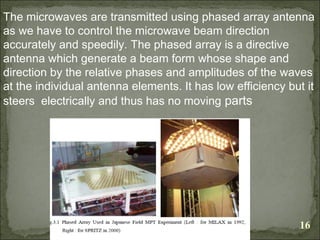
The document discusses the concept of Solar Power Satellites (SPS) as a solution for sustainable energy generation, utilizing solar energy collected in space to produce electricity for Earth through microwave power transmission. It outlines the components of SPS, benefits such as continuous energy availability and low environmental impact, and addresses challenges including construction, legal concerns, and environmental safety. A future research program is suggested to gather necessary data for informed deployment decisions regarding SPS technology.