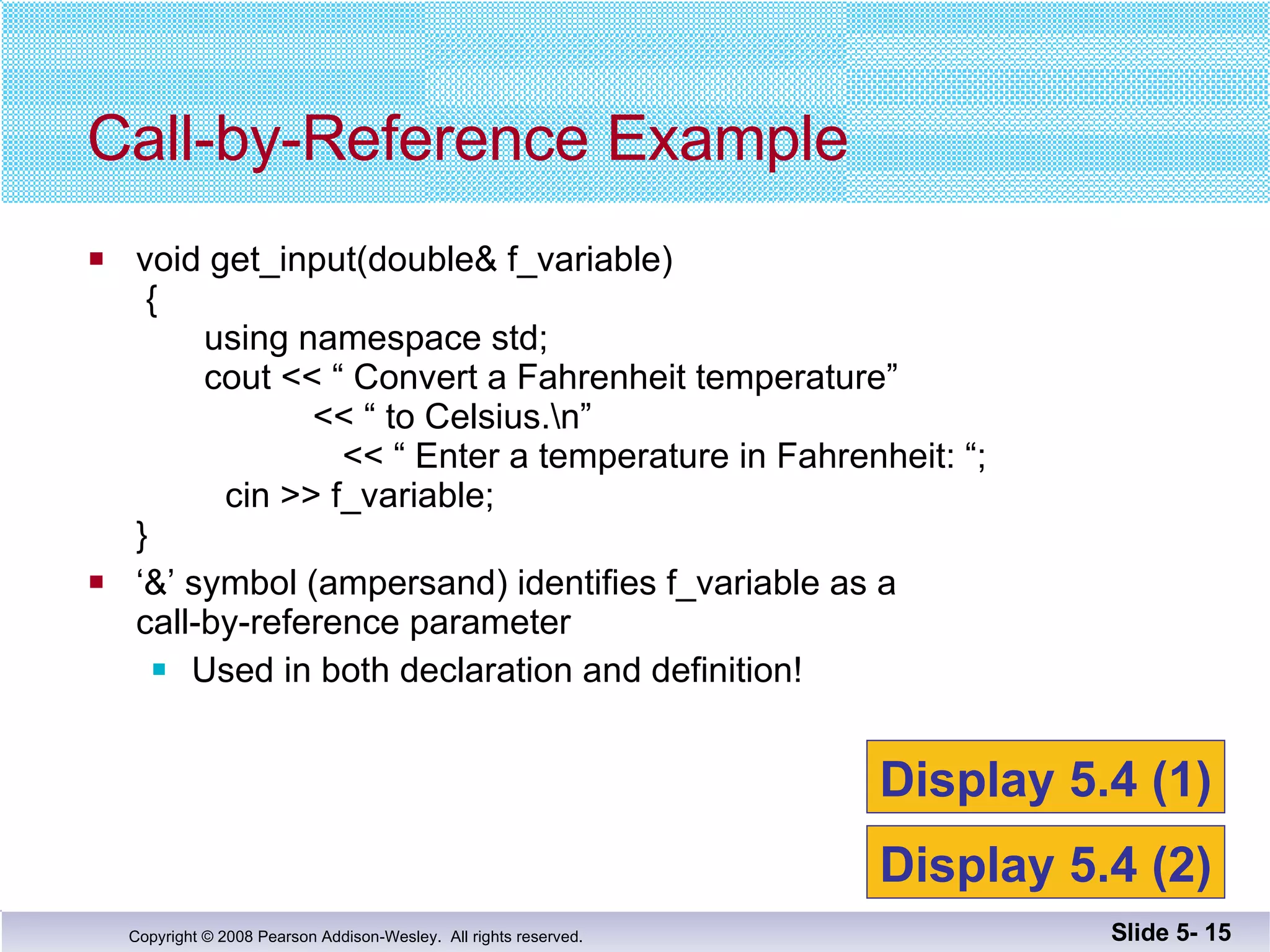
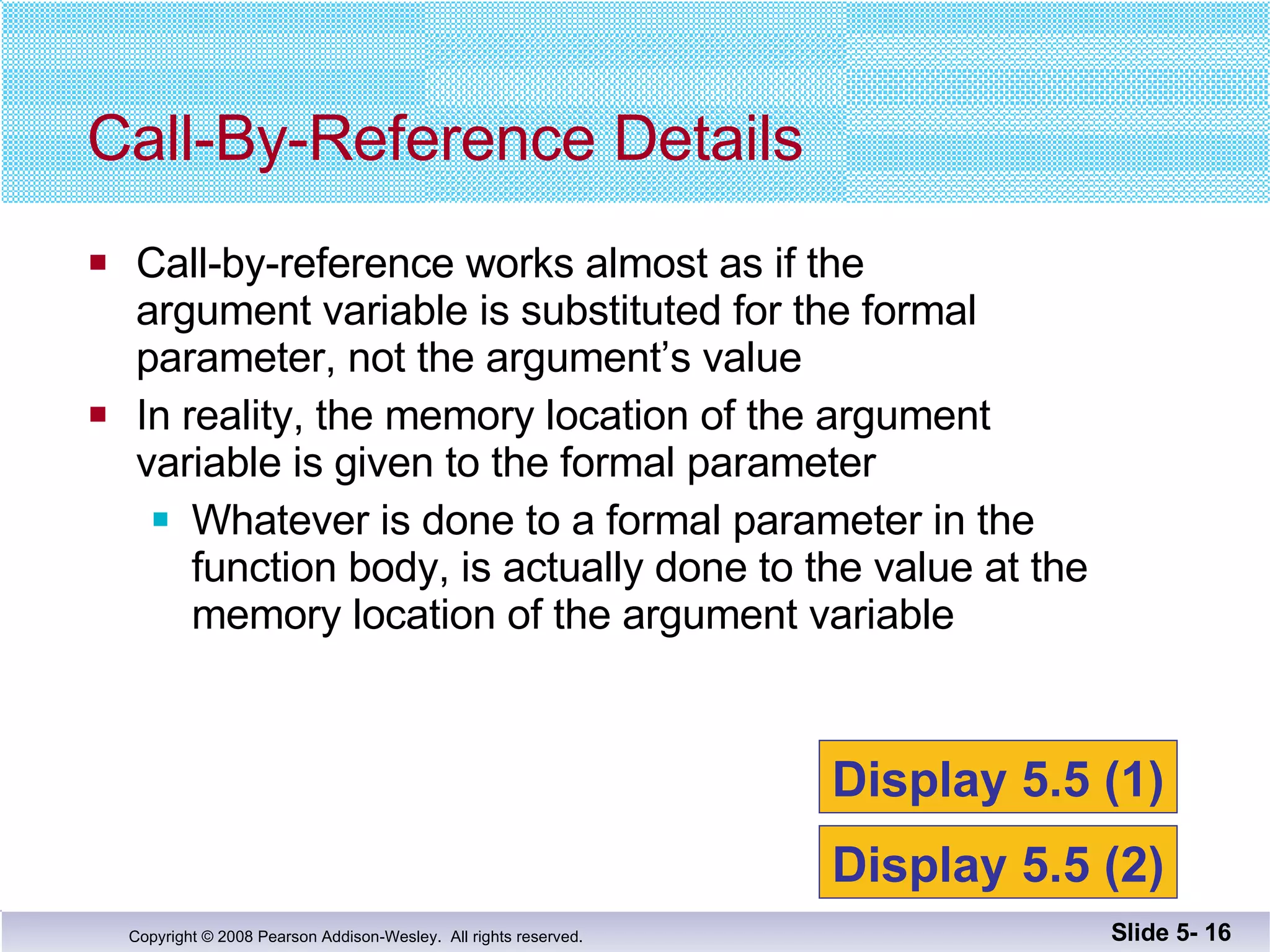
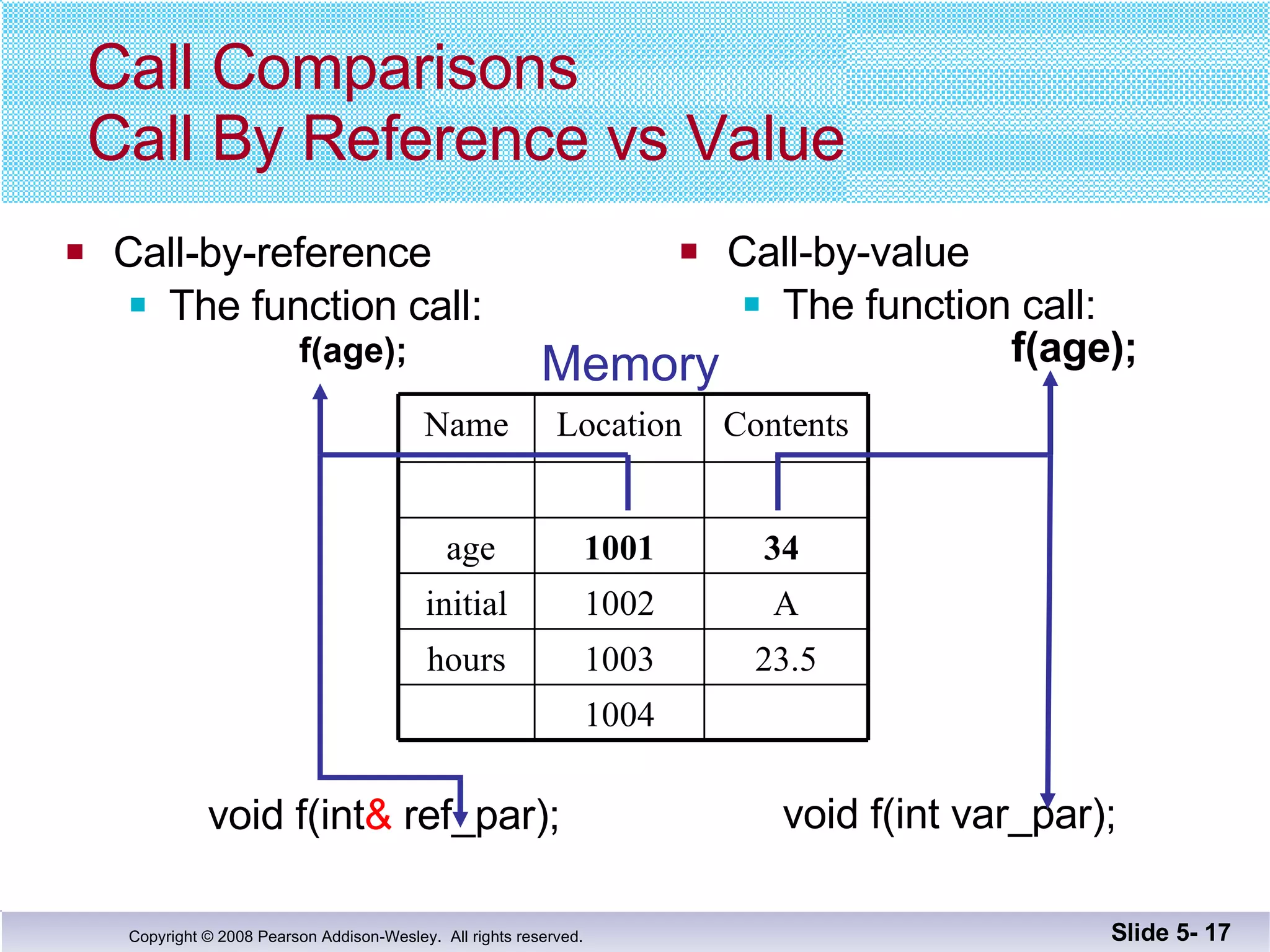
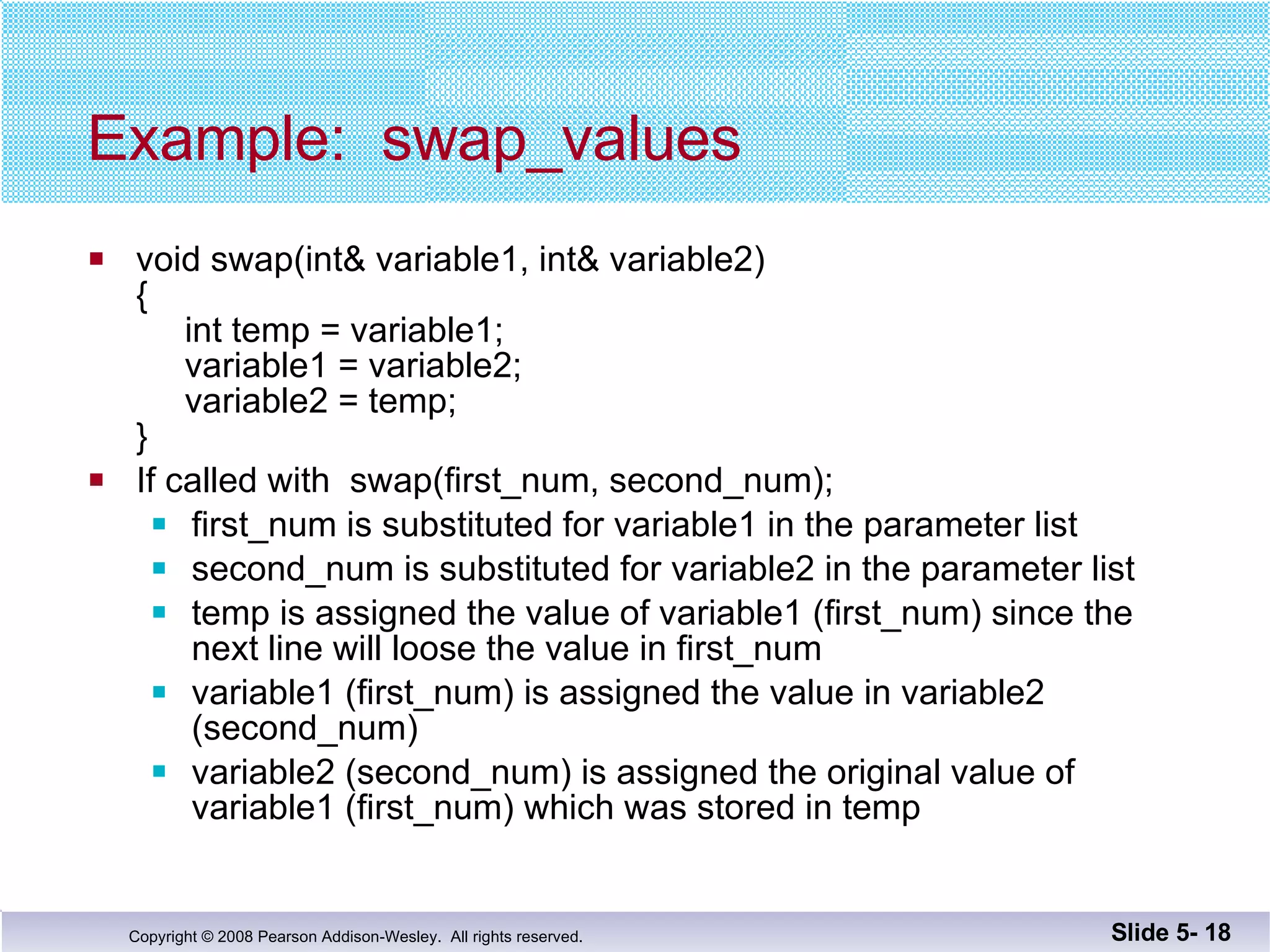
