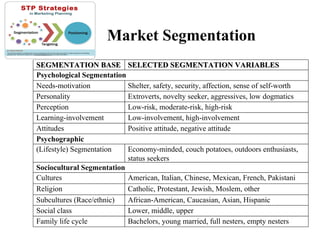
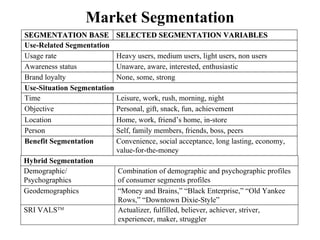
The document provides an in-depth exploration of market segmentation, detailing its definition and phases, including the process of identifying target markets and developing marketing strategies. Various bases for segmentation such as geographic, demographic, psychological, and sociocultural are outlined, as well as hybrid approaches that combine different segmentation variables. Additionally, it discusses the importance of understanding consumer needs and motivations to facilitate product positioning and effective communication.