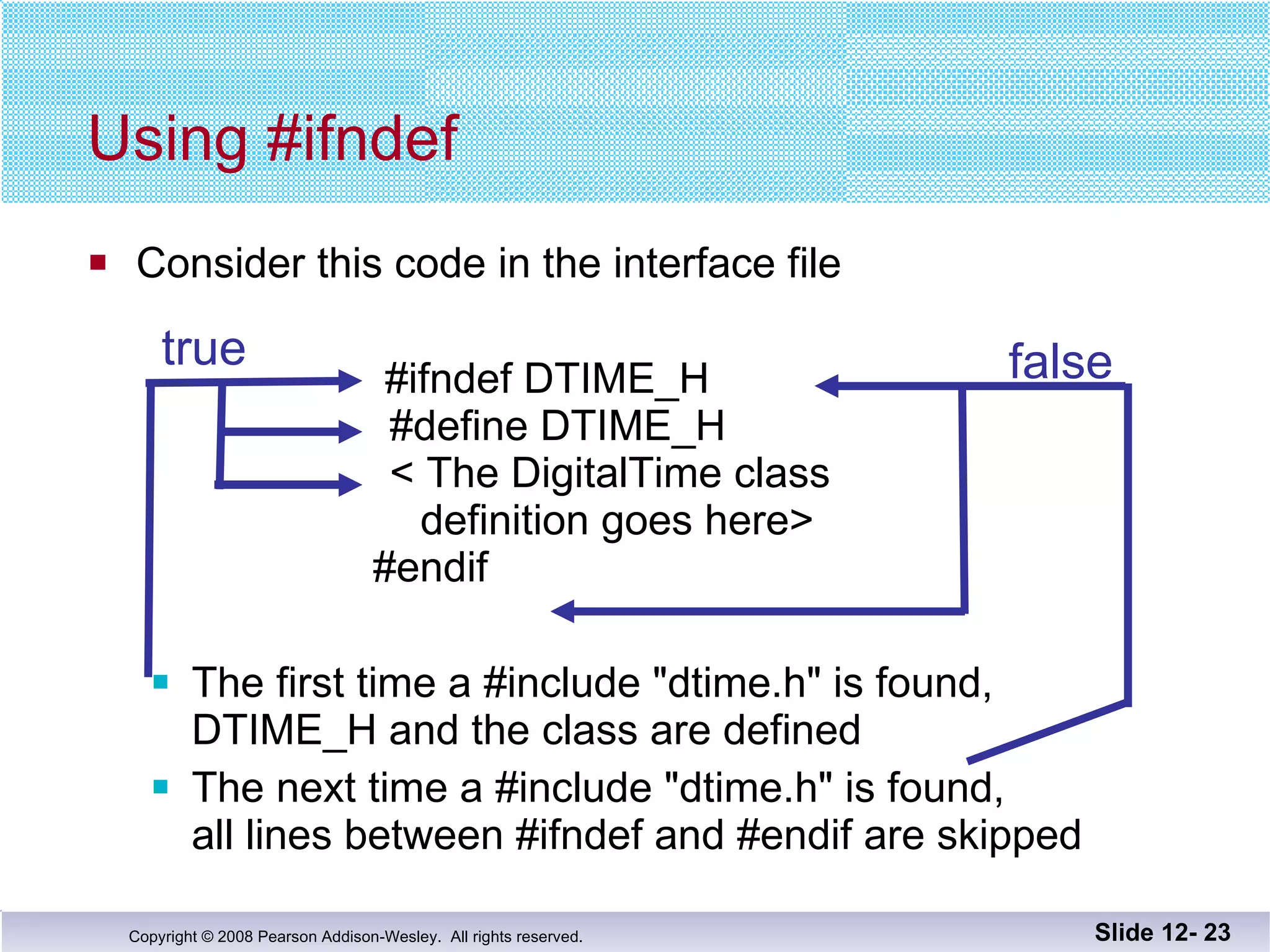
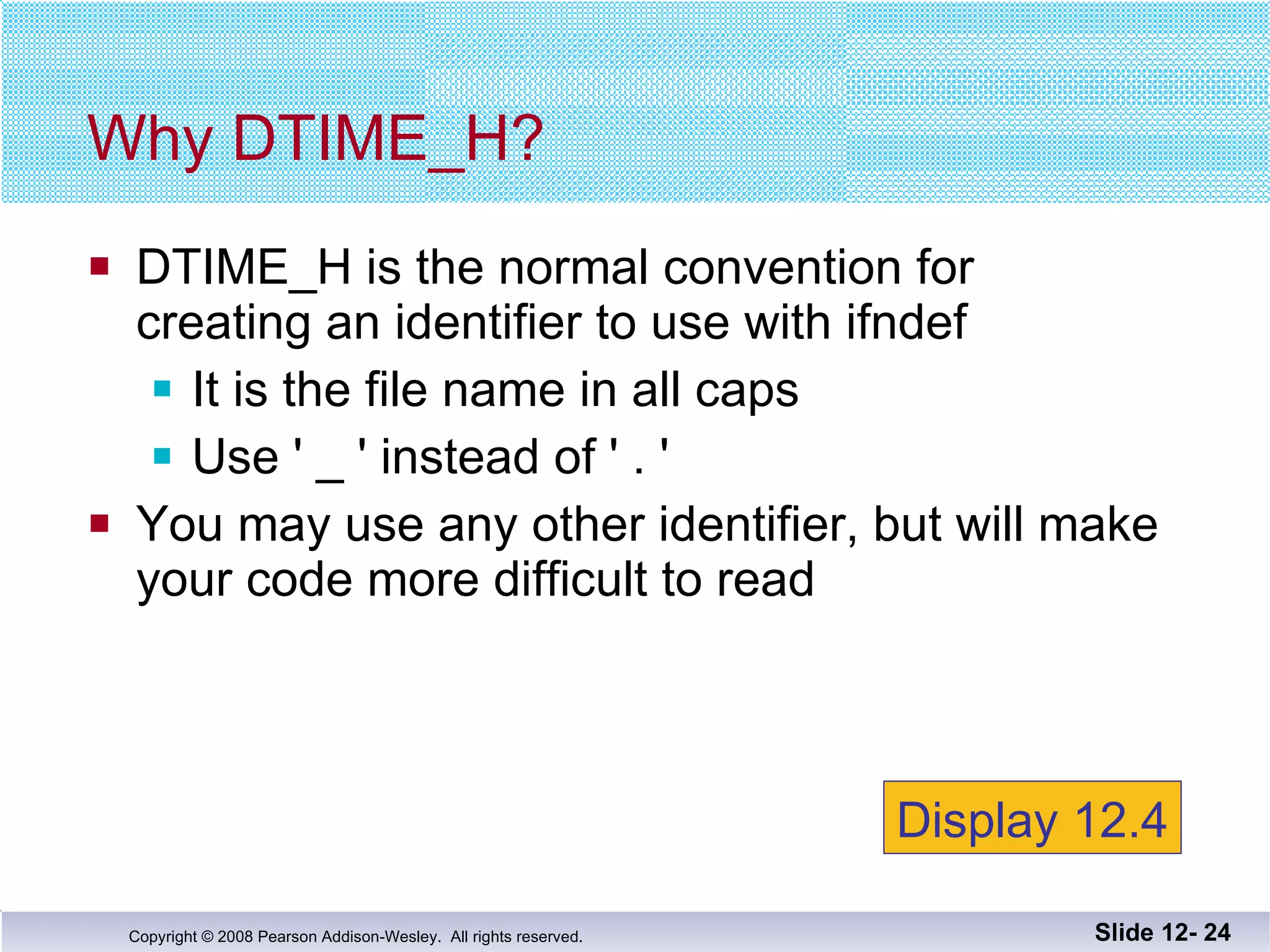
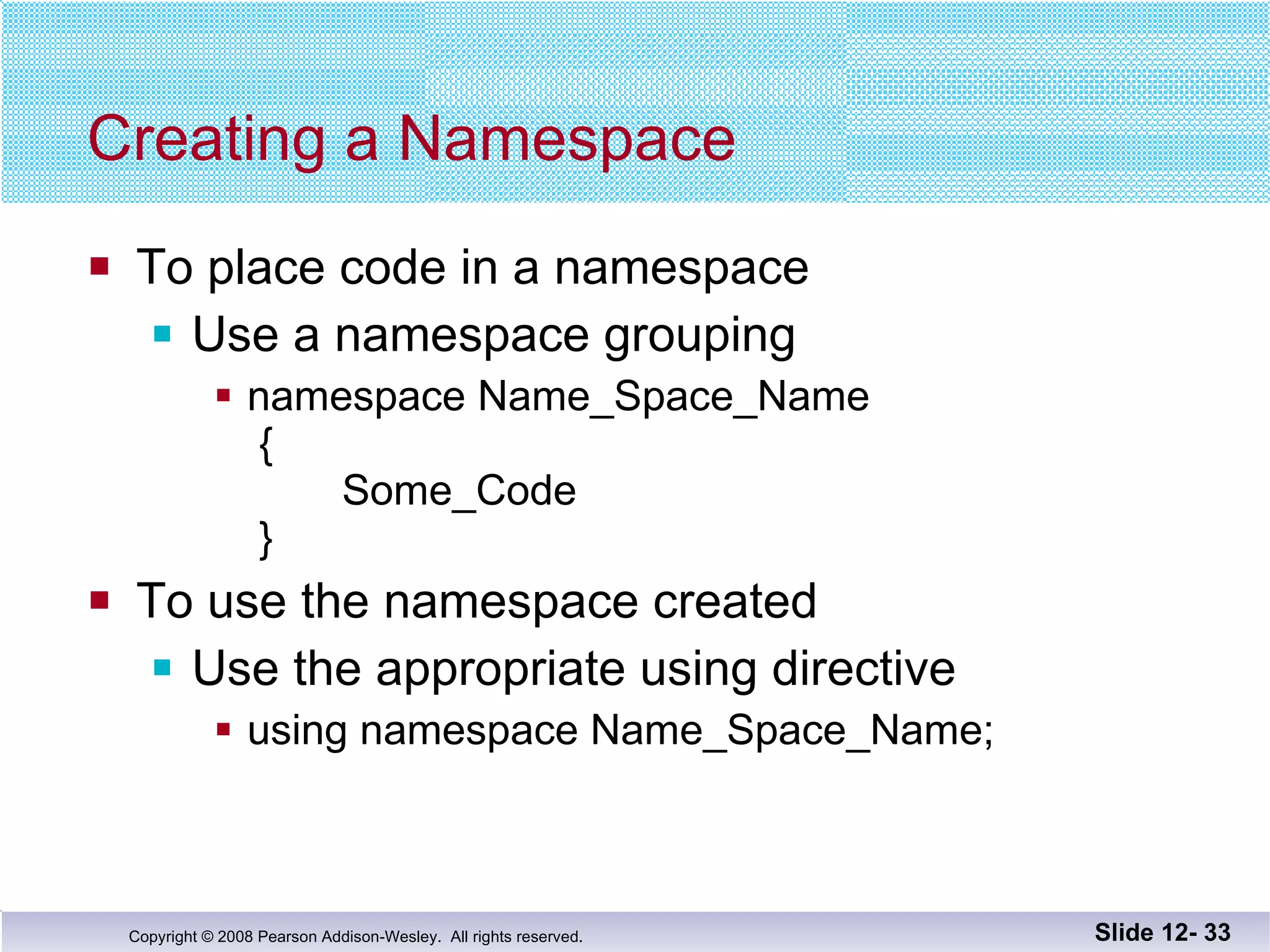
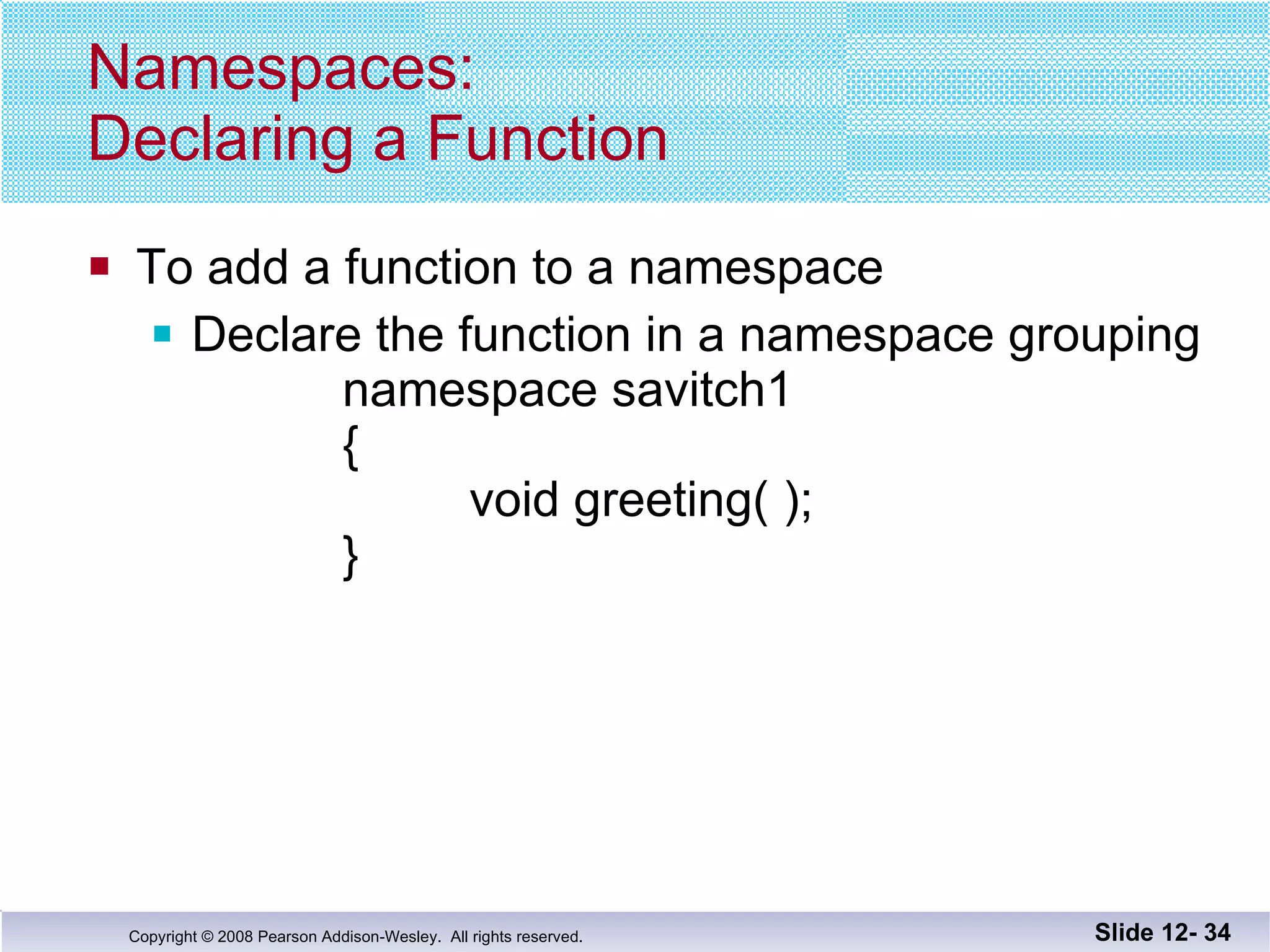
