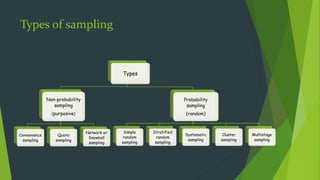
Sampling is a procedure used to make inferences about a larger population by studying a representative subset of it. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where units have a known, non-zero chance of being selected; and non-probability sampling, where units are selected through convenience. Some common sampling methods include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. The goal is to select a sample that efficiently and cost-effectively represents the population while addressing requirements like representativeness, measurability, and feasibility.