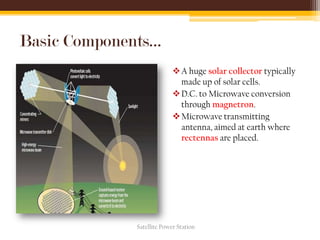
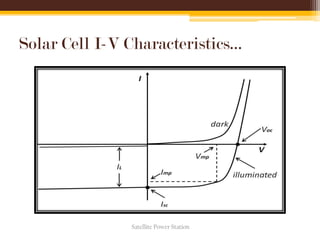
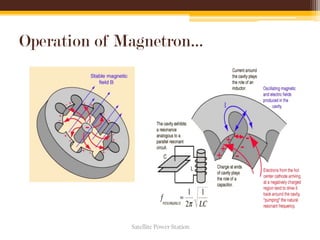
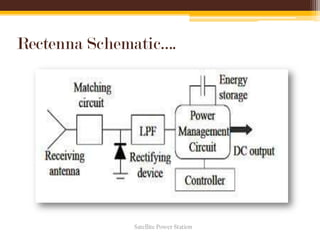
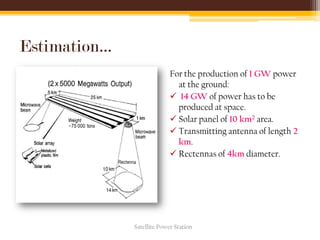
The document discusses the concept and feasibility of satellite power stations (SPS), which collect solar energy in space and transmit it via microwaves to Earth. It outlines the historical development, key components like solar collectors and rectennas, and the technical challenges of implementing SPS, such as cost and environmental impact. The document concludes with references and acknowledges the potential of SPS as an innovative energy solution.