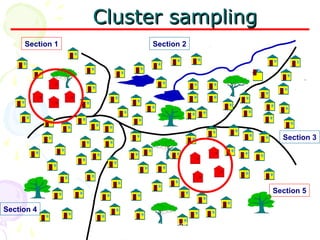
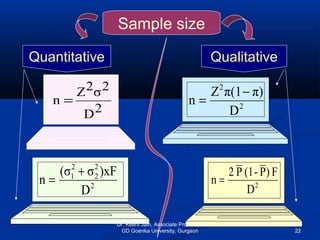
The document discusses important statistical terms related to sampling. It defines population as the set of all measurements of interest to the researcher, and sample as a subset of the population. Sampling is done to get information about large populations at lower cost and with greater accuracy compared to studying the entire population. The document outlines different types of sampling methods including probability and non-probability sampling, and provides examples like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster sampling. It also discusses factors like sampling size, sampling error, and type 1 and type 2 errors.