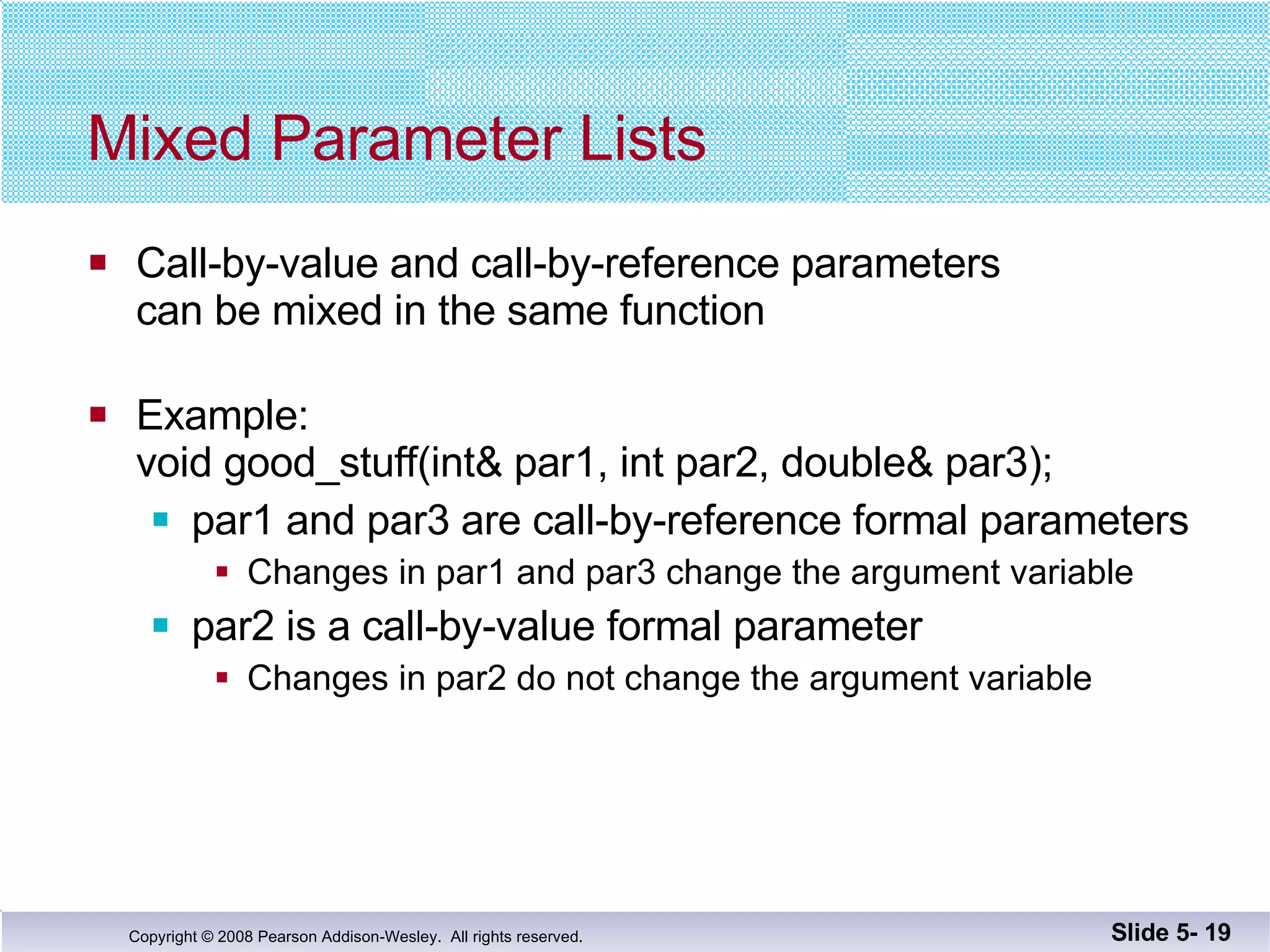
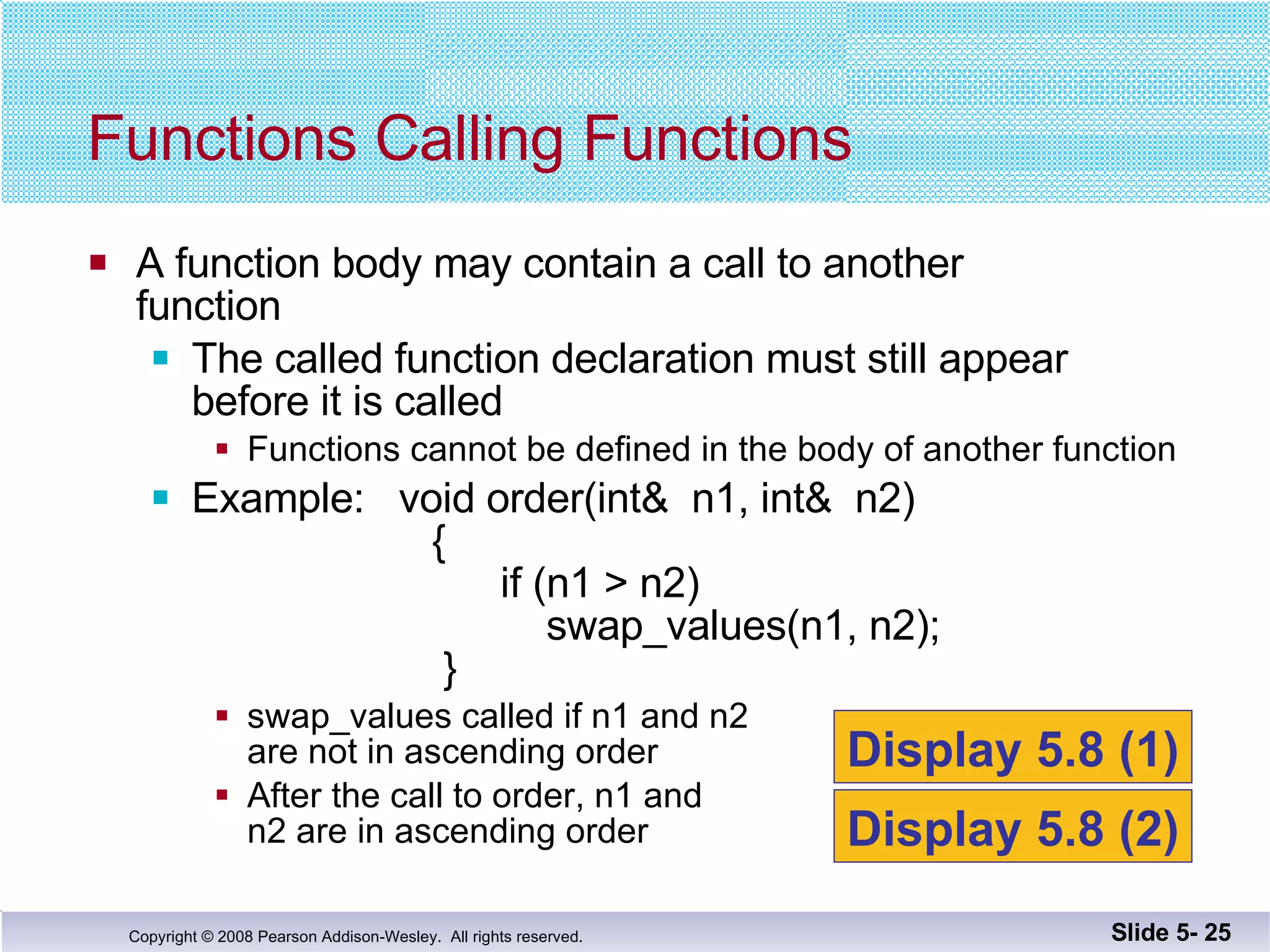
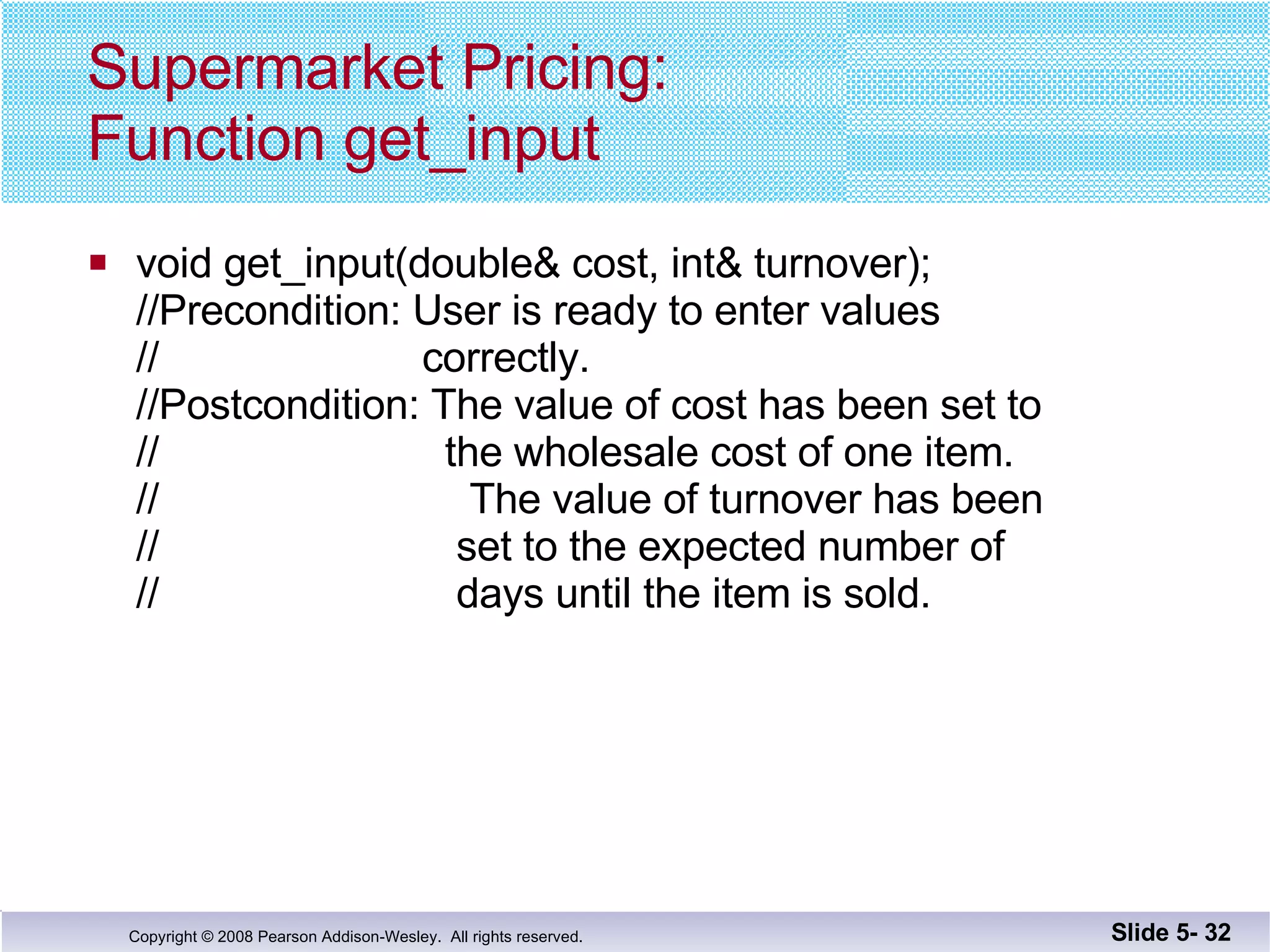
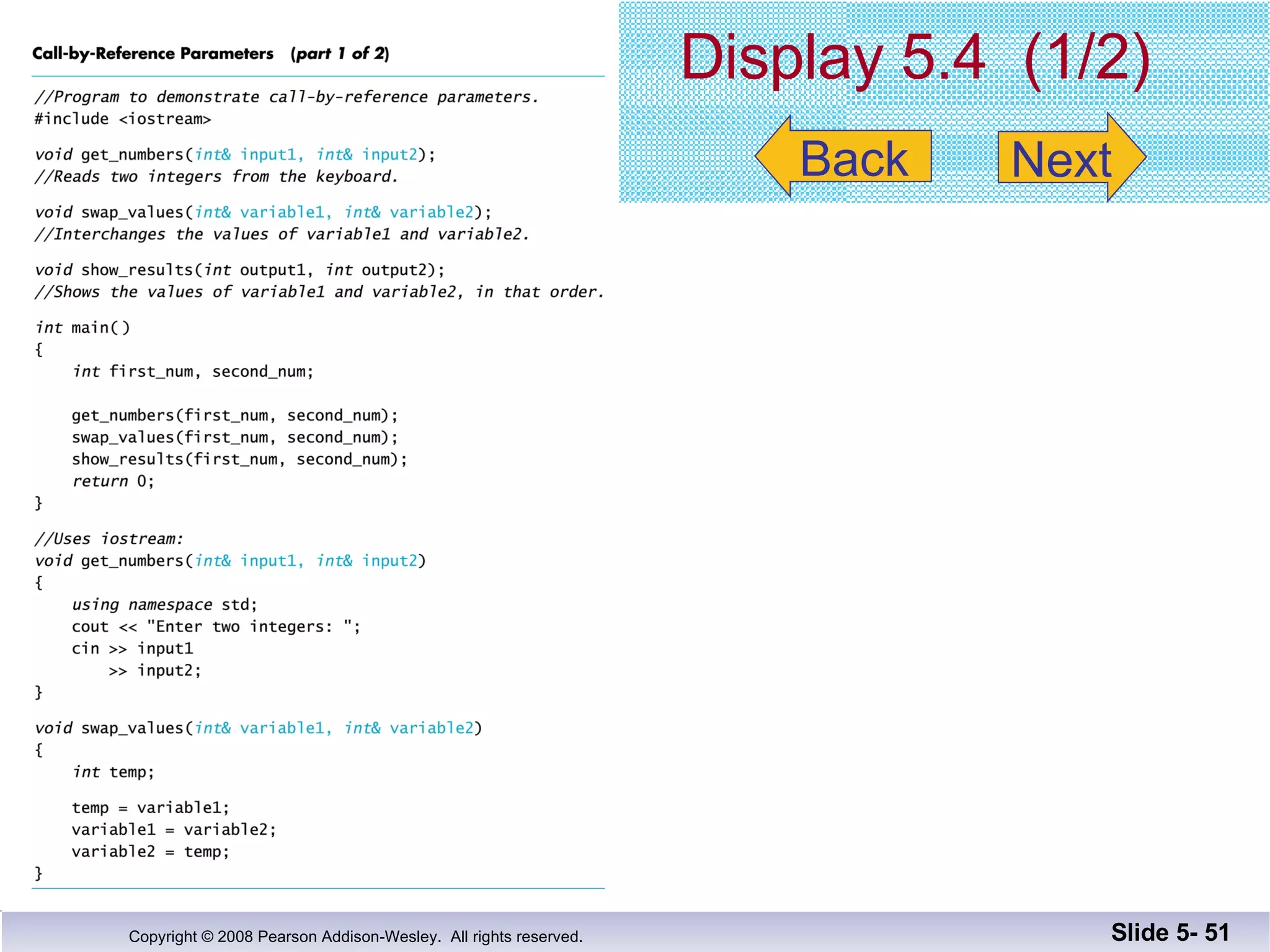