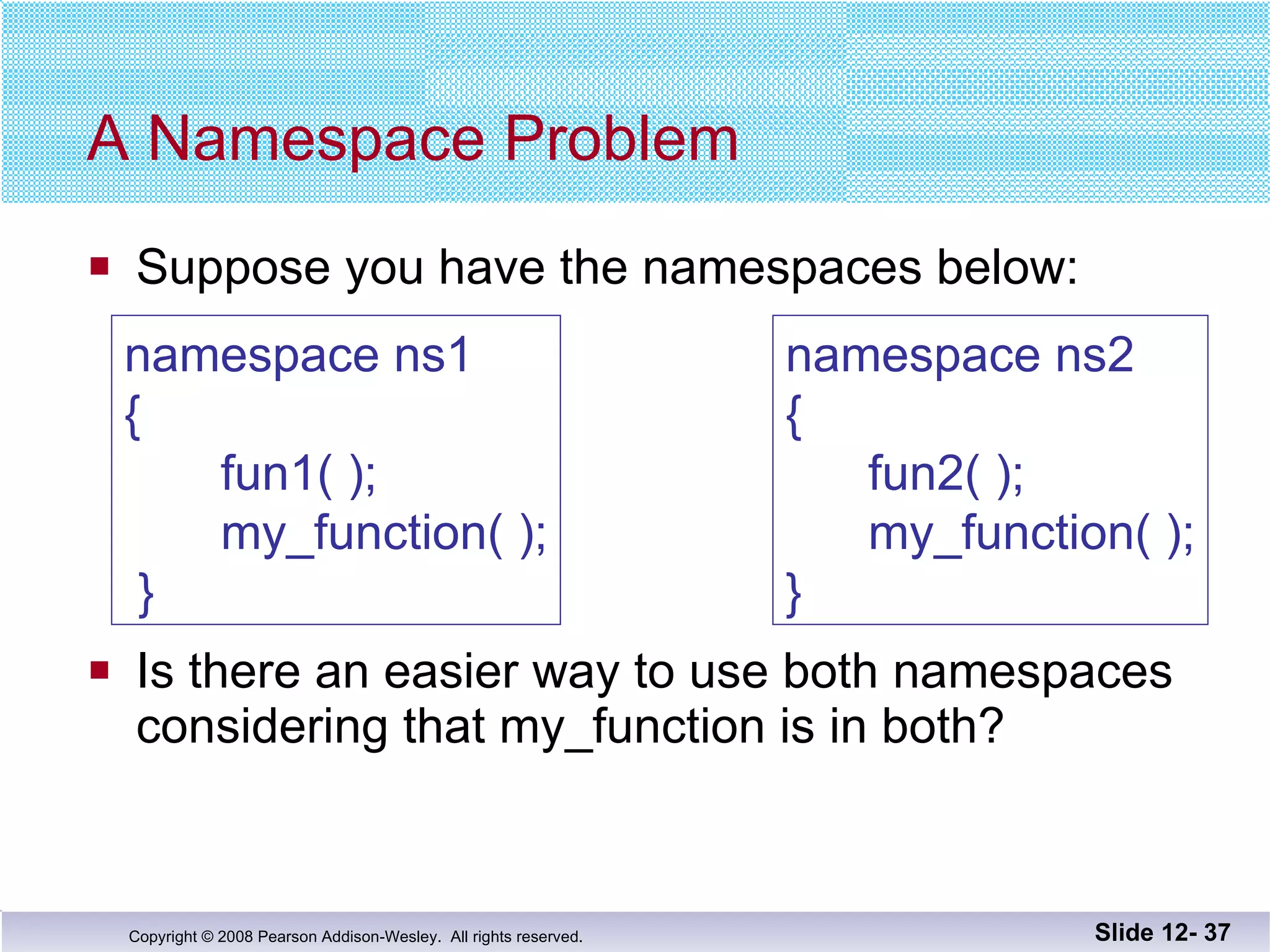
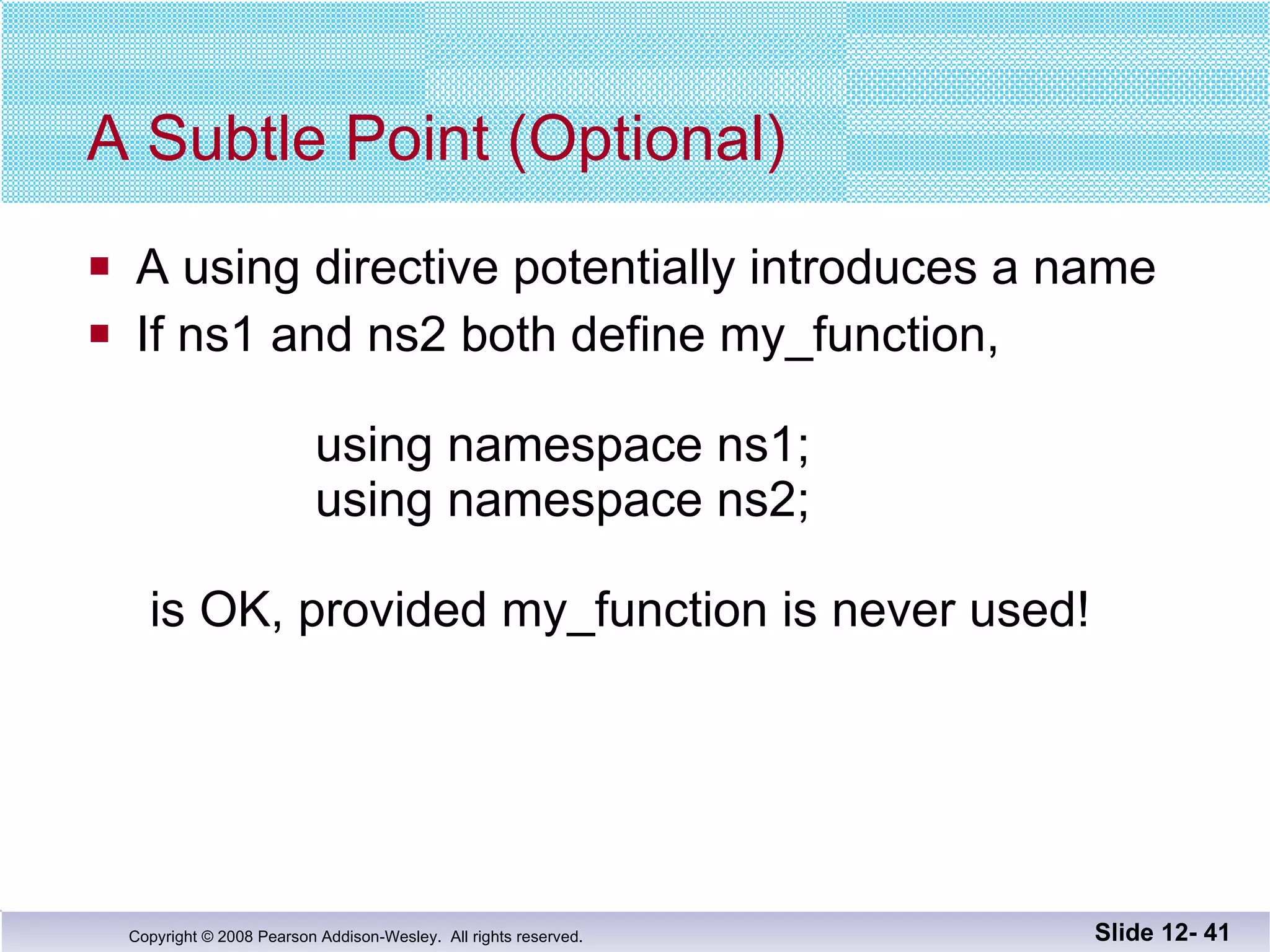
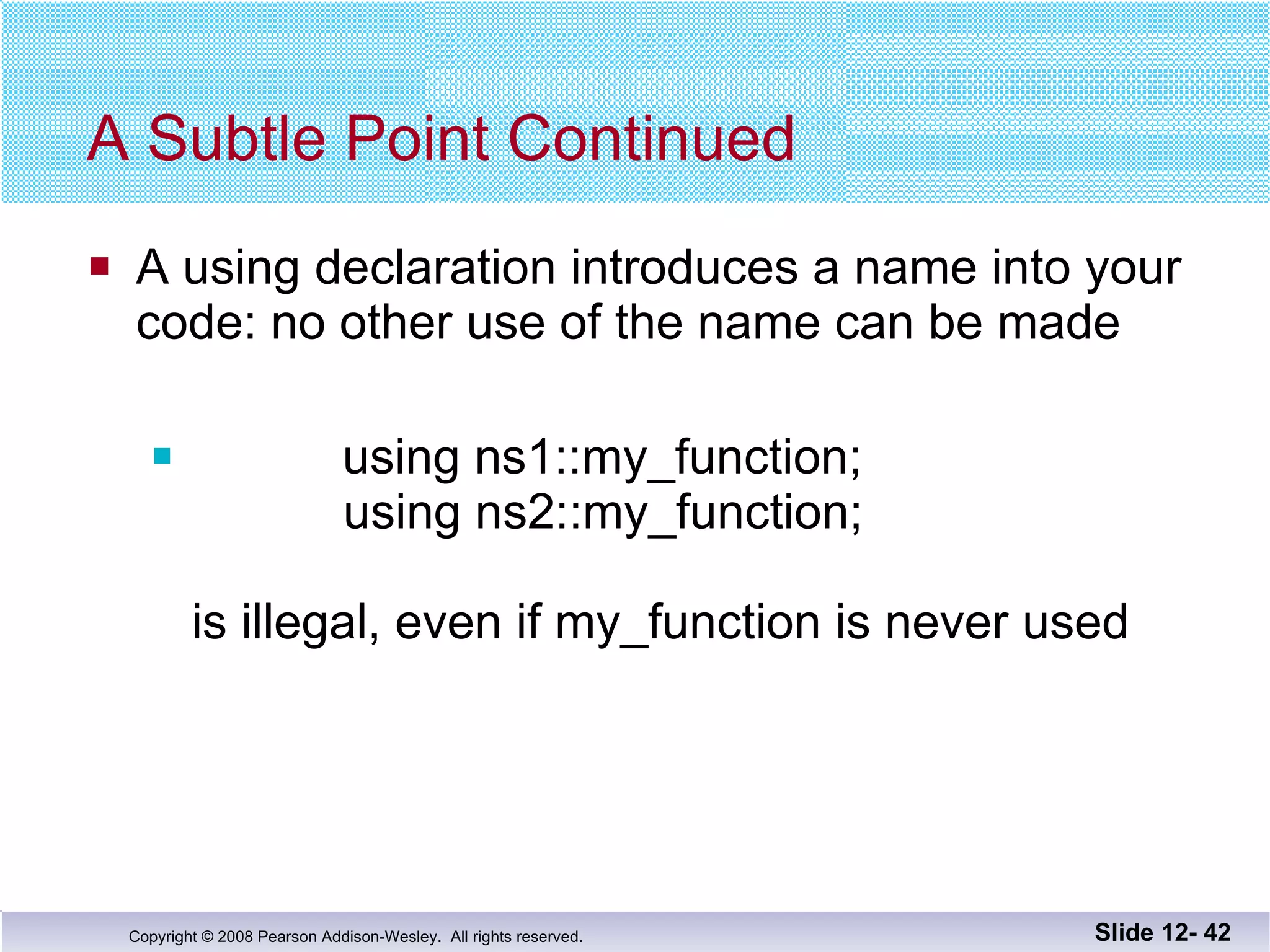
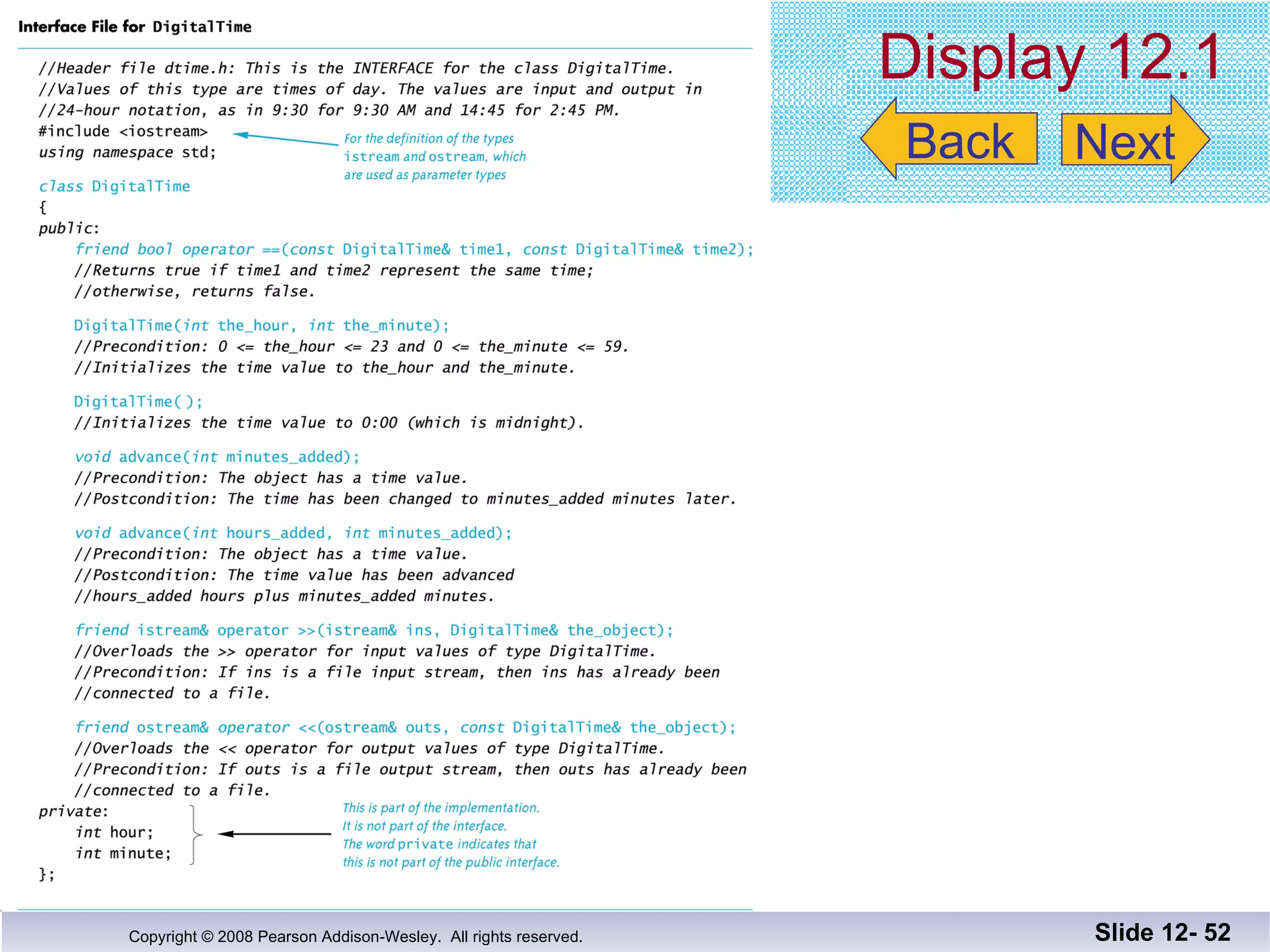
