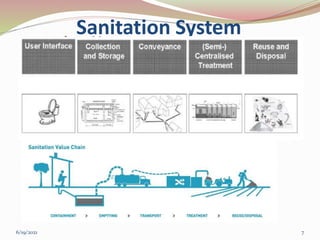
The document discusses sanitation, providing definitions and describing its objectives and relationship to public health and the environment. Sanitation refers to the provision of facilities and services for the safe disposal of human waste and maintenance of hygienic conditions. The objectives of sanitation include providing a healthy living environment, protecting natural resources, and breaking the cycle of disease transmission. Proper sanitation is needed to promote public health by preventing the spread of diseases and improving quality of life, as well as to protect the environment from pollution and water resource contamination.