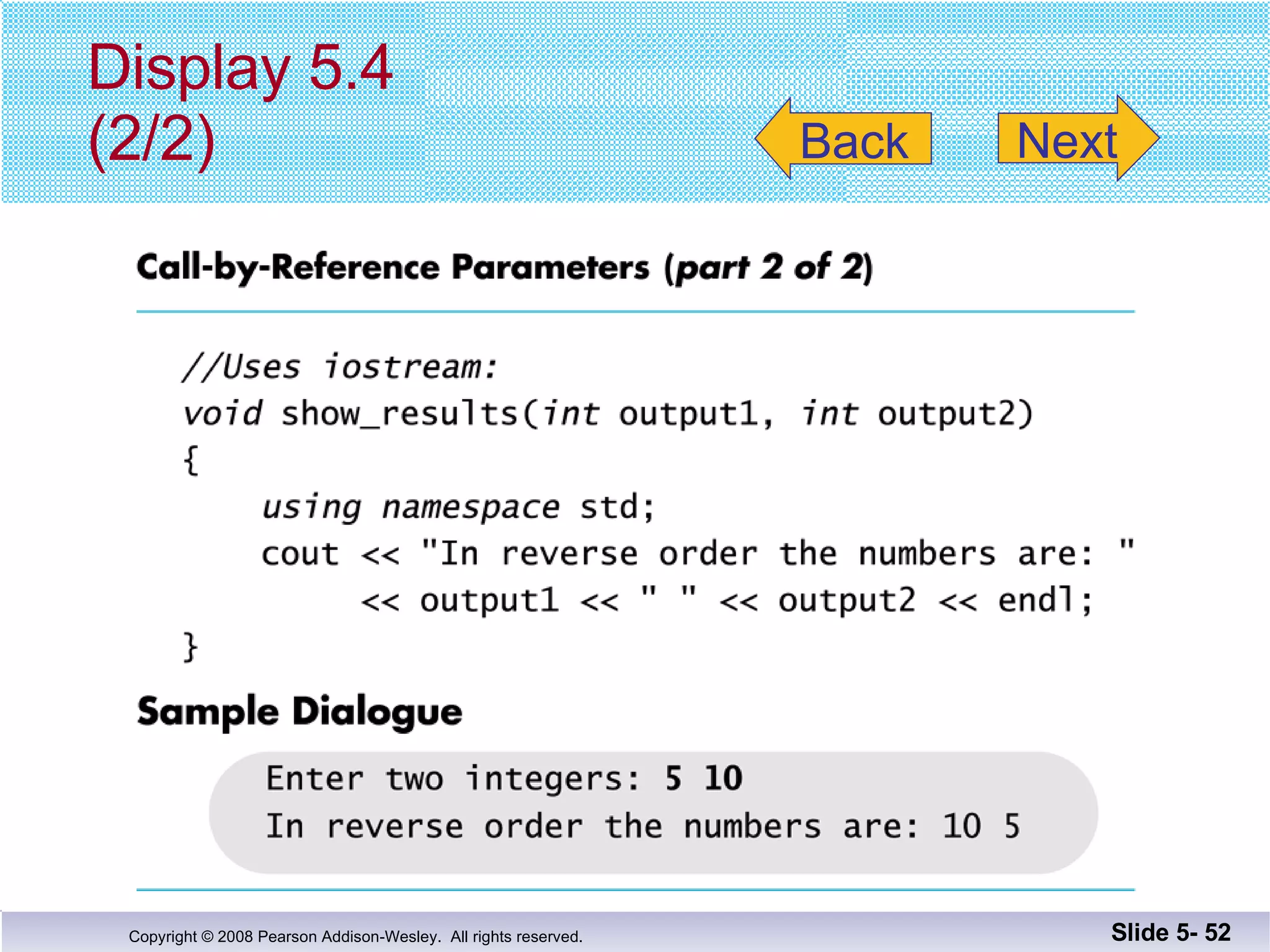
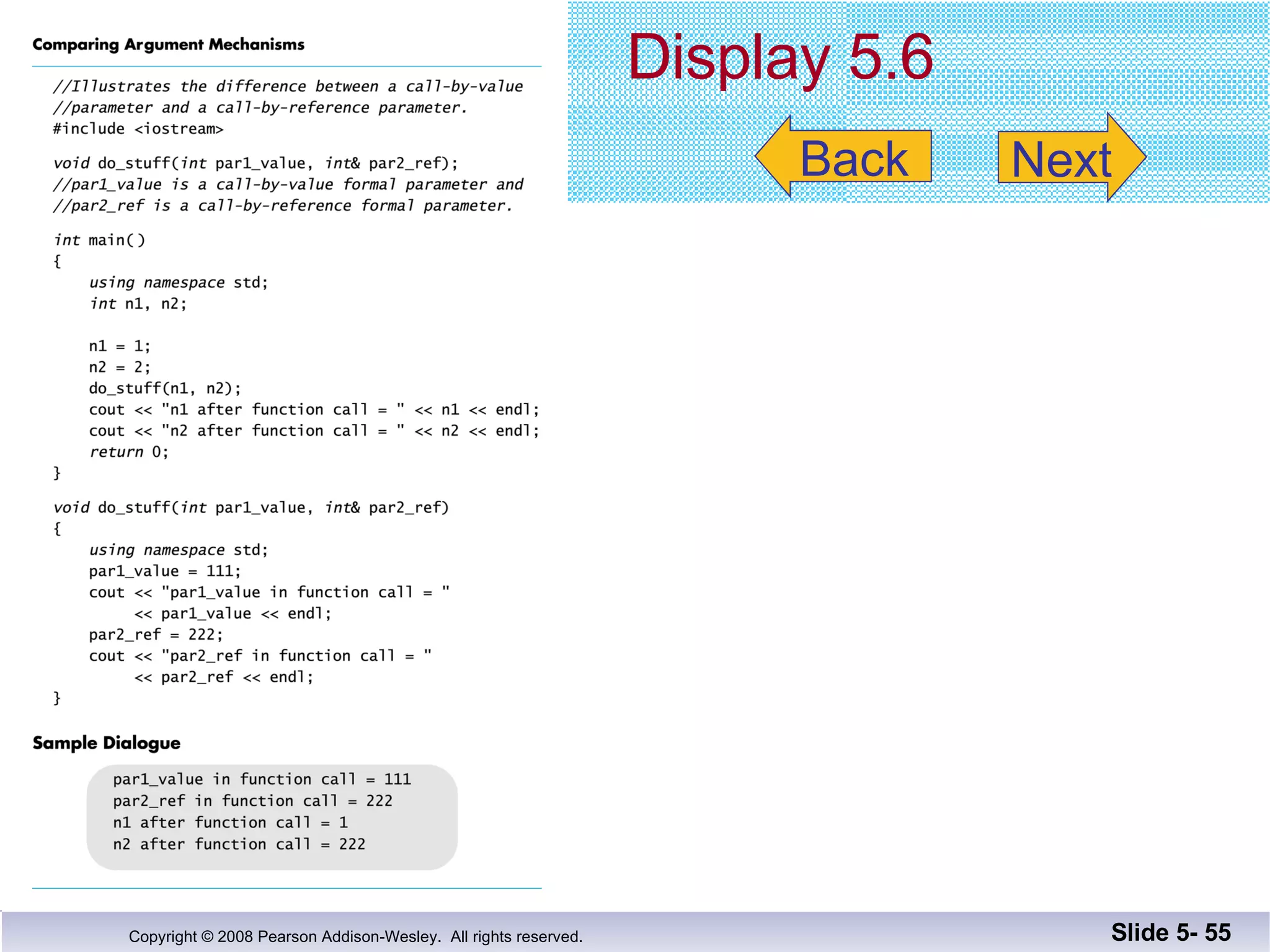
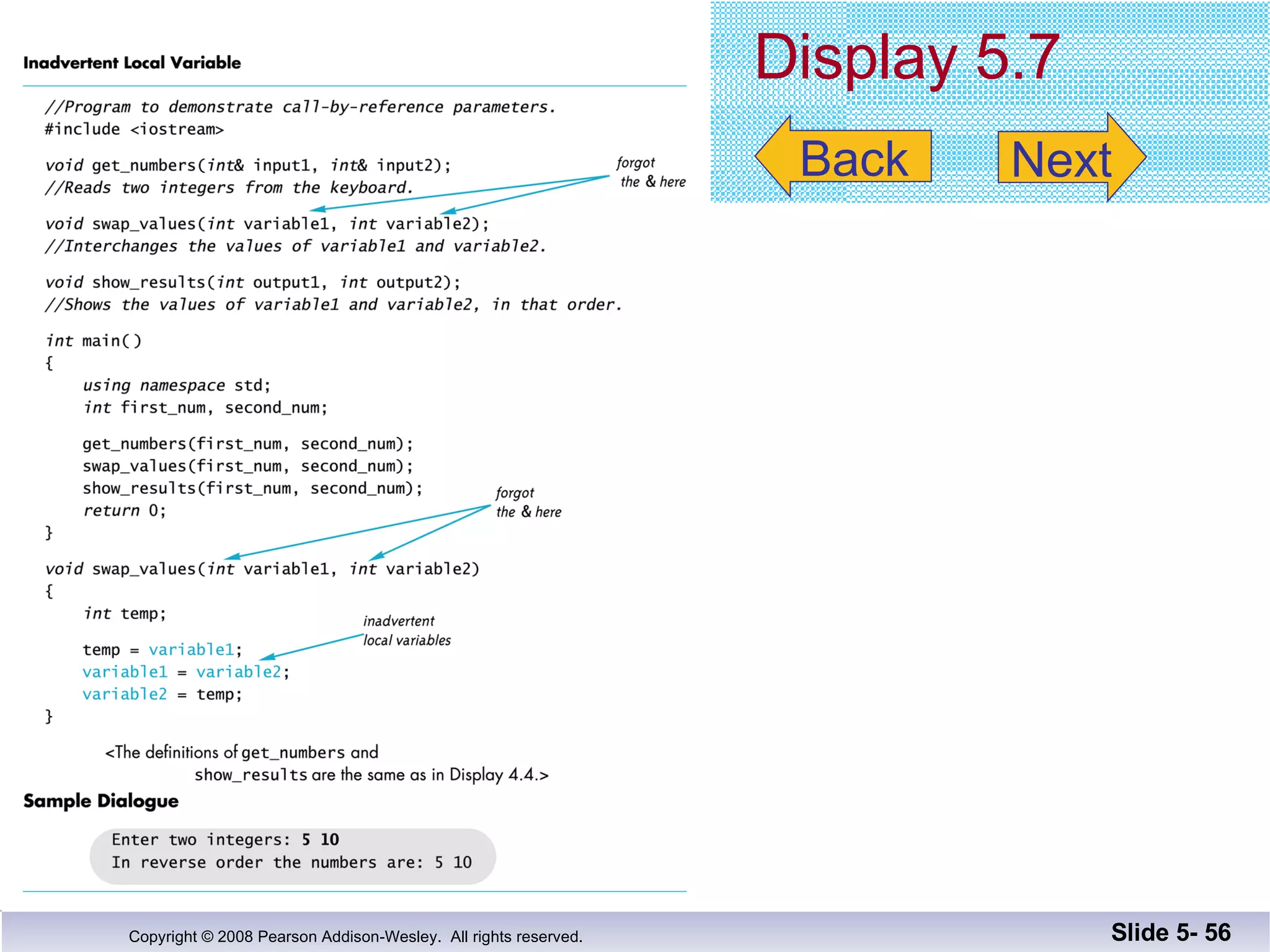
- Call-by-reference parameters allow a function to modify the argument variable in the calling context. They are declared with an ampersand and substitute the memory location rather than value of the argument.
