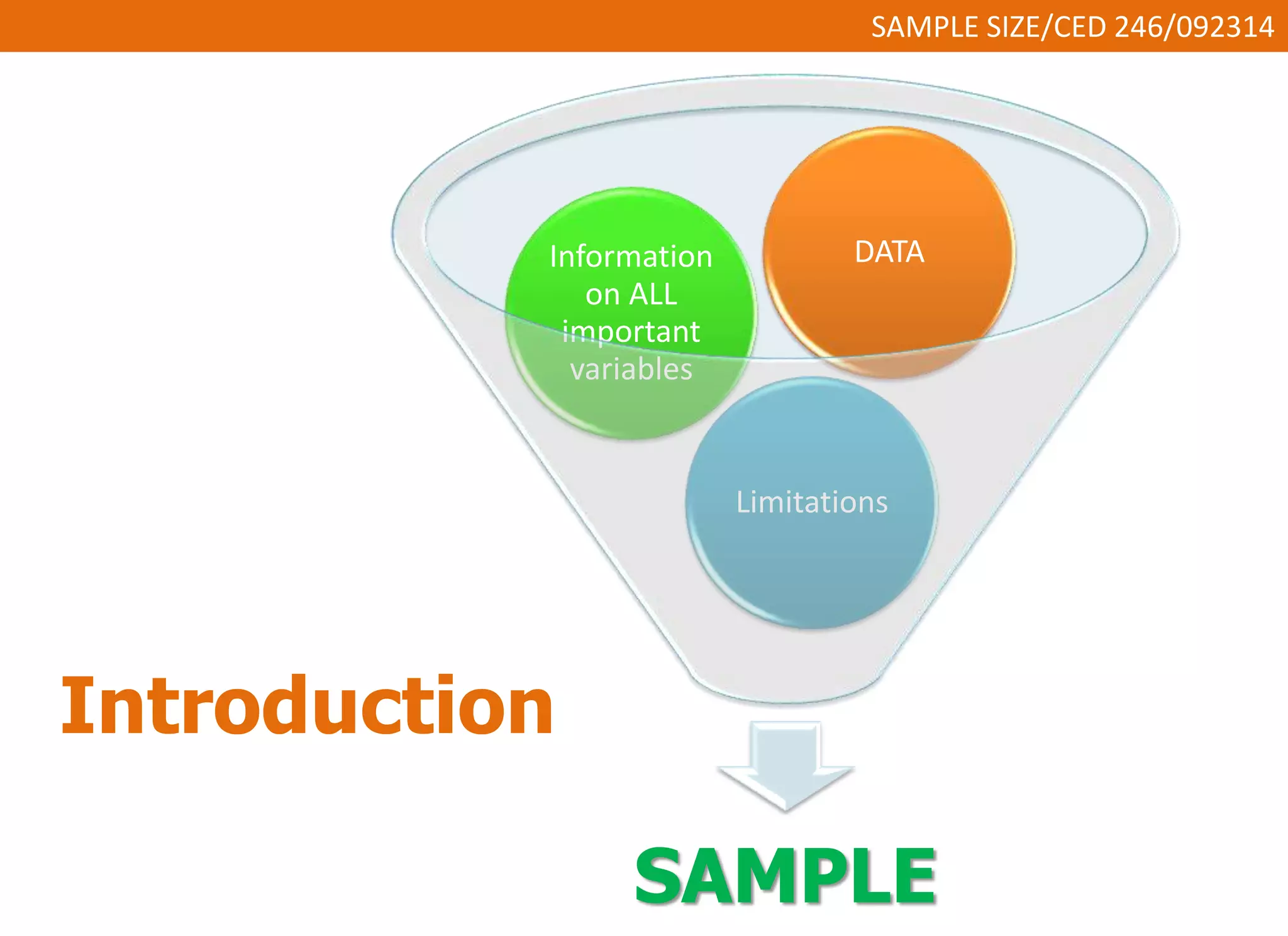
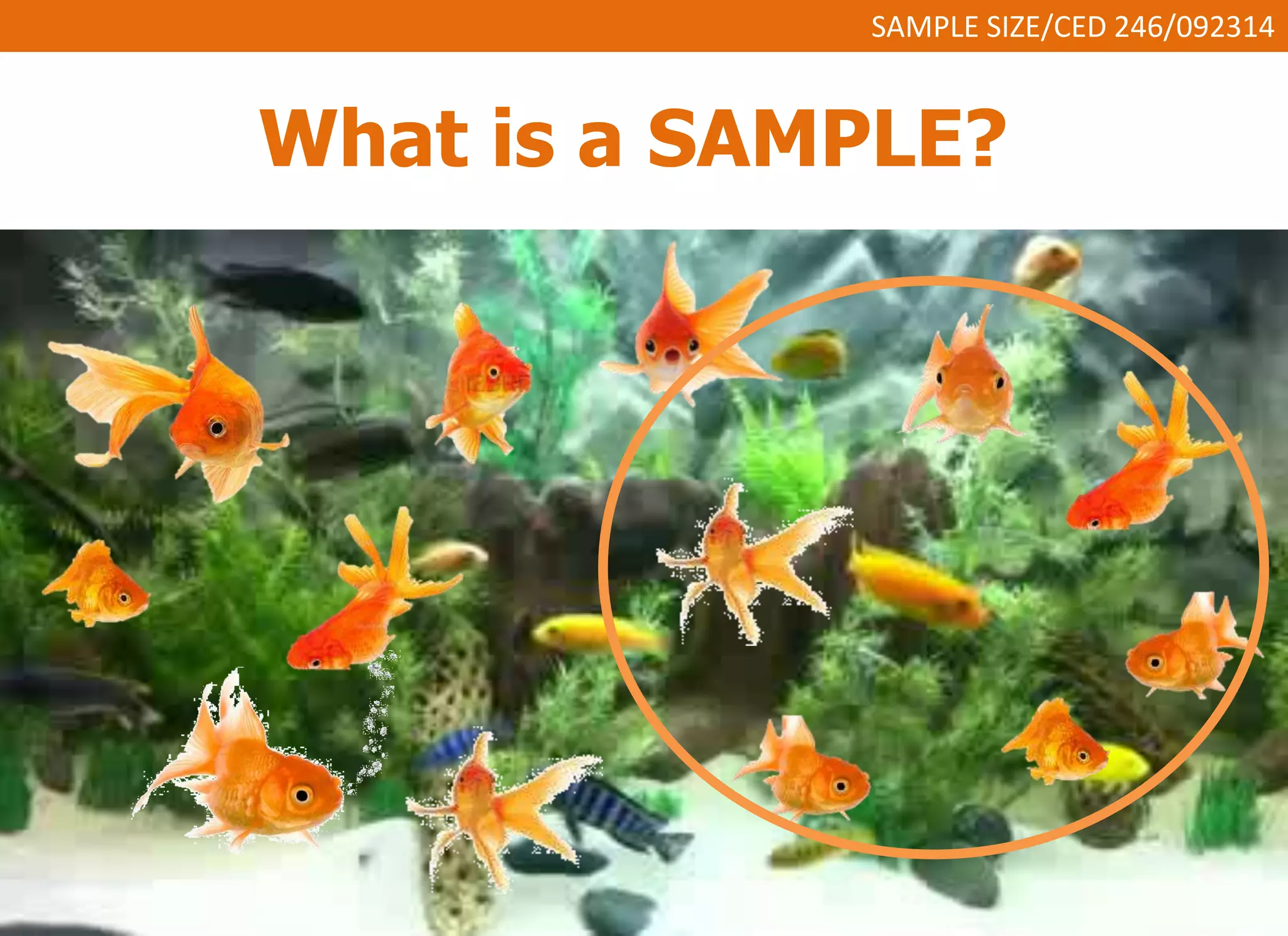
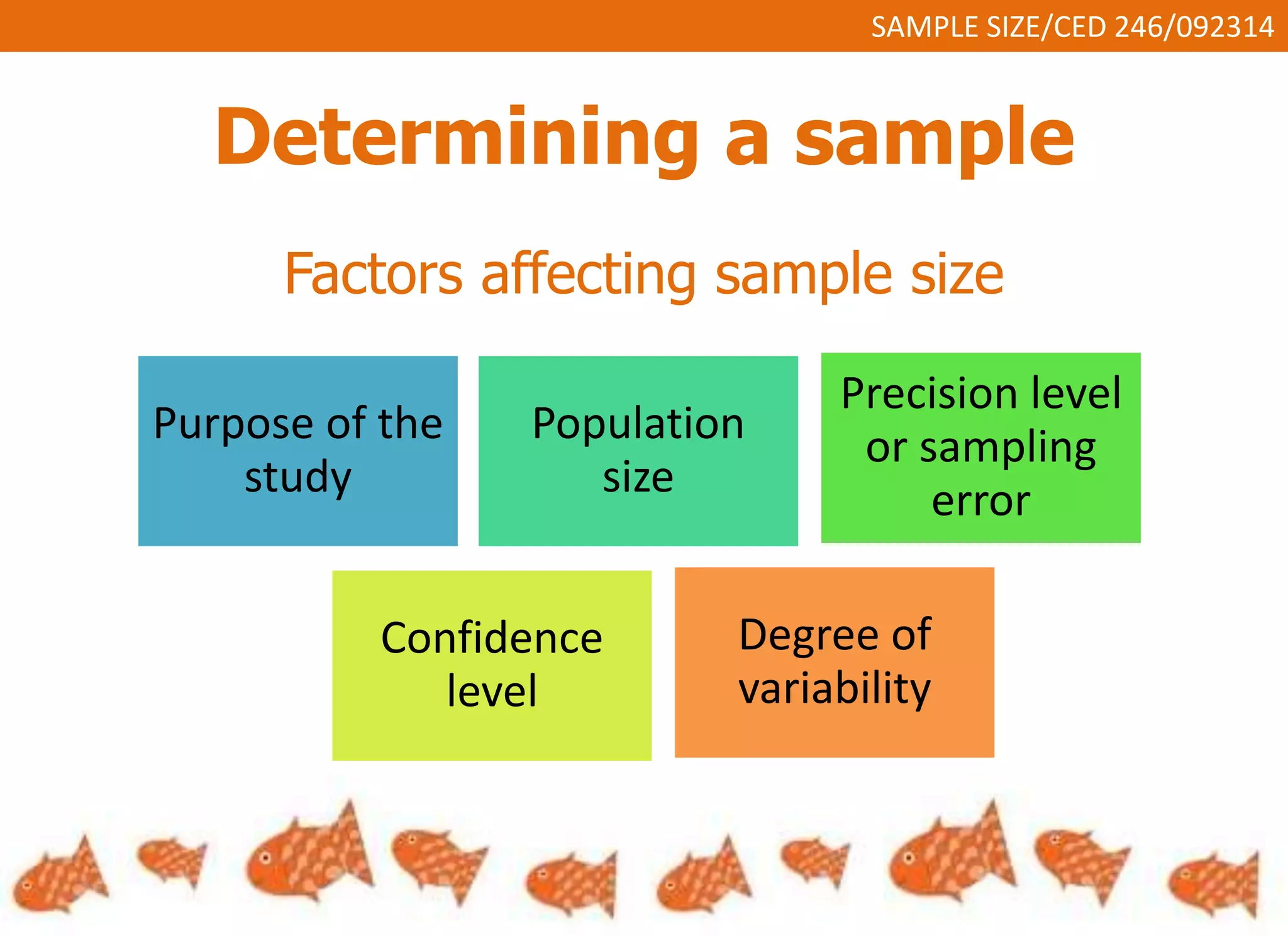
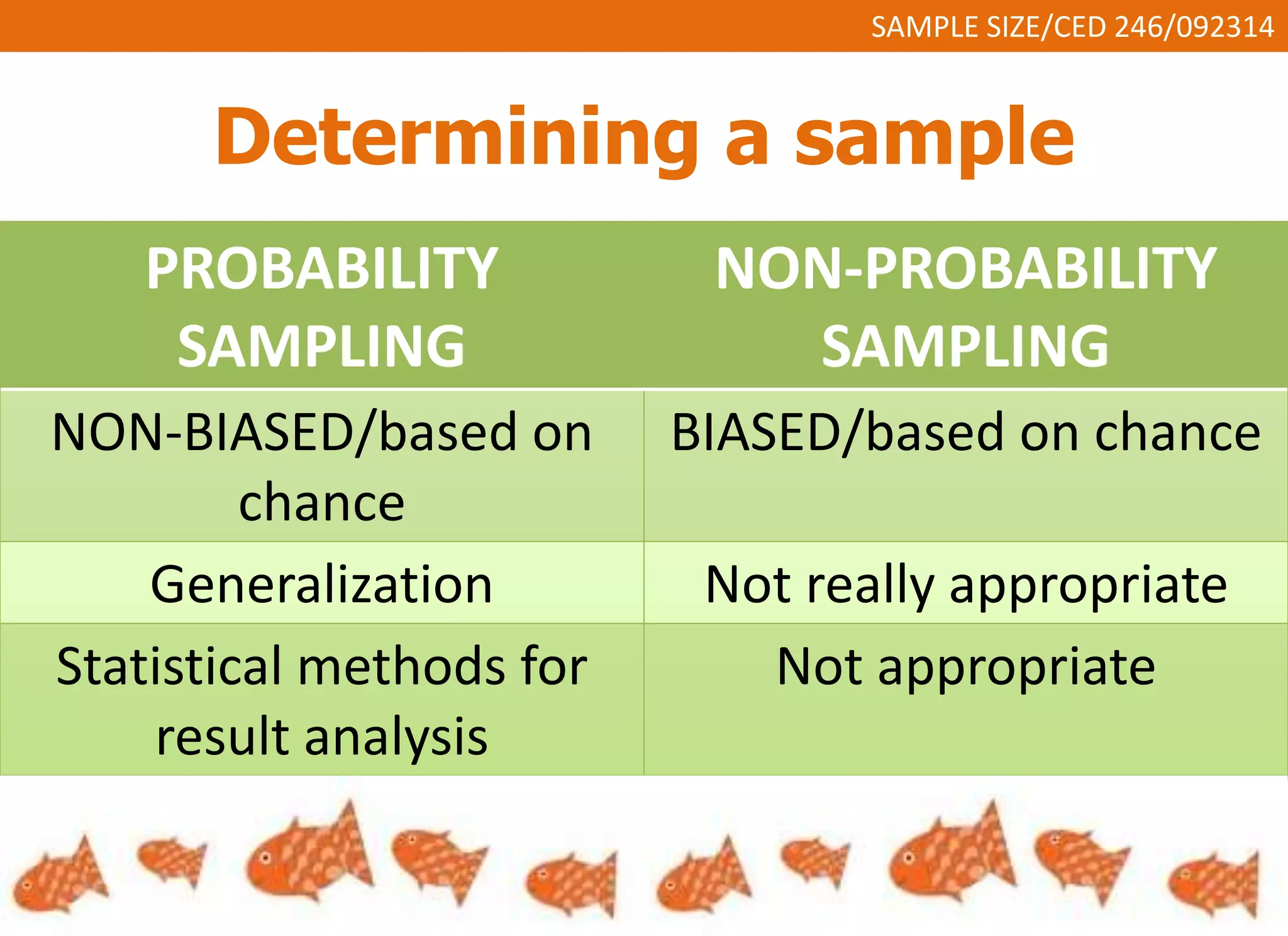
