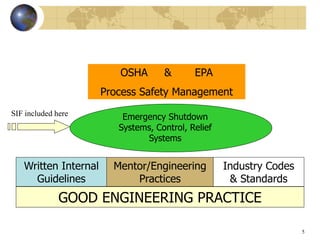
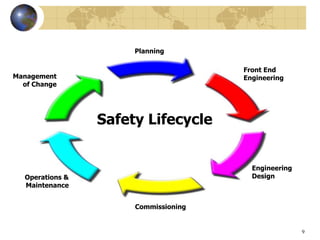
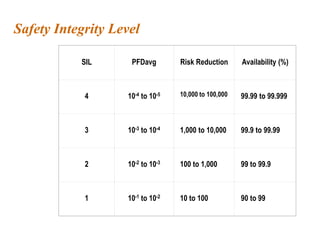
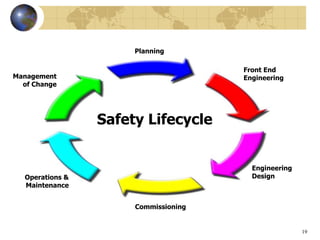
Safety instrumented systems (SIS) are designed to respond to hazardous conditions in industrial plants. An SIS monitors for conditions that could lead to hazards and responds by taking actions to prevent or mitigate hazards. Examples include high fuel gas pressure shutting off main valves or high reactor temperature opening a coolant valve. Standards like ISA 84.01 and IEC 61508/61511 provide guidelines for engineering practices to ensure SIS integrity through their lifecycle from planning and design to operations and maintenance. A key aspect is assessing risk and assigning a safety integrity level to guide system reliability design.