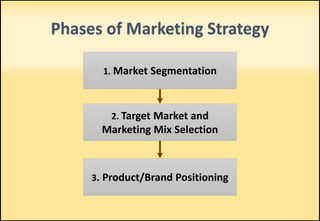
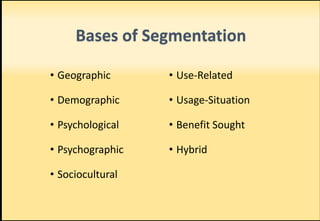
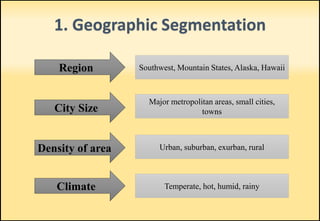
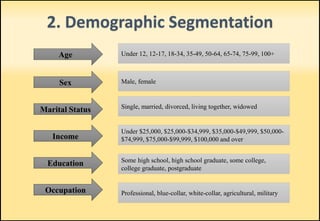
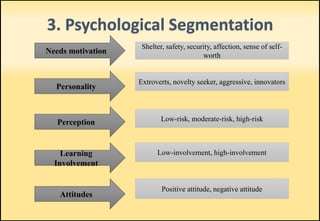
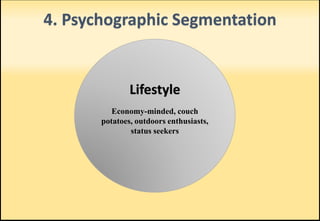
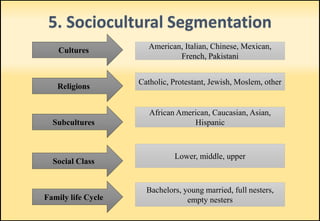
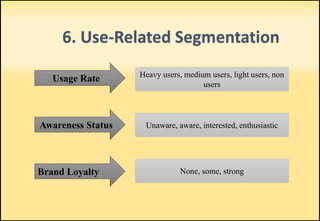
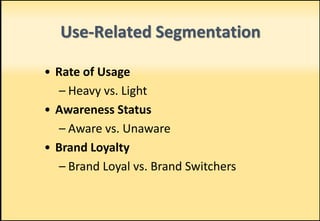
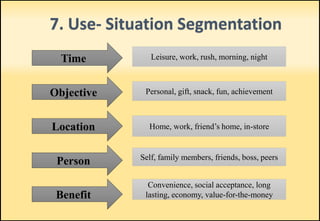
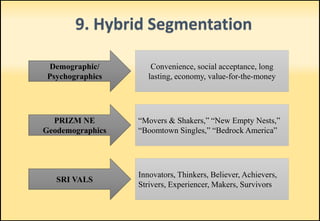
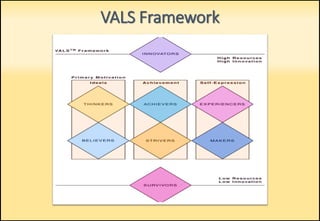
The document outlines market segmentation, defining it as the process of dividing a potential market into distinct subsets of consumers. It details various segmentation bases including geographic, demographic, psychographic, sociocultural, use-related, usage-situation, and benefit segmentation. Additionally, it discusses the importance of understanding consumer needs and implementing effective targeting strategies for market segments.