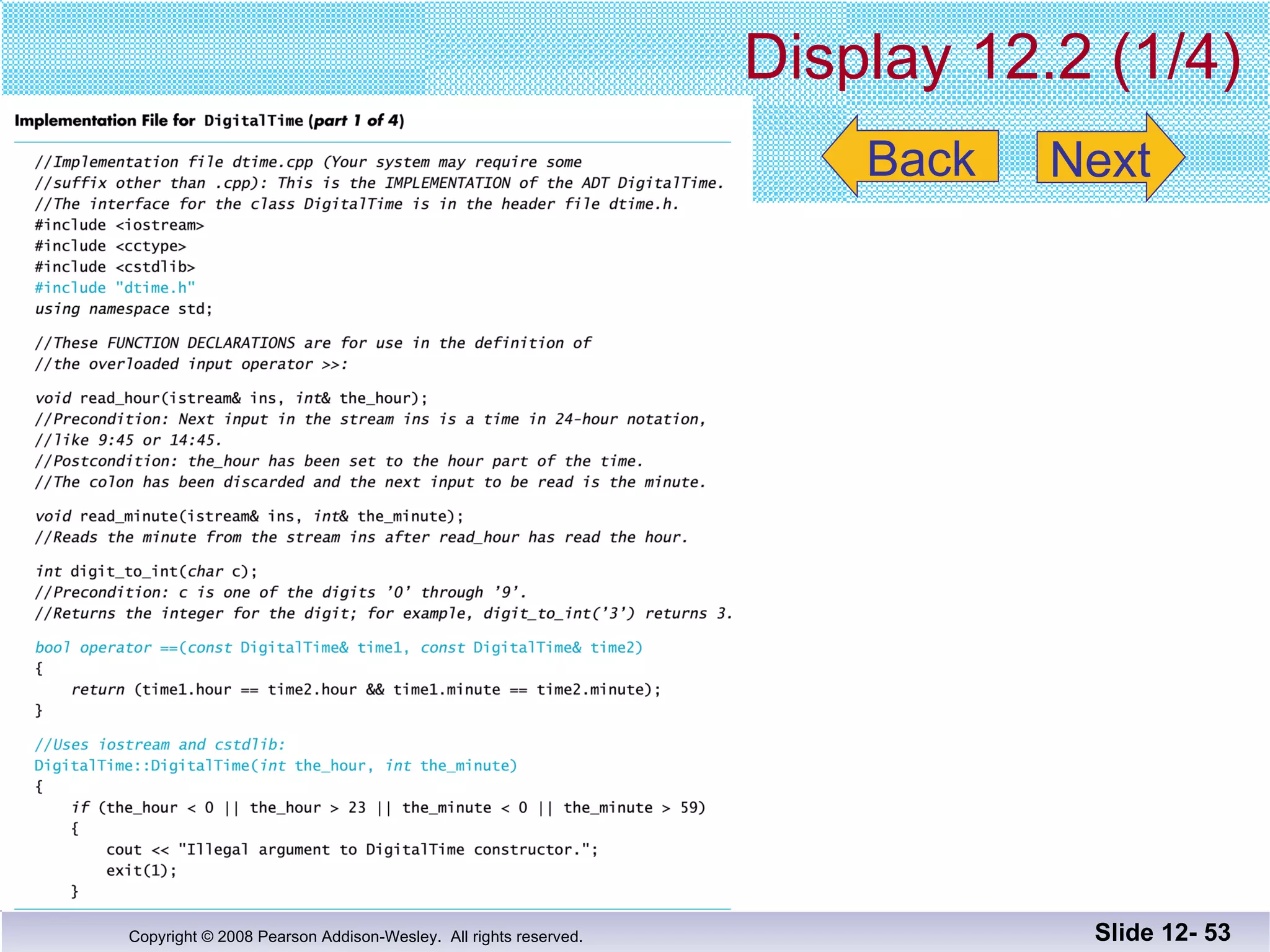
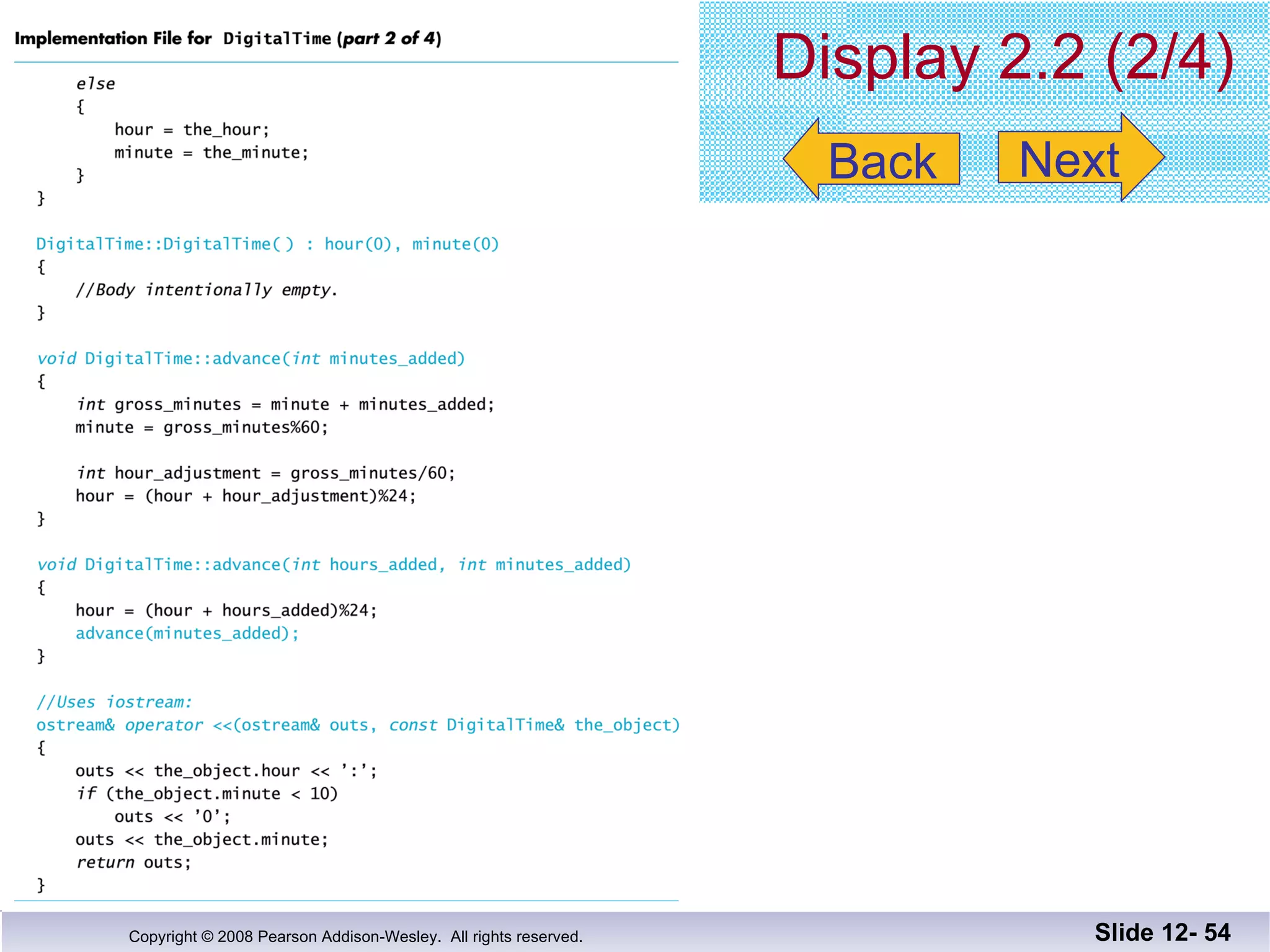
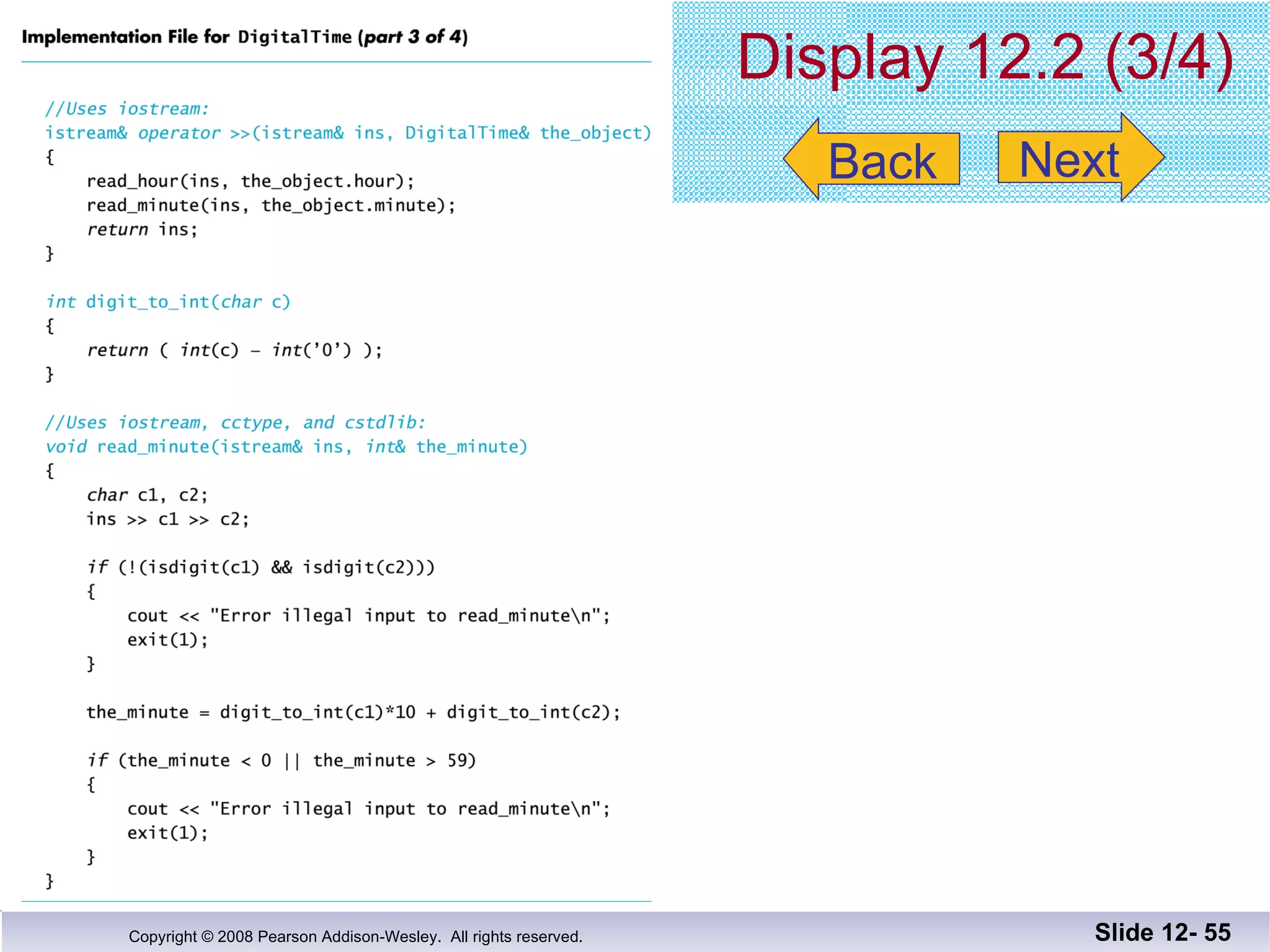