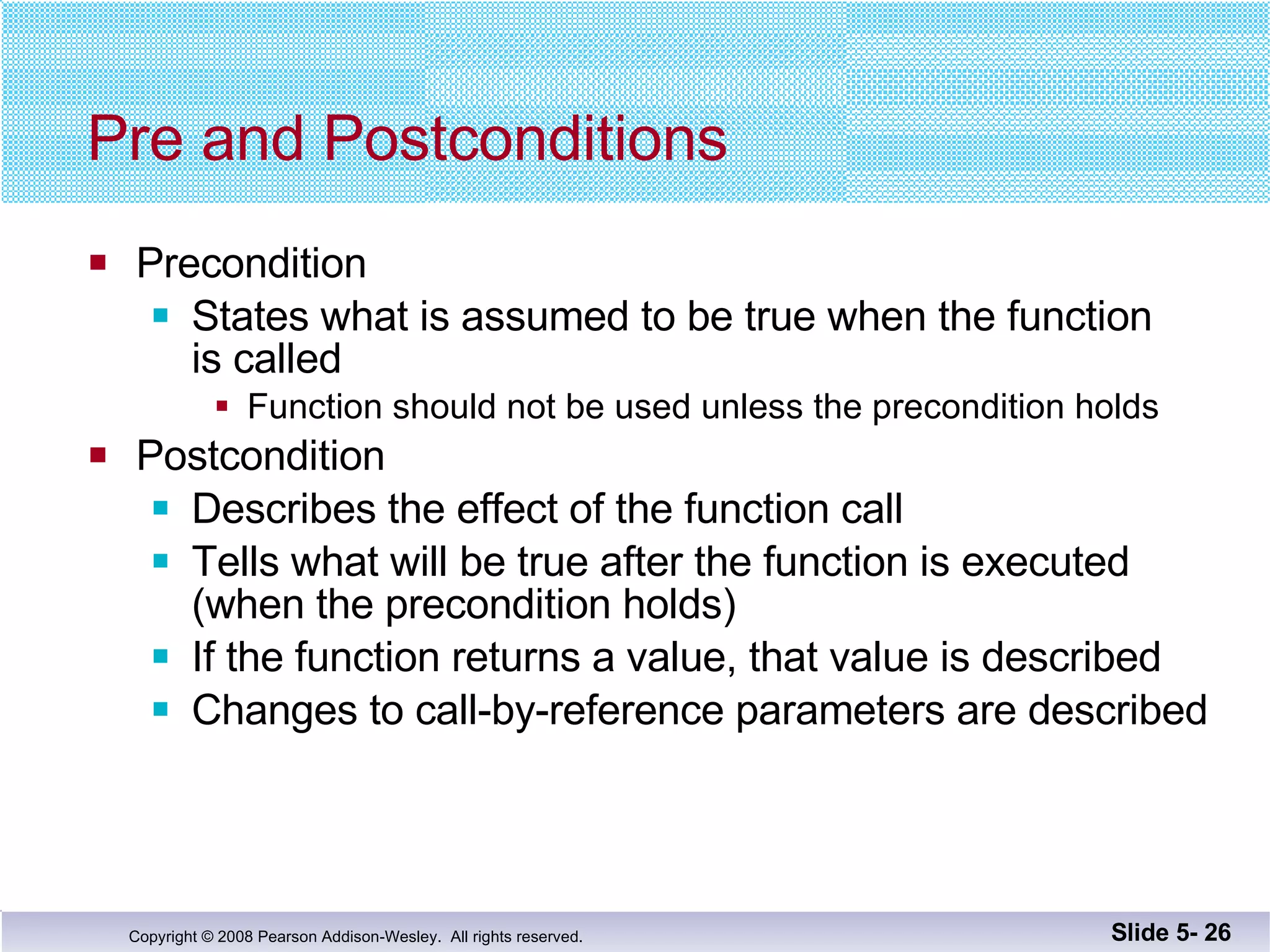
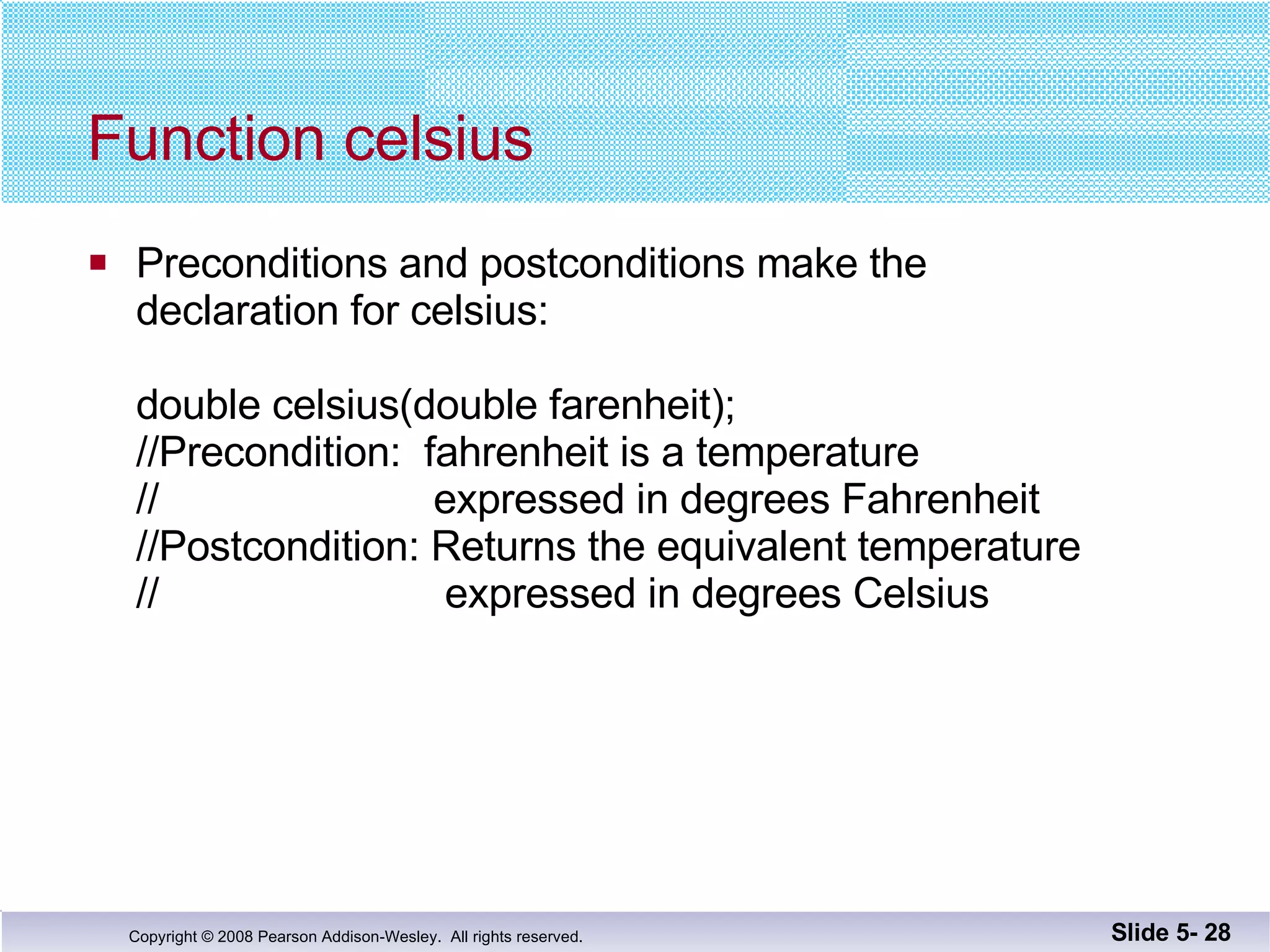
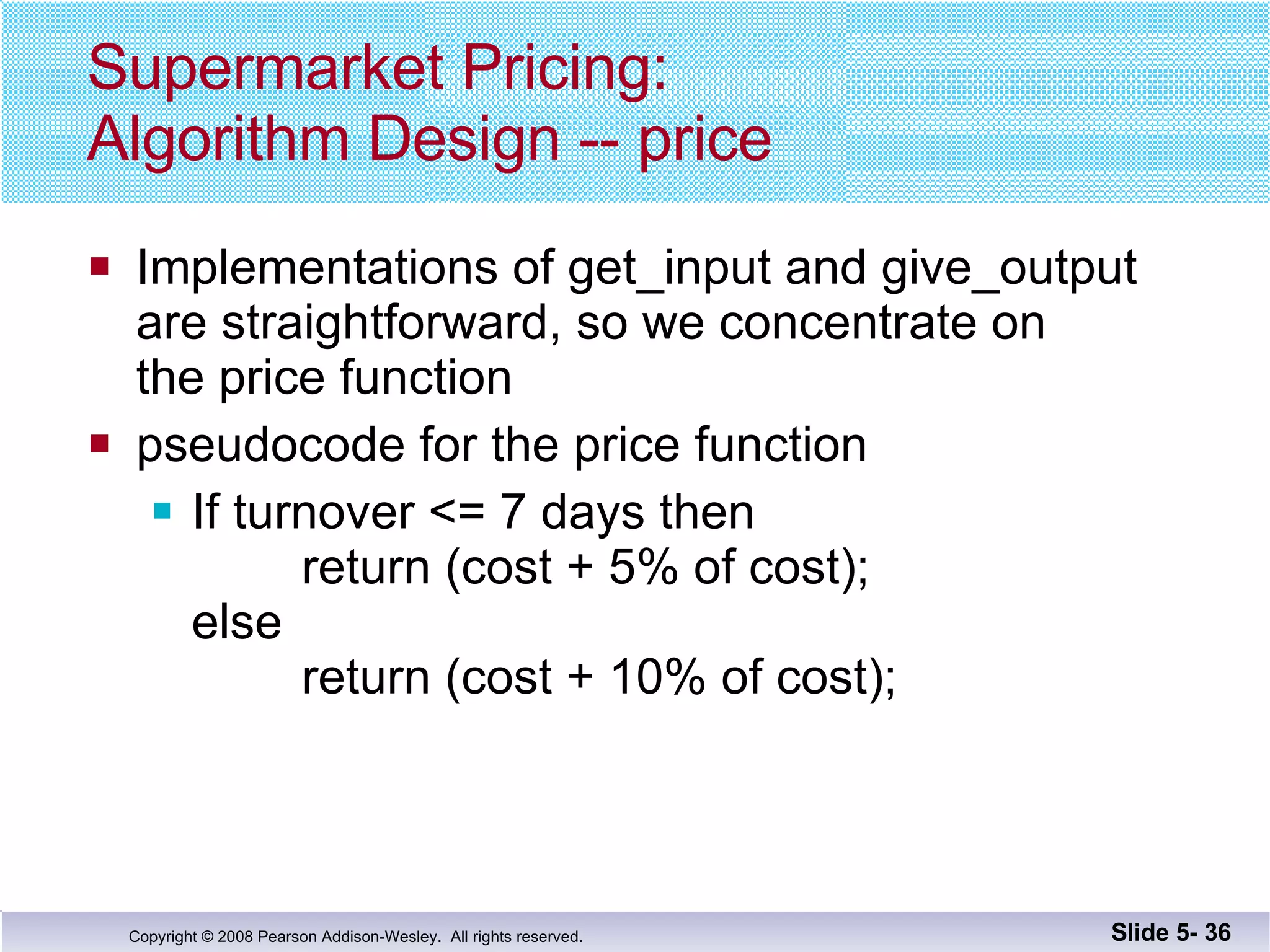
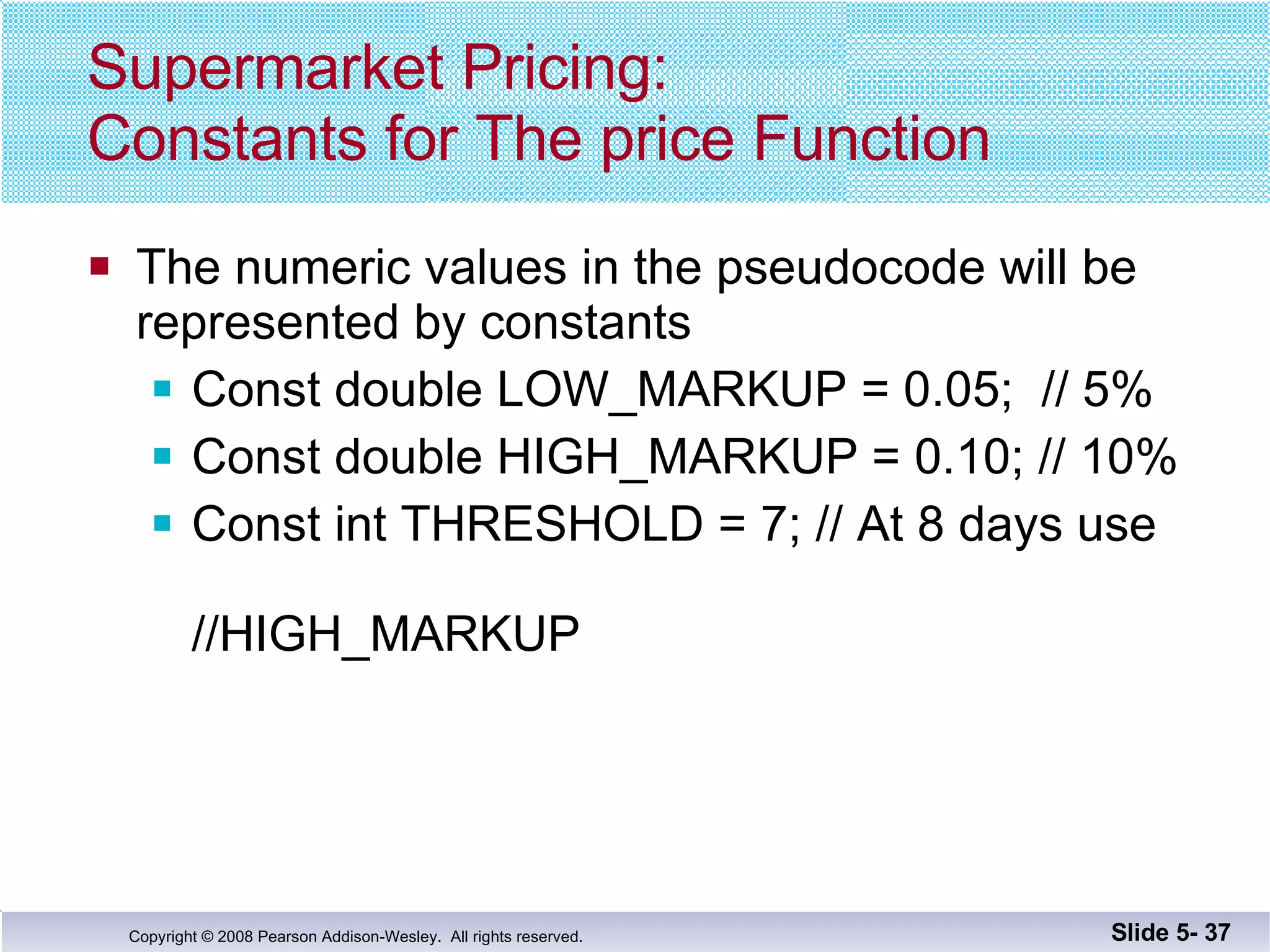
- Functions should be designed using procedural abstraction principles. Preconditions and postconditions specify what a function does without detailing how.
