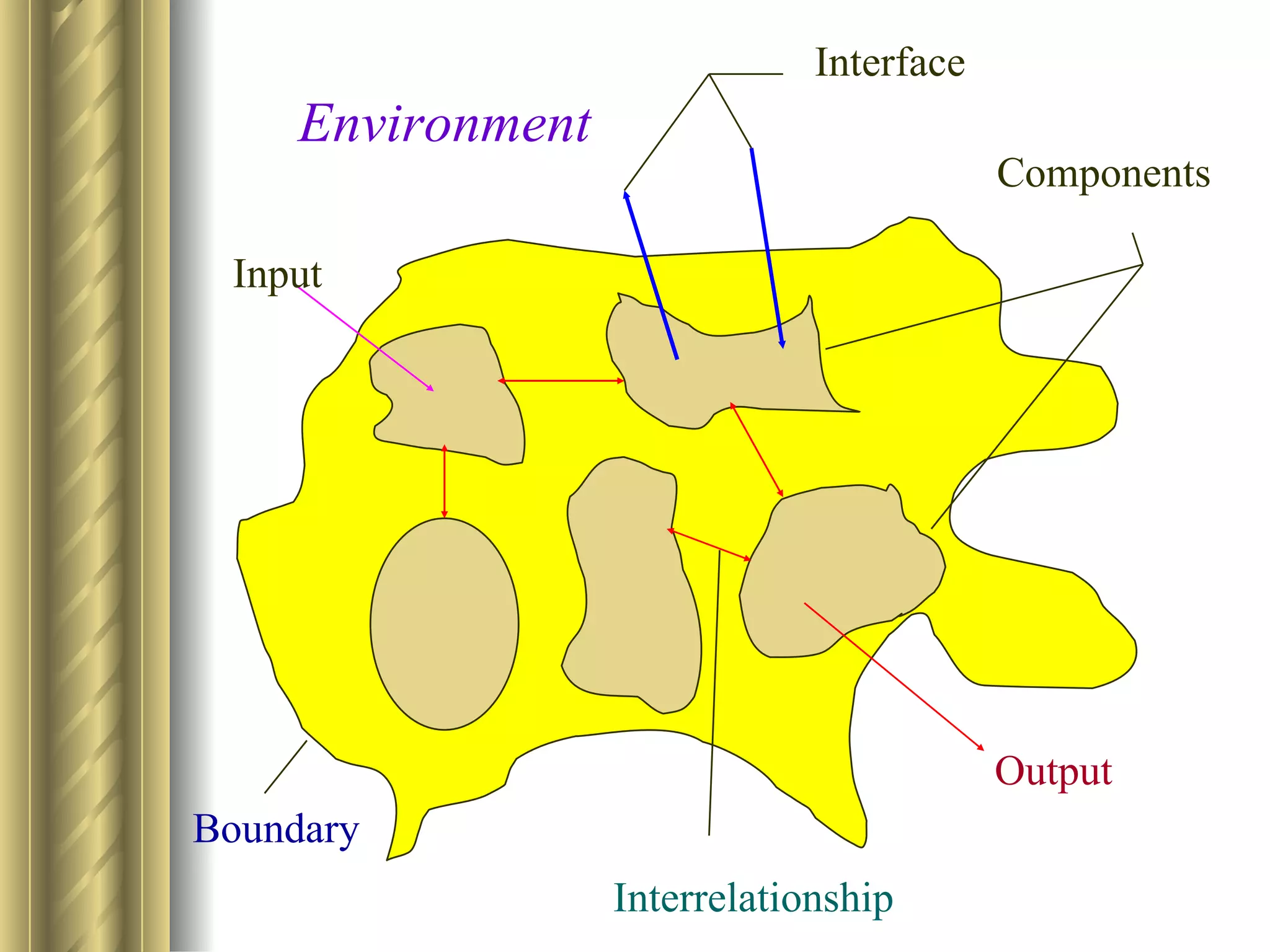