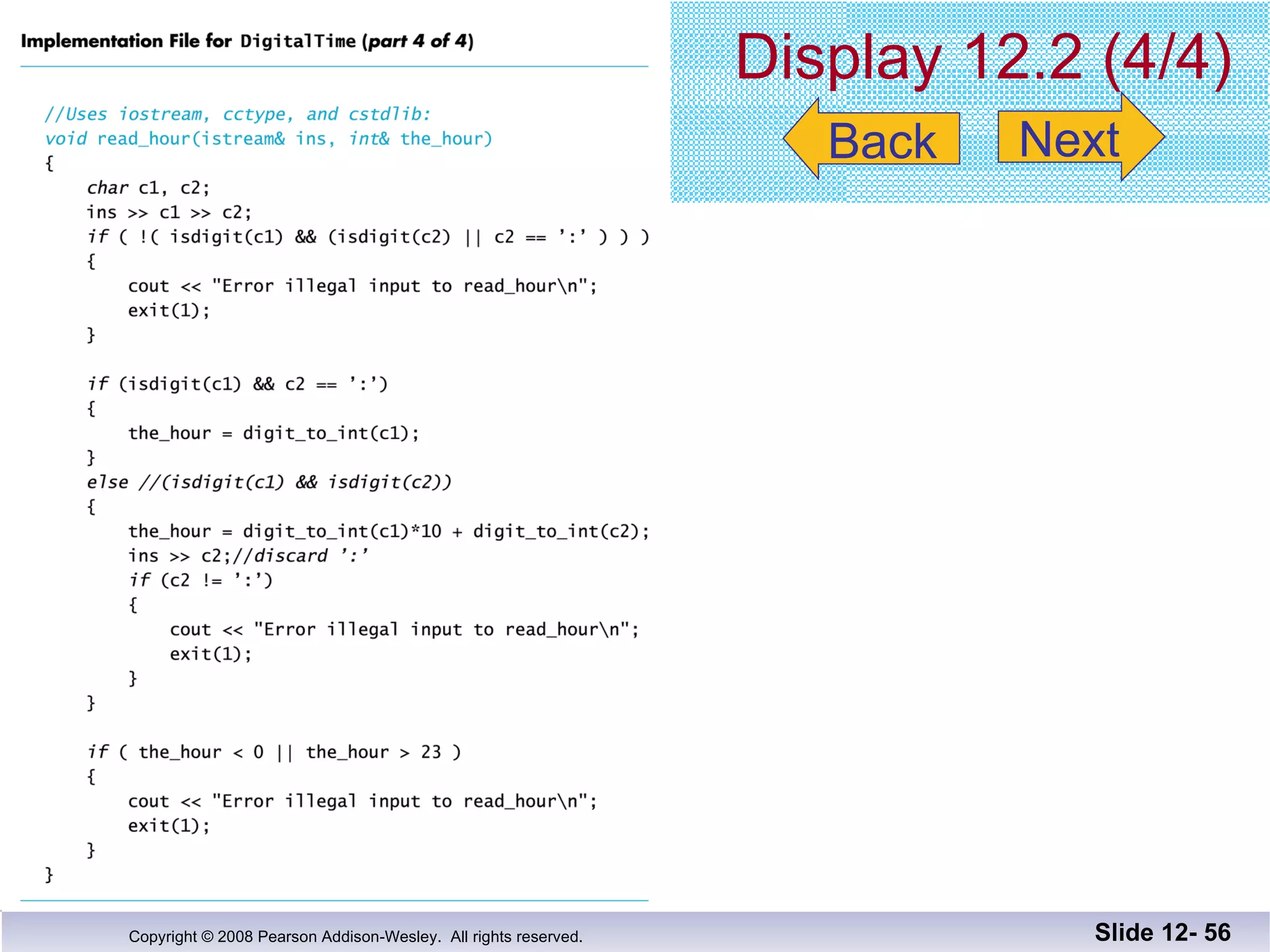
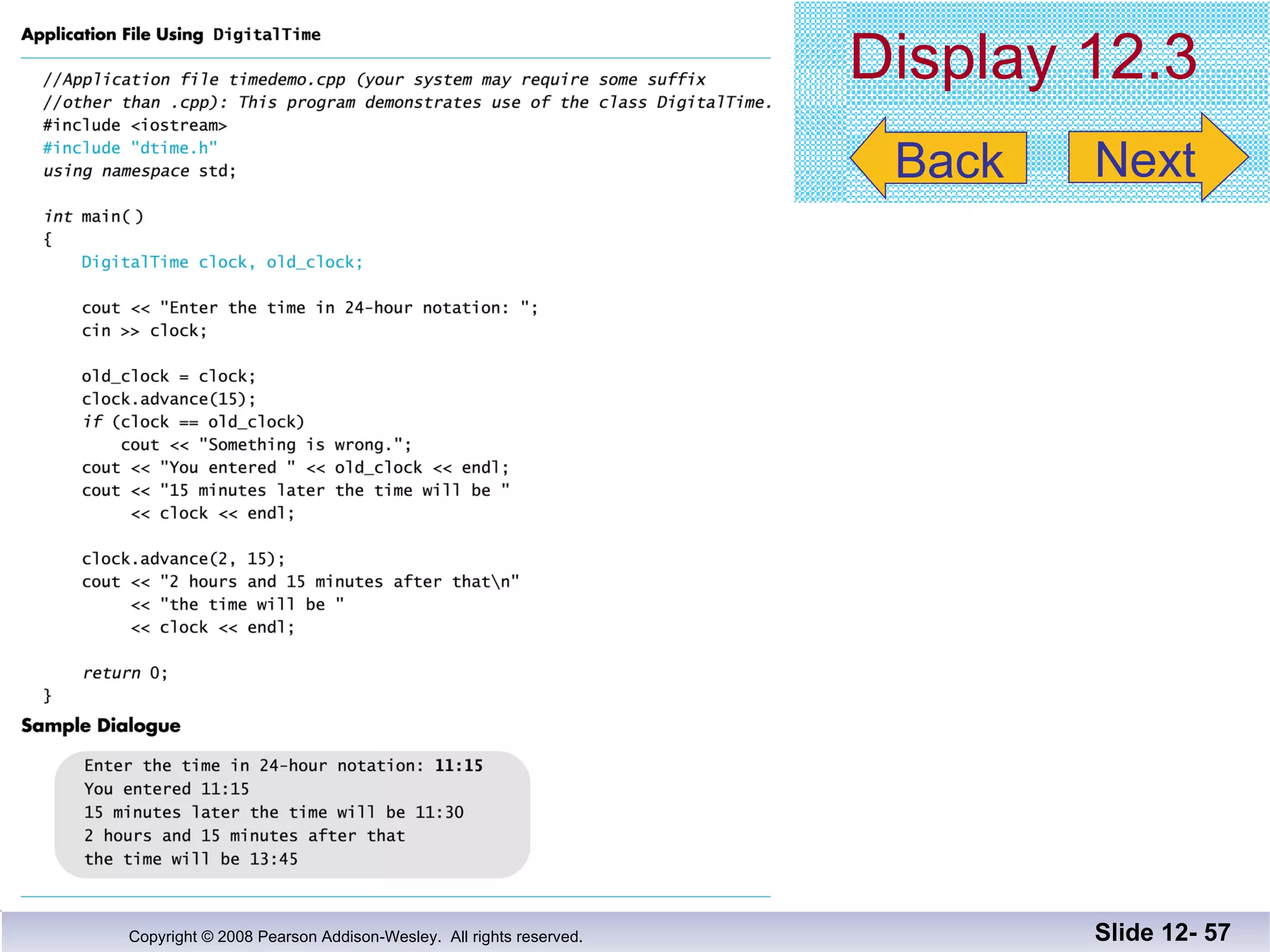
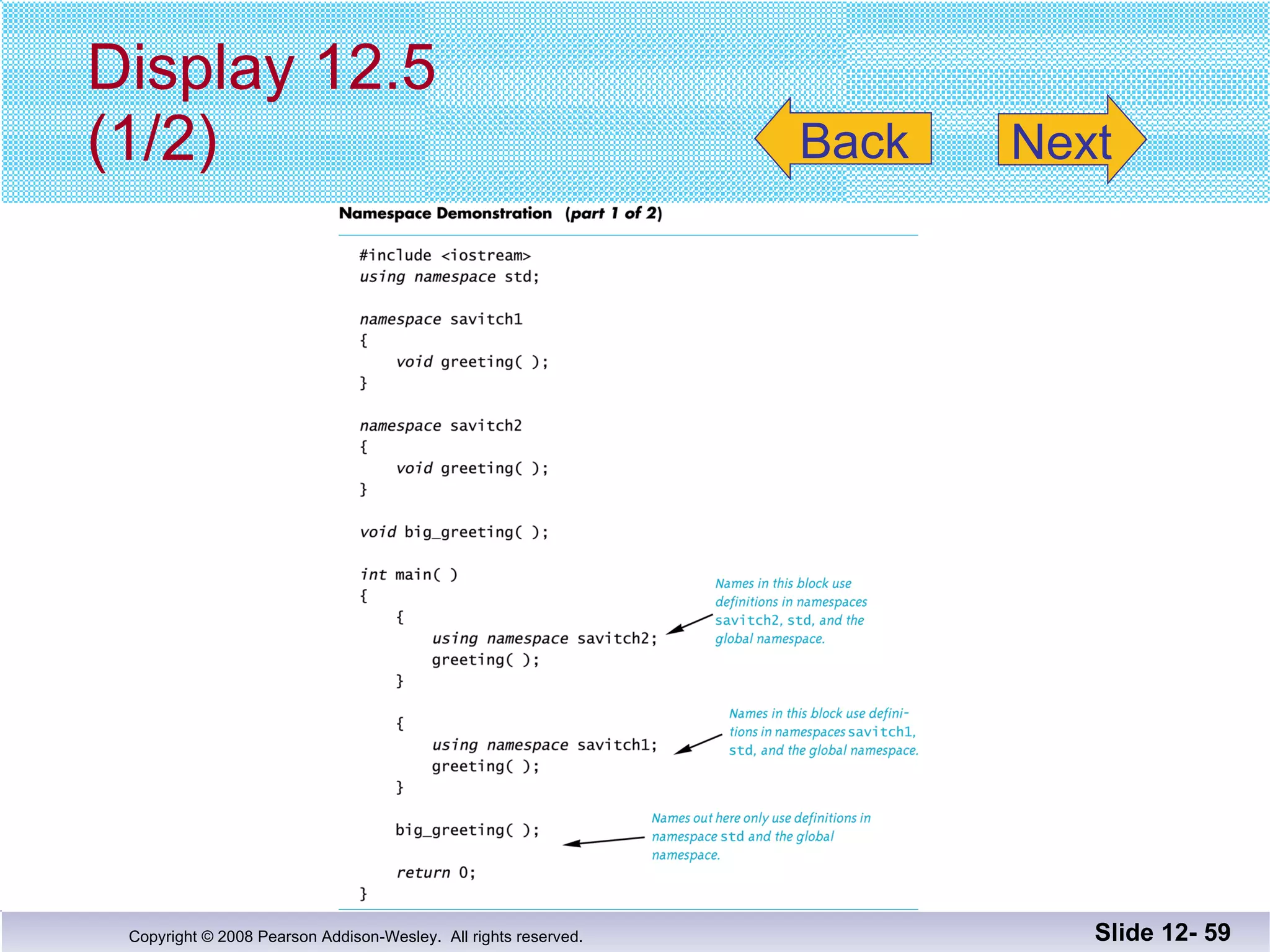
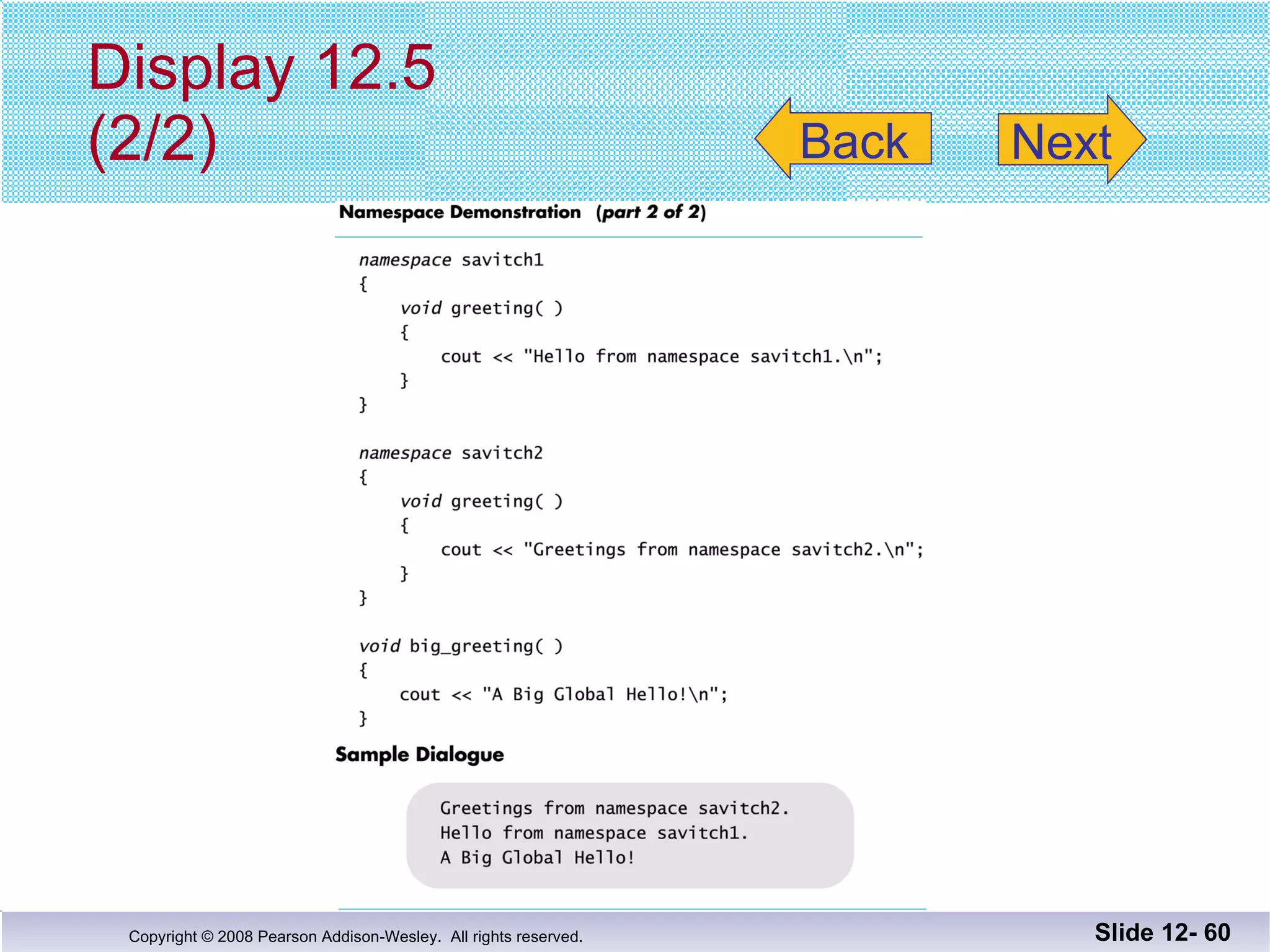
