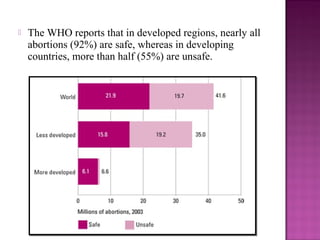
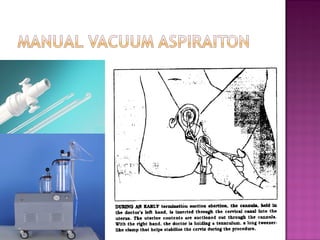
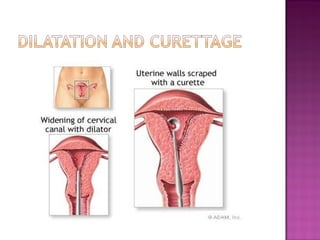
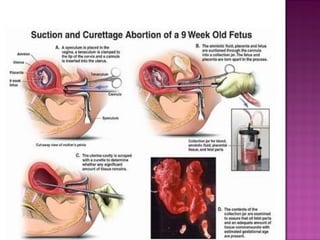
The document describes a case study of a 25-year-old unmarried woman who presented with heavy menstrual bleeding and was diagnosed with septic incomplete abortion and severe anemia. She was treated surgically and received blood transfusions and antibiotics. The document then provides background information on unsafe abortion, its prevalence in Nepal, and the country's abortion law which legalized abortion in certain conditions. It discusses methods of surgical and medical abortion and challenges to accessing safe abortion services in Nepal.