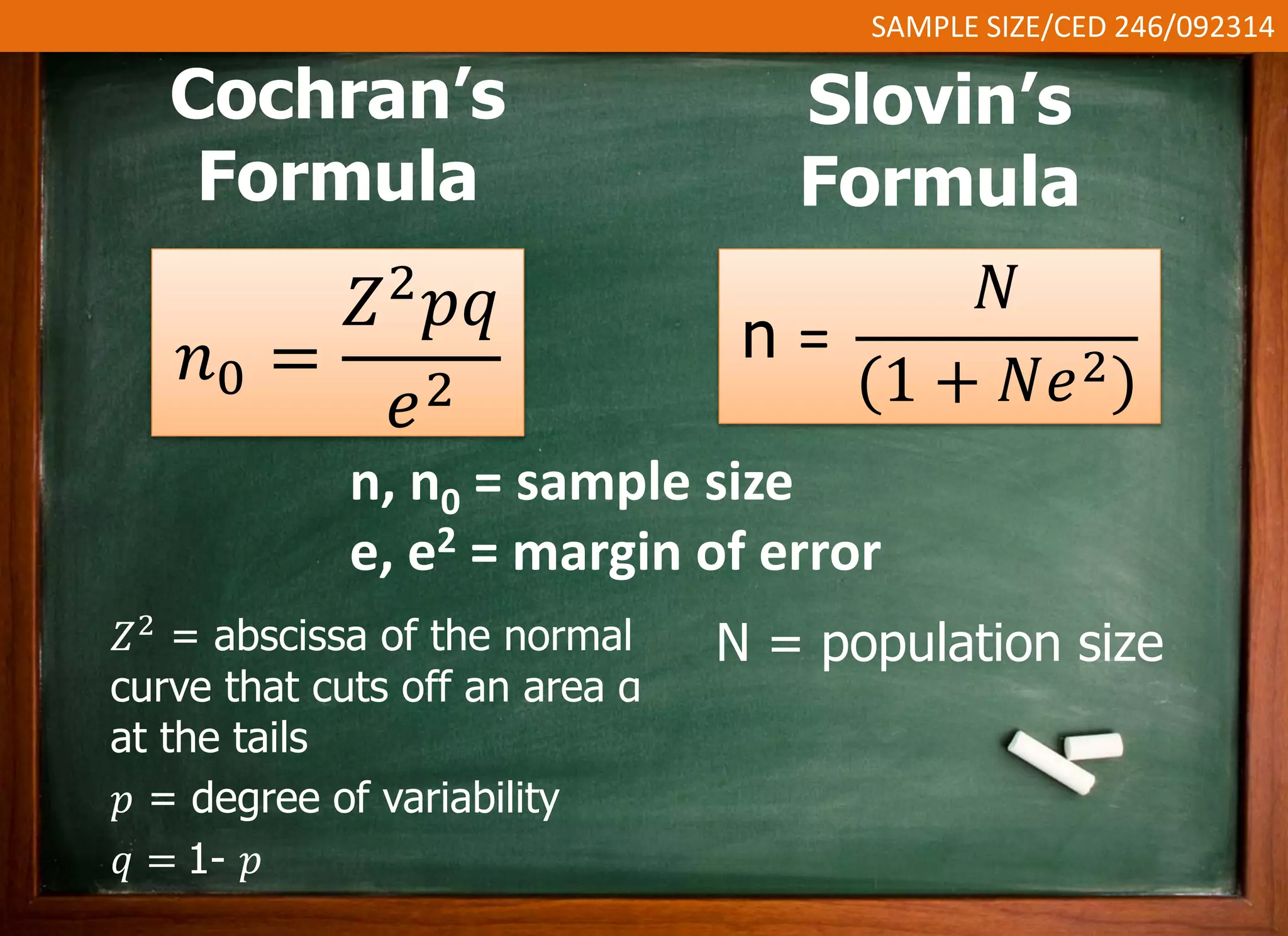
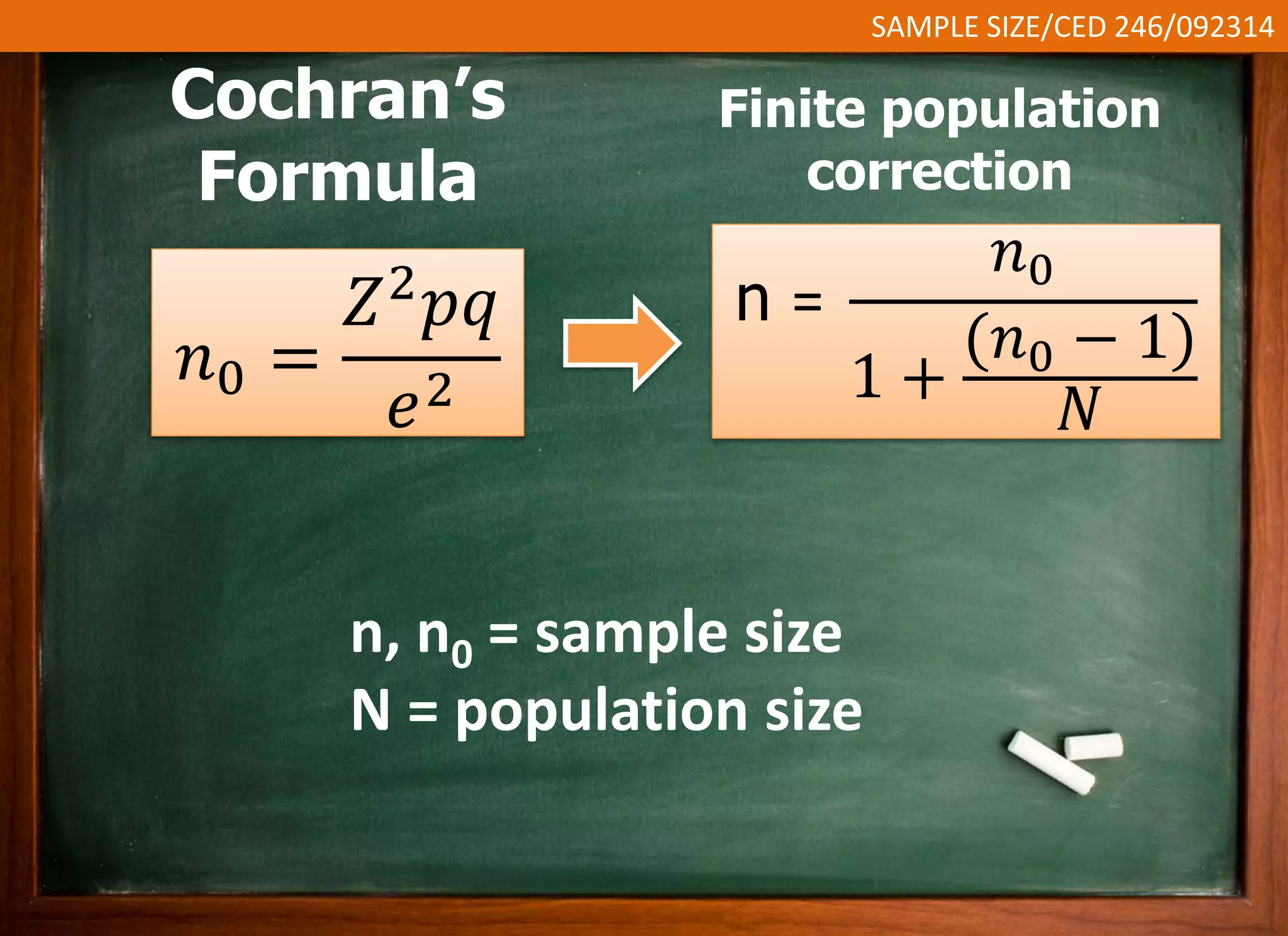
This document discusses sample size and determining an appropriate sample size for evaluation purposes. It introduces the concepts of a sample, population size, precision level, confidence level, and variability in determining sample size. Several sampling strategies are presented, including probability and non-probability sampling. Formulas are provided for calculating sample size, such as Slovin's formula and Cochran's formula which take into account factors like margin of error, population size, and degree of variability. Guidelines are given for selecting an appropriate sample size based on the purpose of the study and available population.