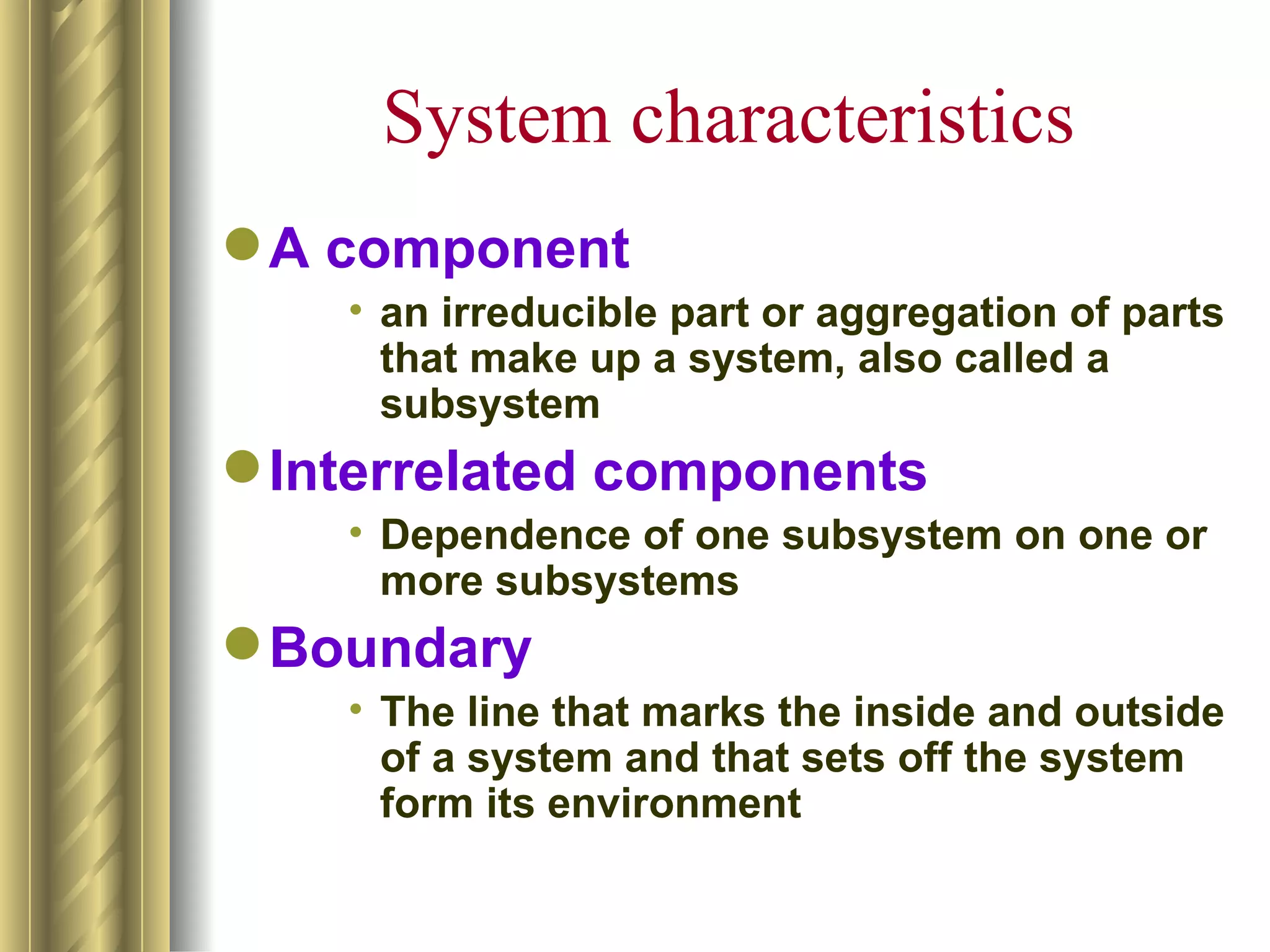