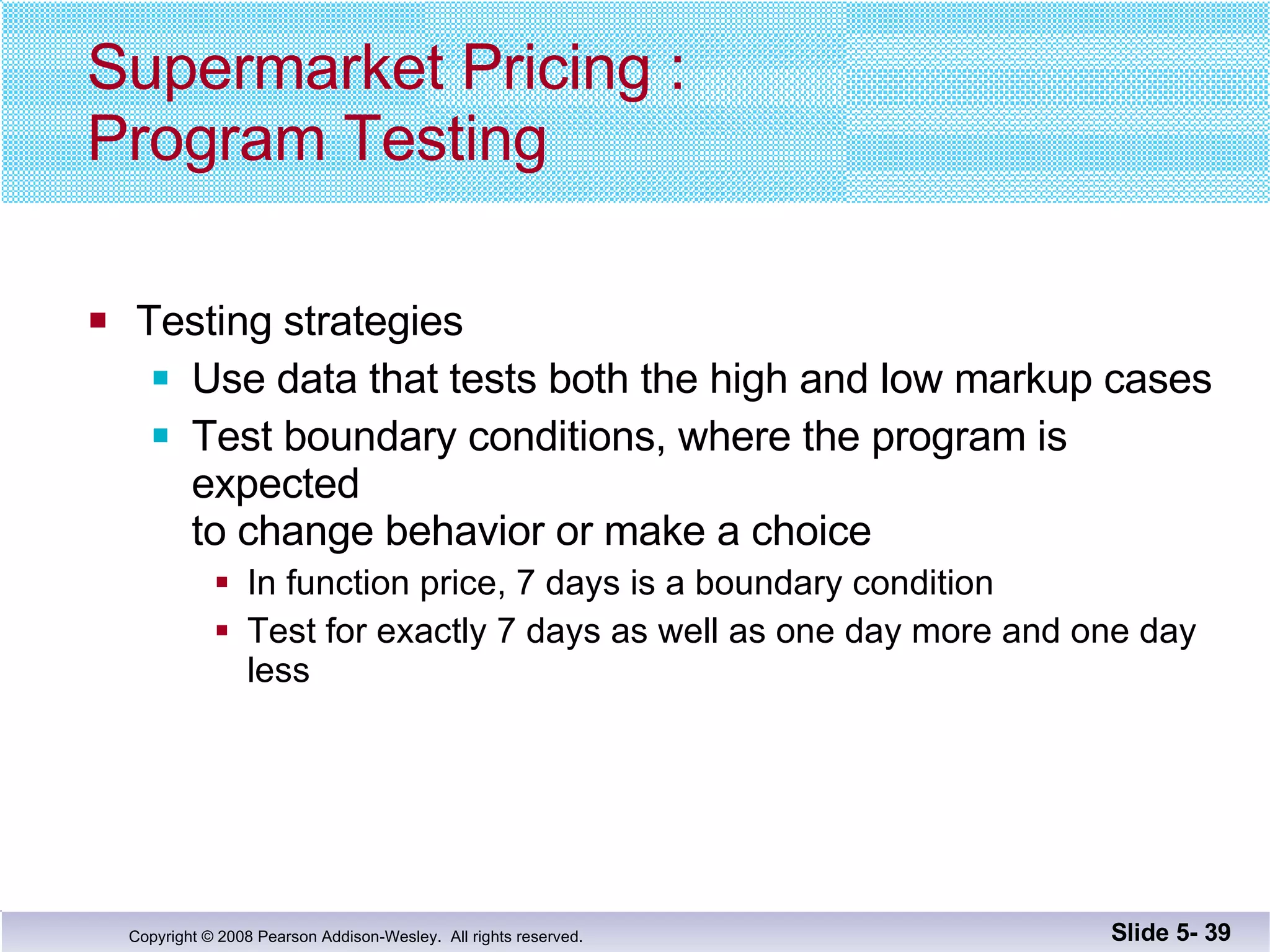
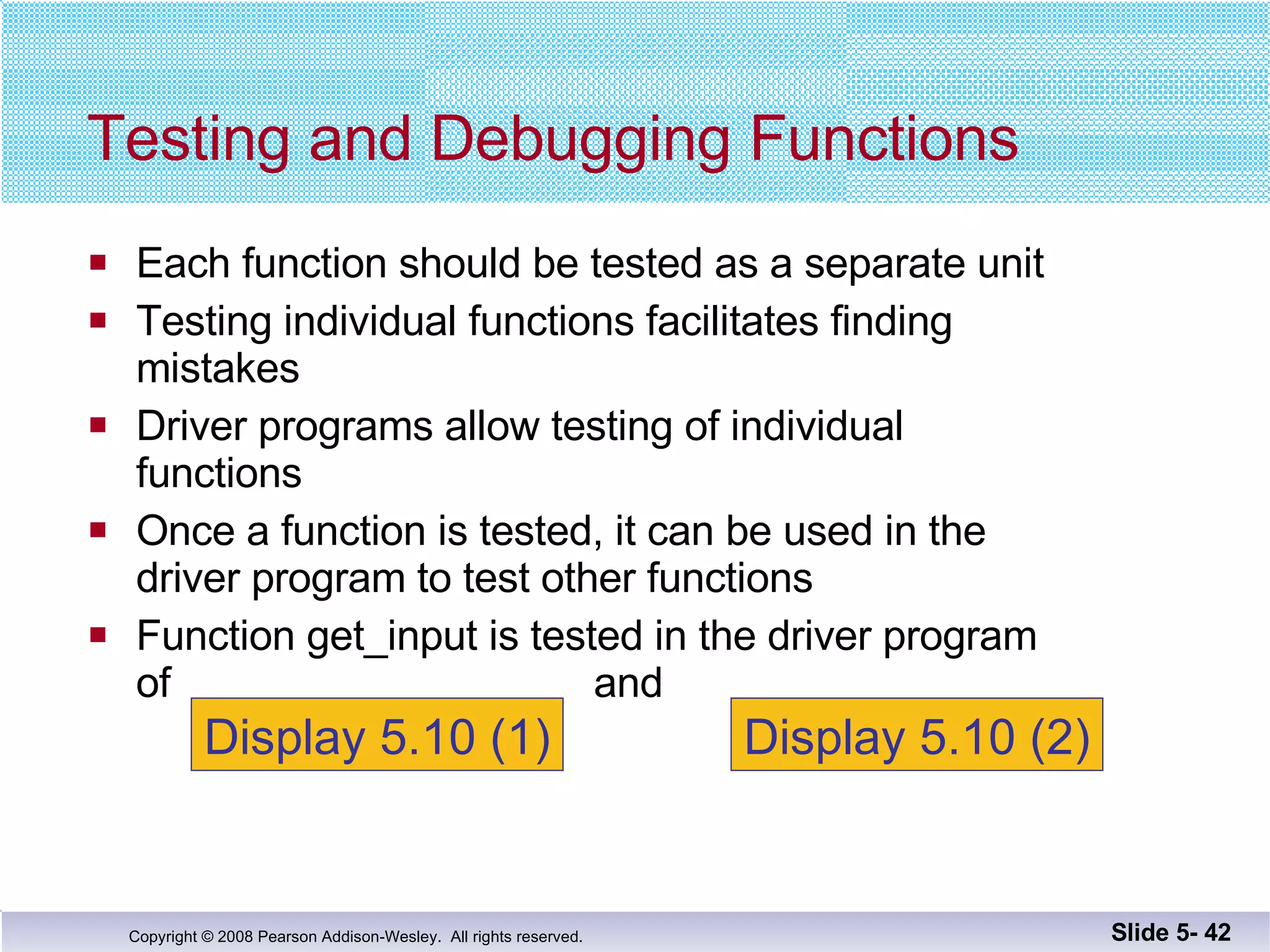
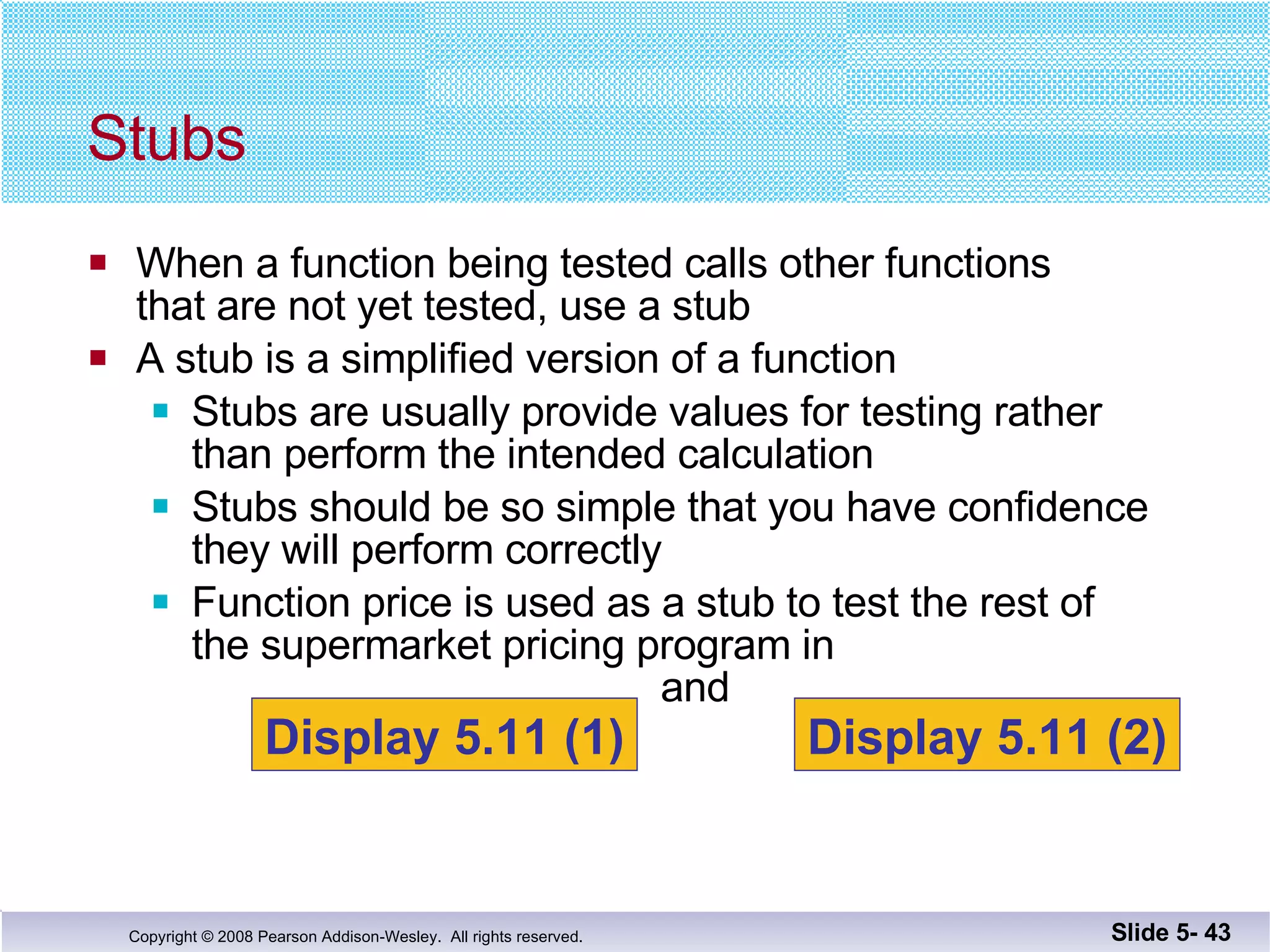
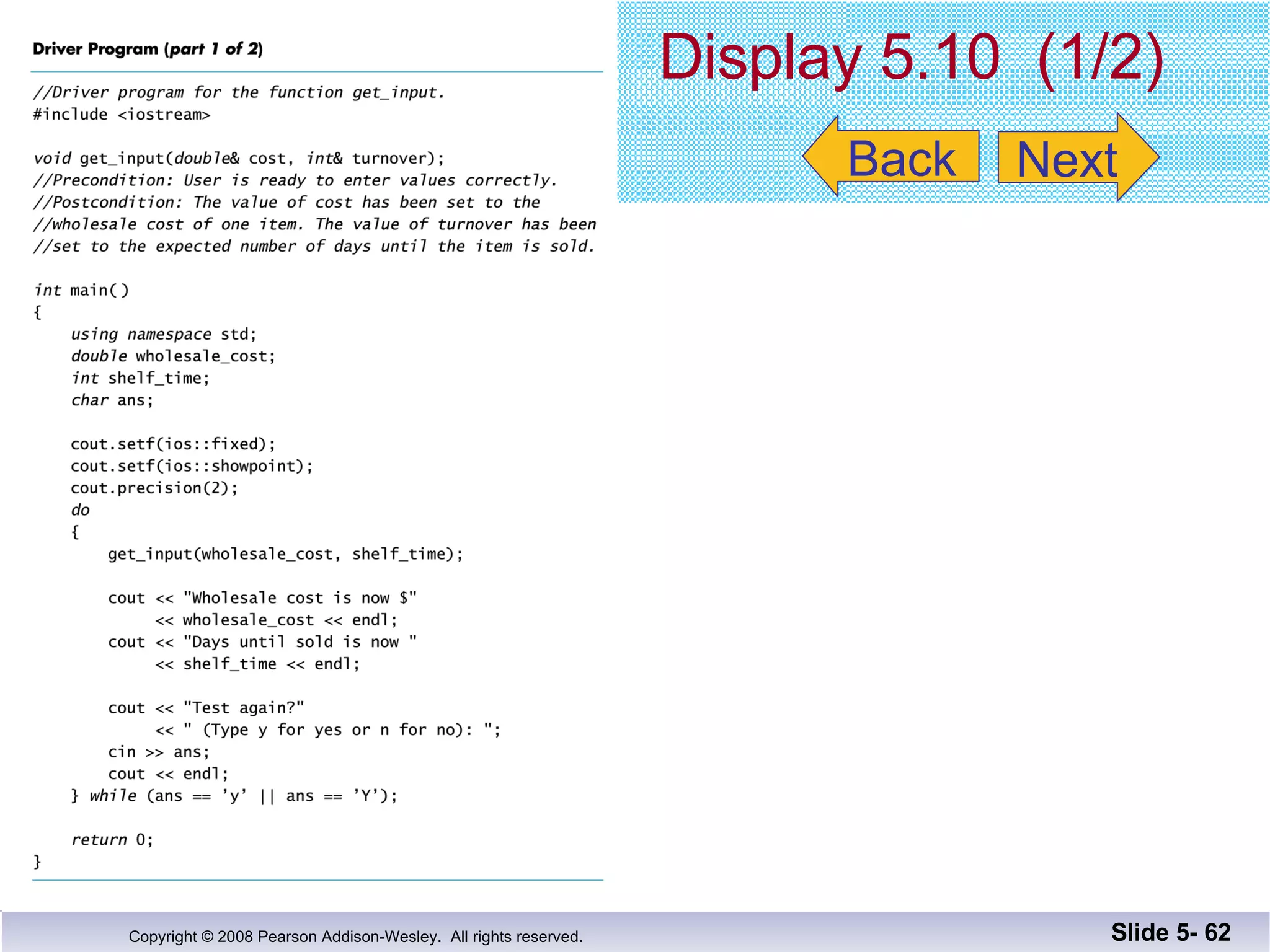
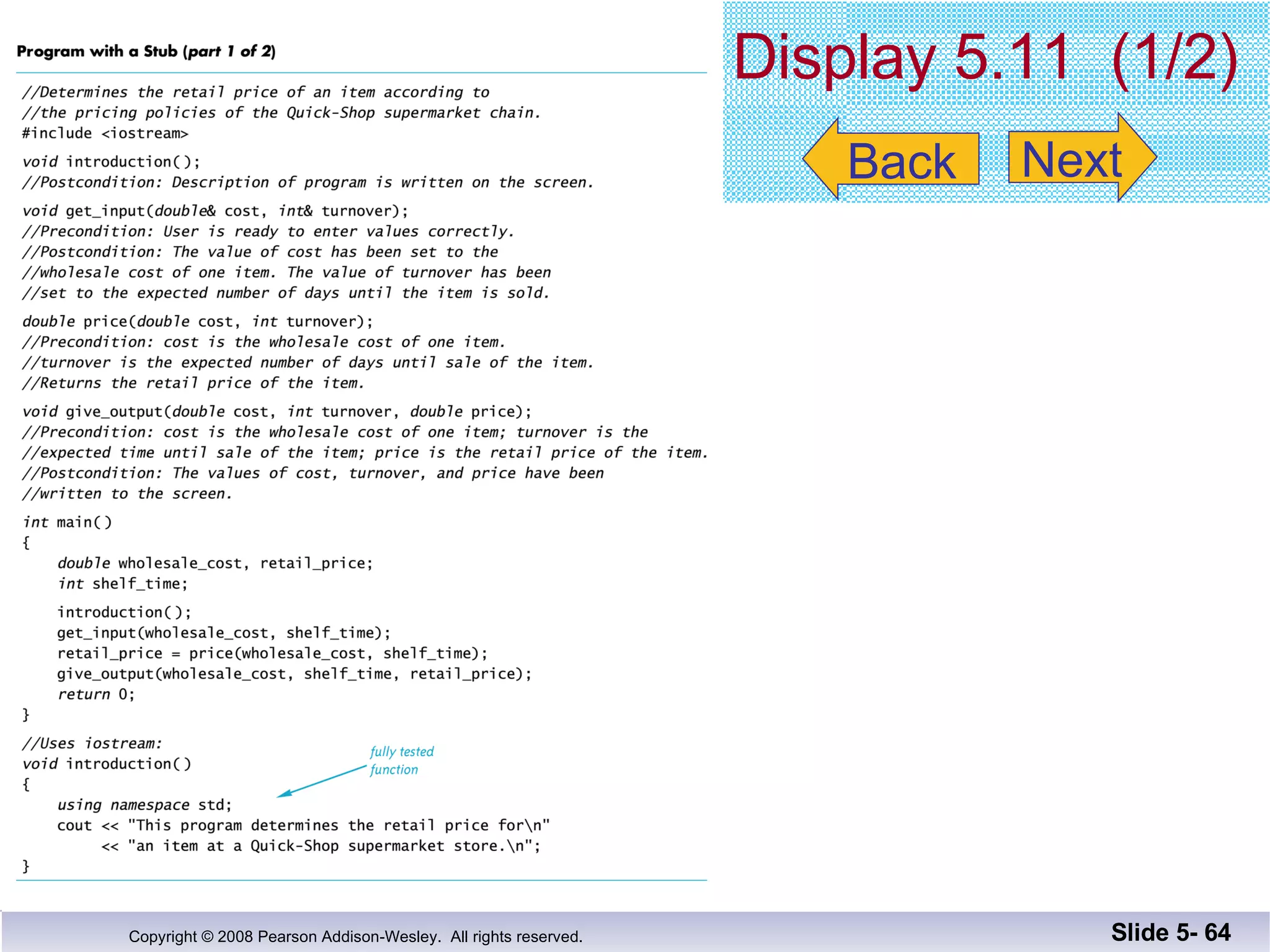
