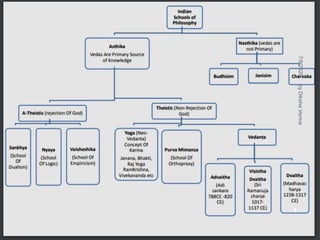
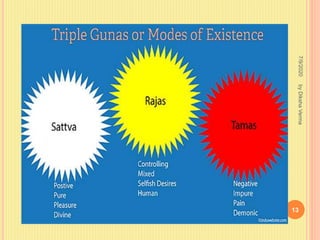
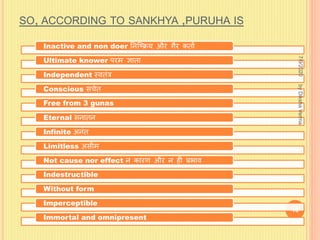
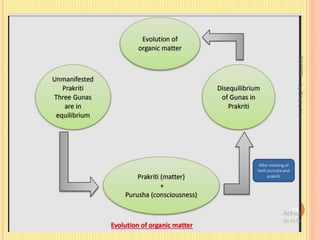
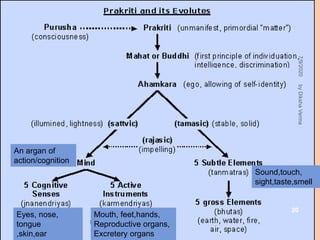
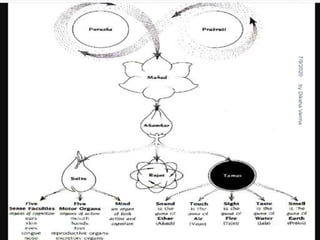
Sankhya philosophy believes in two realities - Purusha (consciousness) and Prakriti (matter). Prakriti is considered the root cause of the universe. It is eternal, the source of all creation, composed of three gunas (qualities), and exists in an unmanifest state. Purusha represents pure consciousness and is multiple in number. It is inactive and free from attributes. The interaction between Purusha and Prakriti leads to the evolution of the universe, with the goal of providing liberation to Purusha.