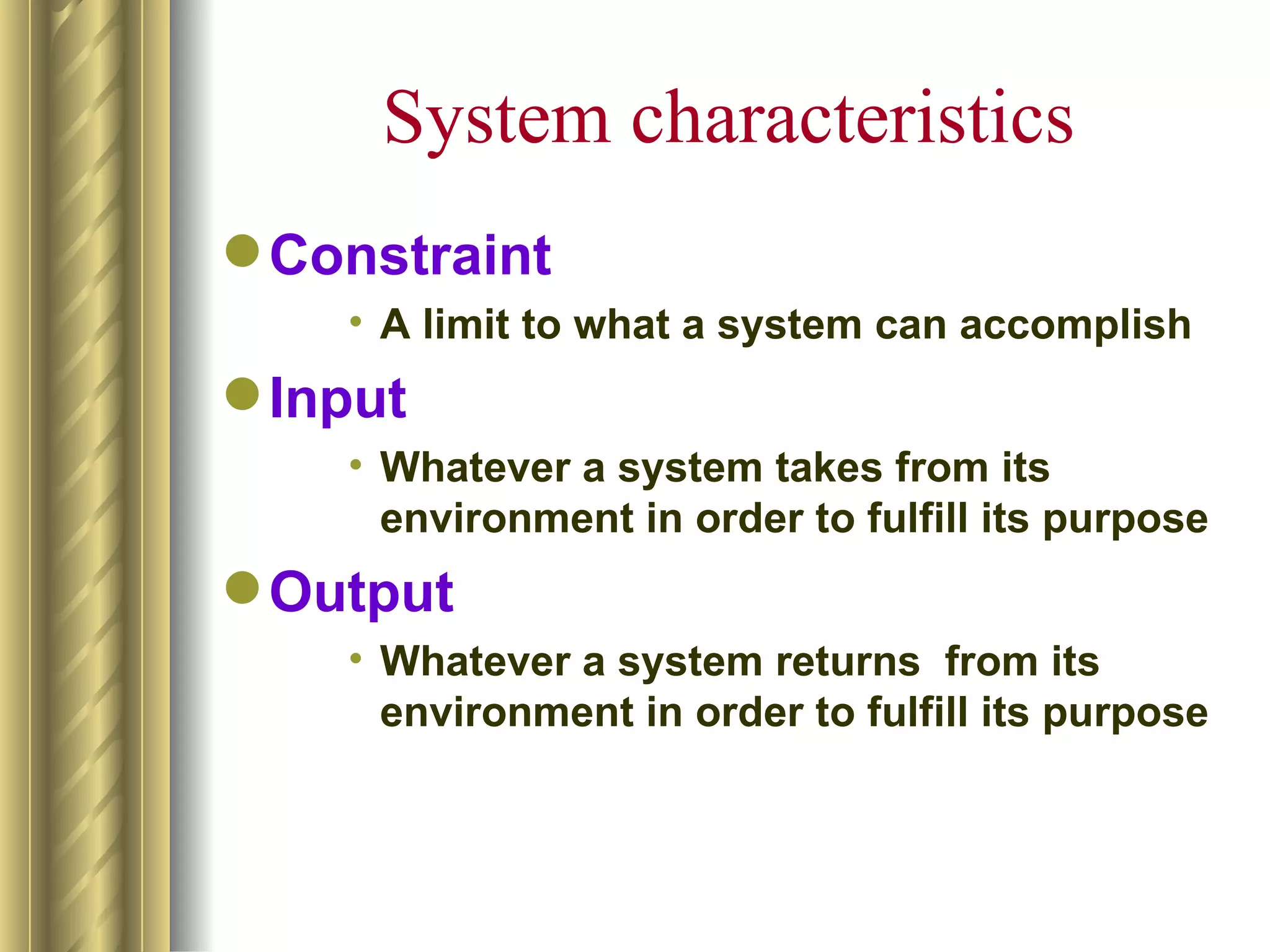
