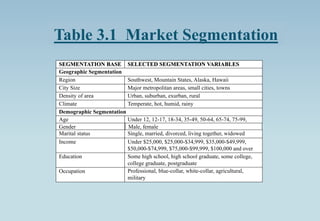
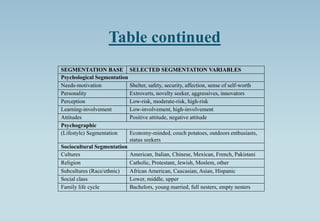
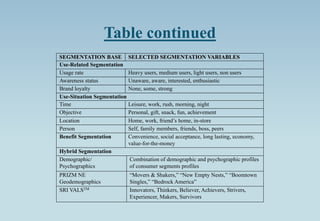
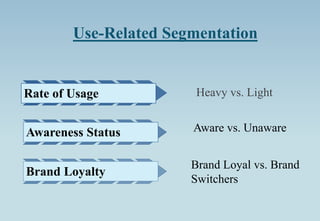
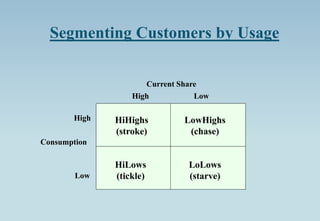
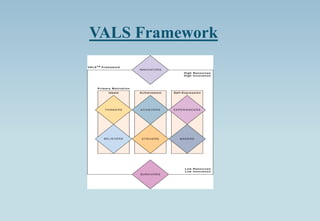
The document outlines the concept of market segmentation, detailing its significance in dividing potential markets into distinct consumer subsets for targeted marketing. It identifies various bases for segmentation, including geographic, demographic, psychological, and sociocultural factors, along with strategies for effective targeting. Additionally, it discusses different approaches for implementing segmentation strategies and the criteria for selecting target segments.