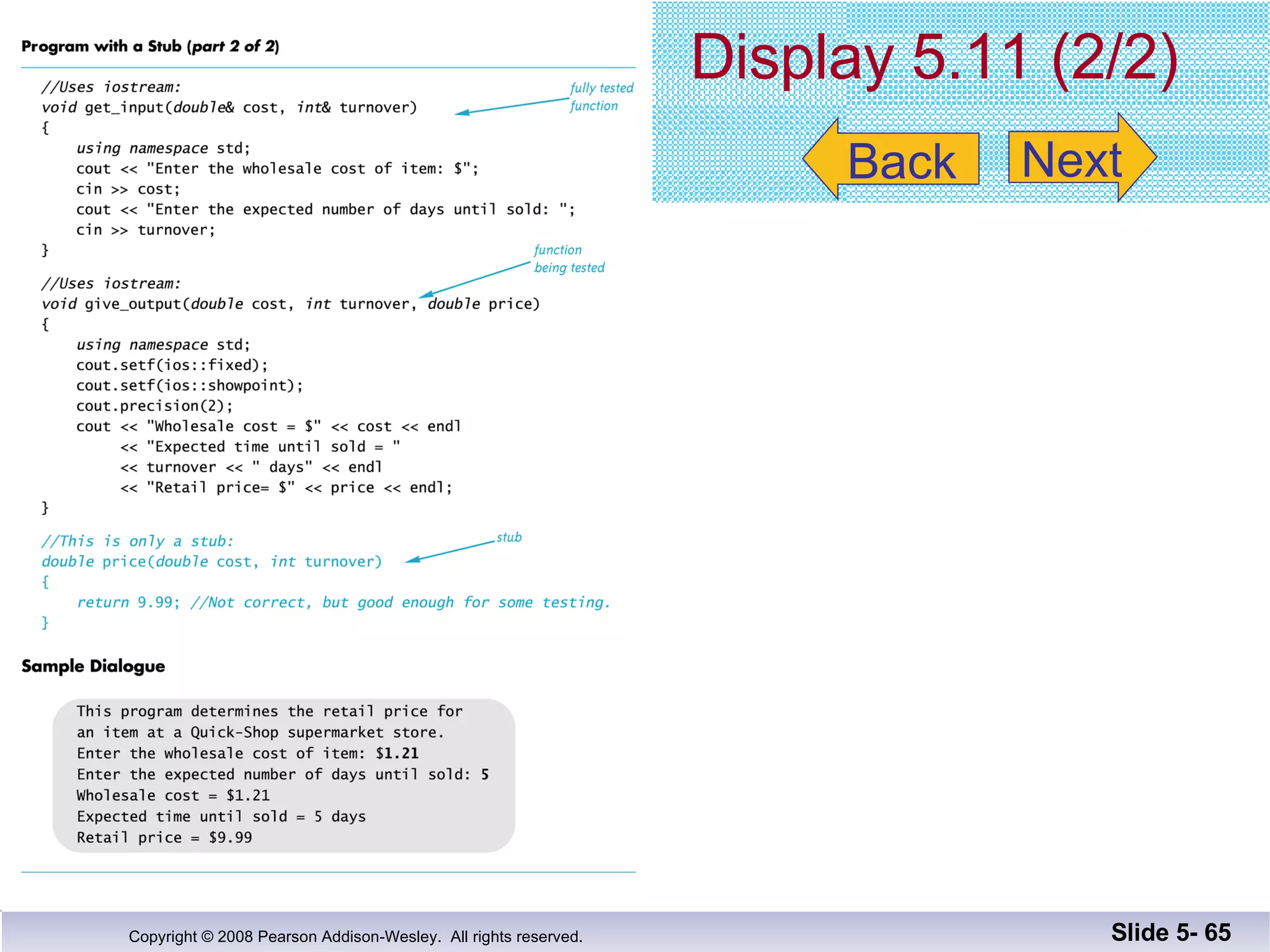
- Individual functions are tested using driver programs before integration. Stubs simplify untested dependencies during development.