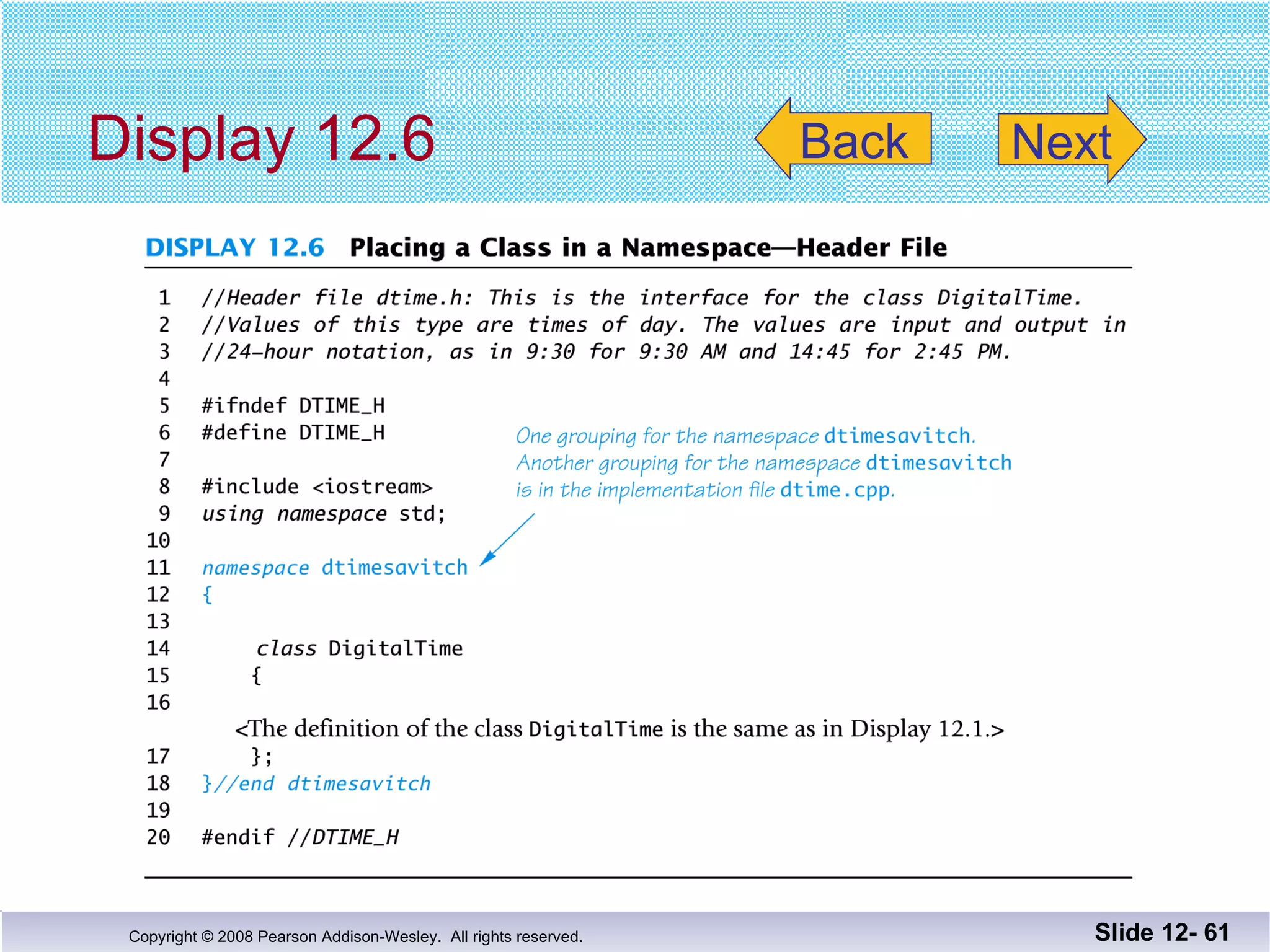
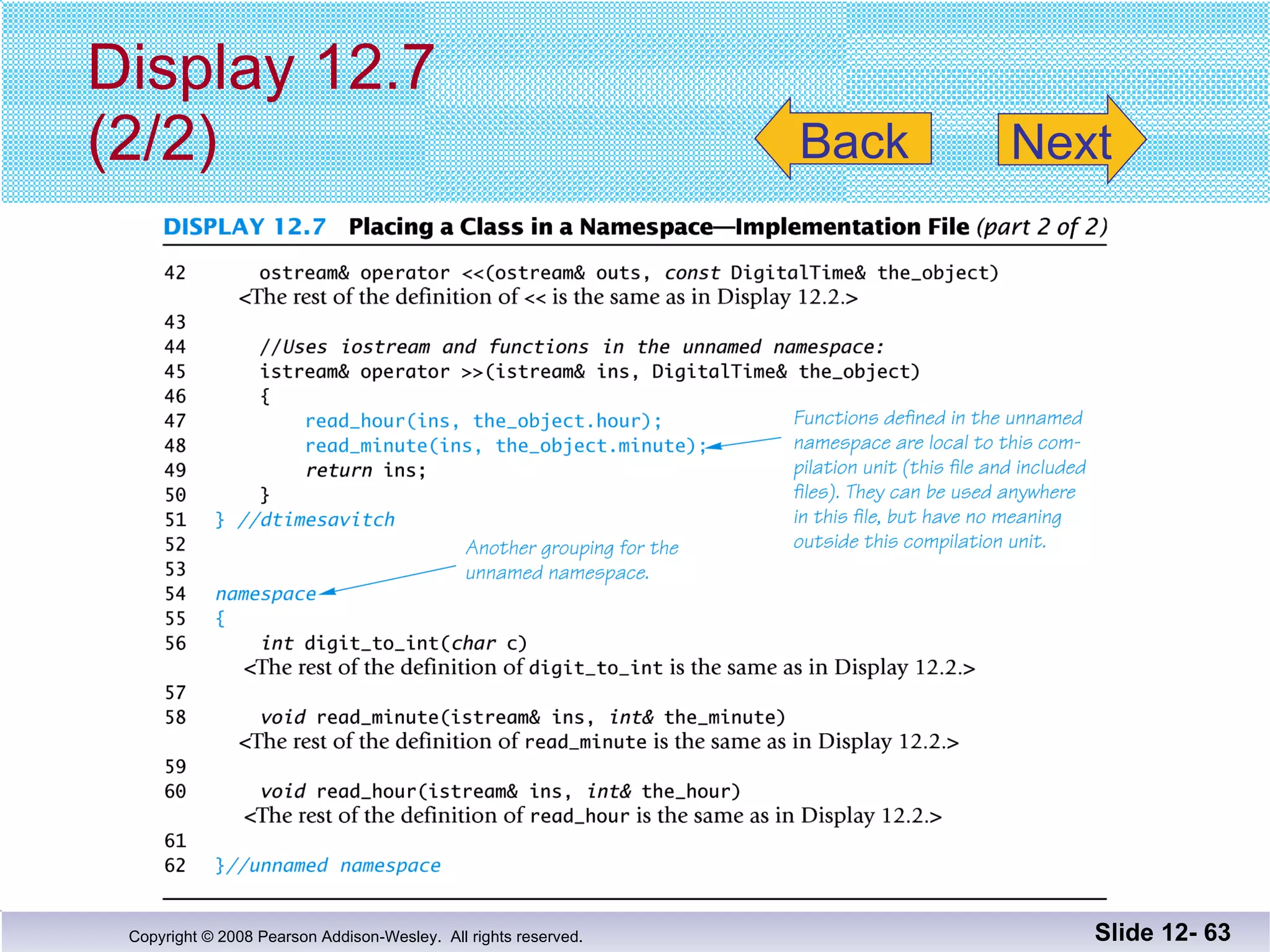
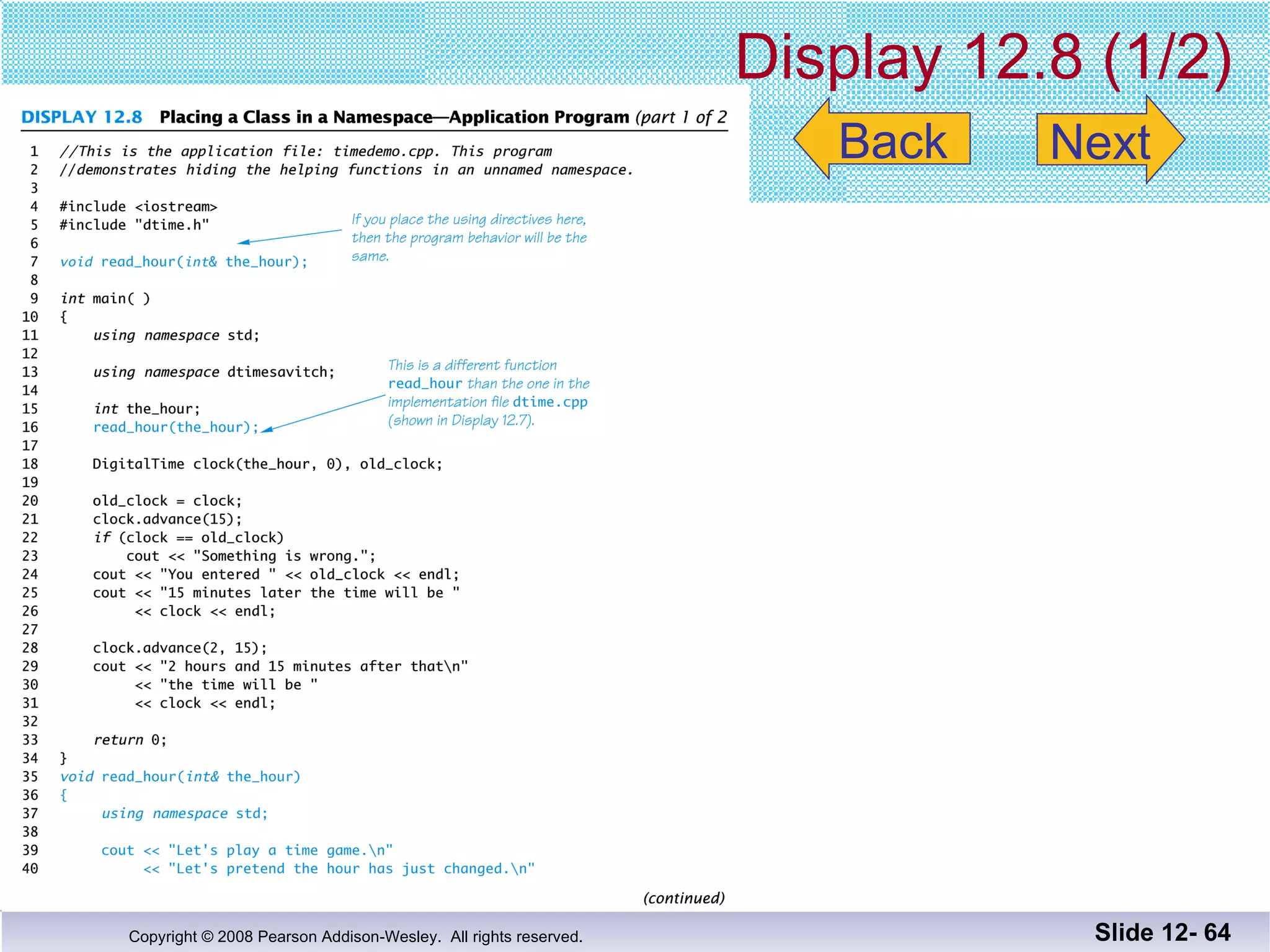
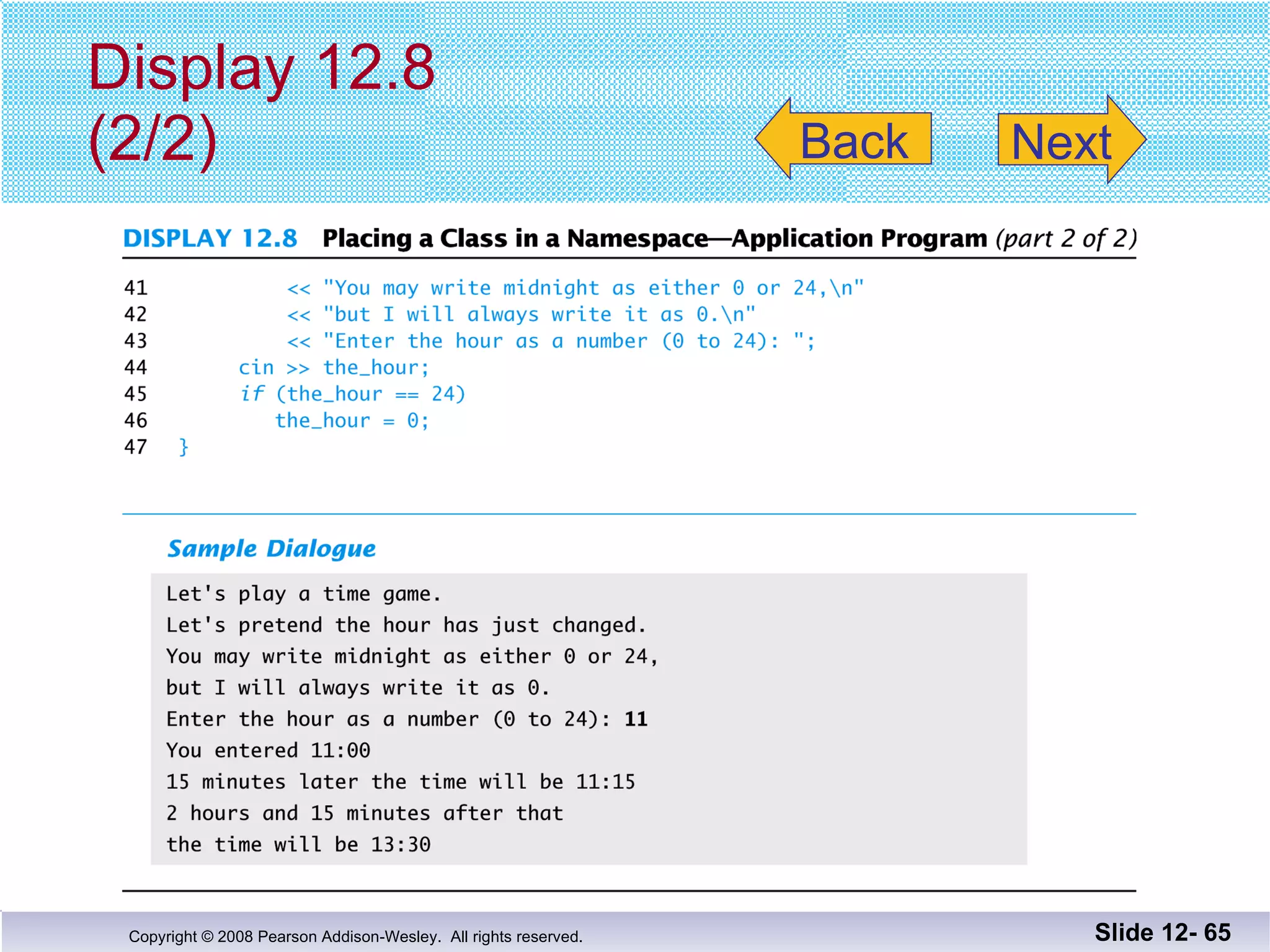
The document discusses separate compilation and namespaces in C++. It explains that separate compilation allows a program to be divided into parts that can be stored in separate files and compiled separately. This allows classes to be reused across multiple programs. Namespaces help avoid name conflicts when different code uses the same name. Code can be grouped into namespaces, and individual names from a namespace can be used via qualification or directives.