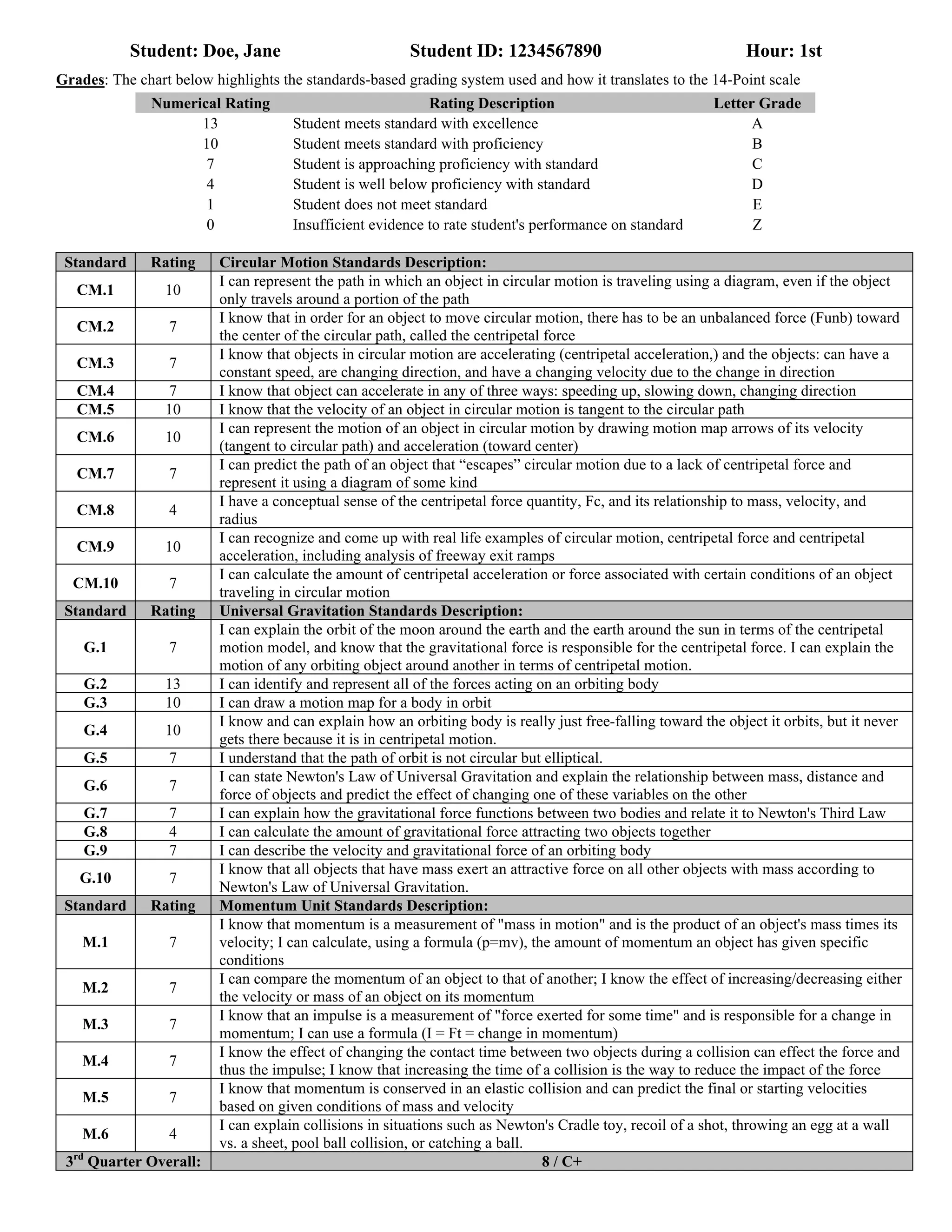
The document outlines the grading standards for a student named Jane Doe, detailing her performance in a physics course focused on circular motion, universal gravitation, and momentum. Each standard is rated on a 14-point scale, with Jane achieving various ratings across different concepts. Her overall grade for the third quarter is an 8, equivalent to a letter grade of C+.