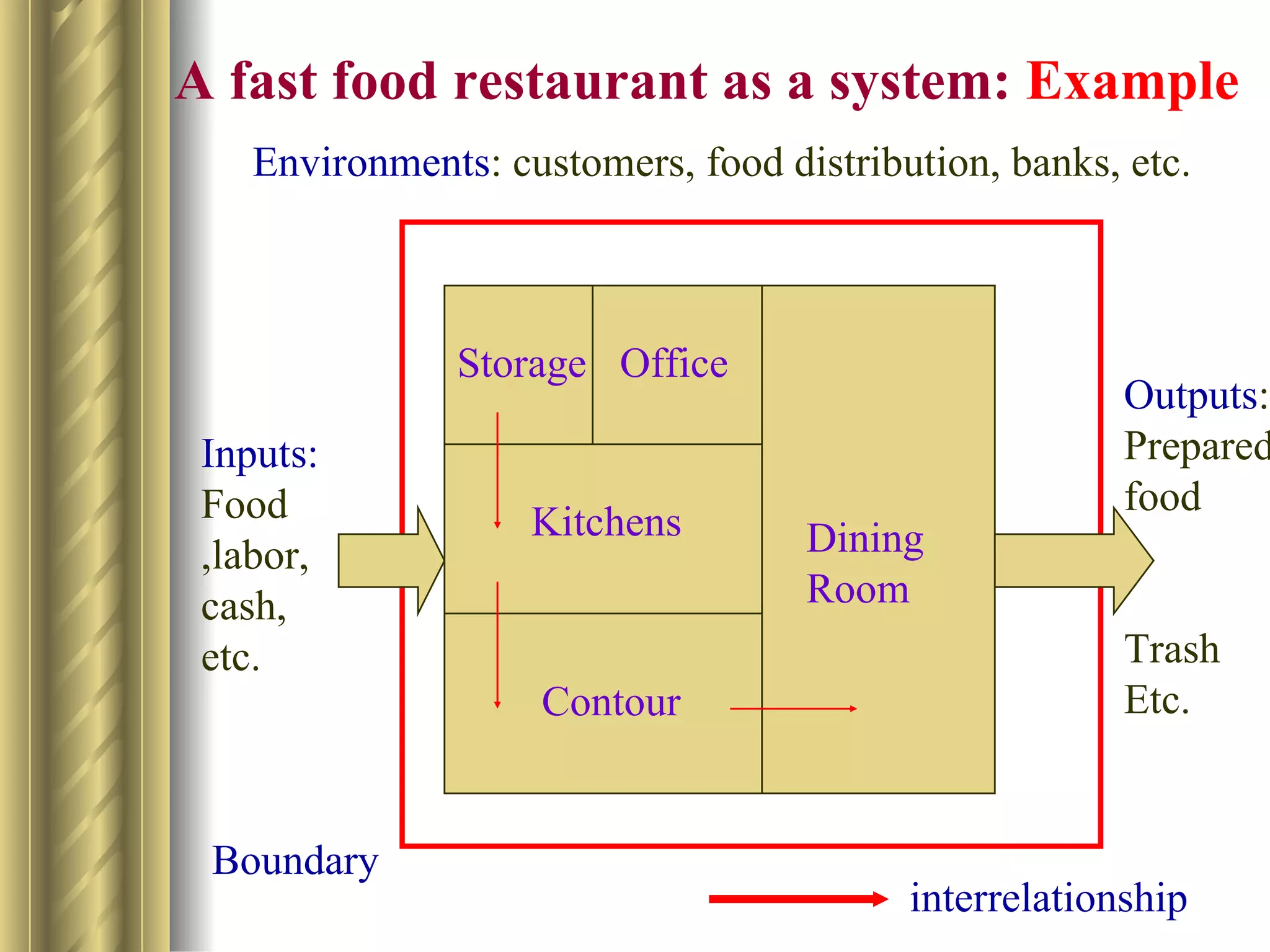
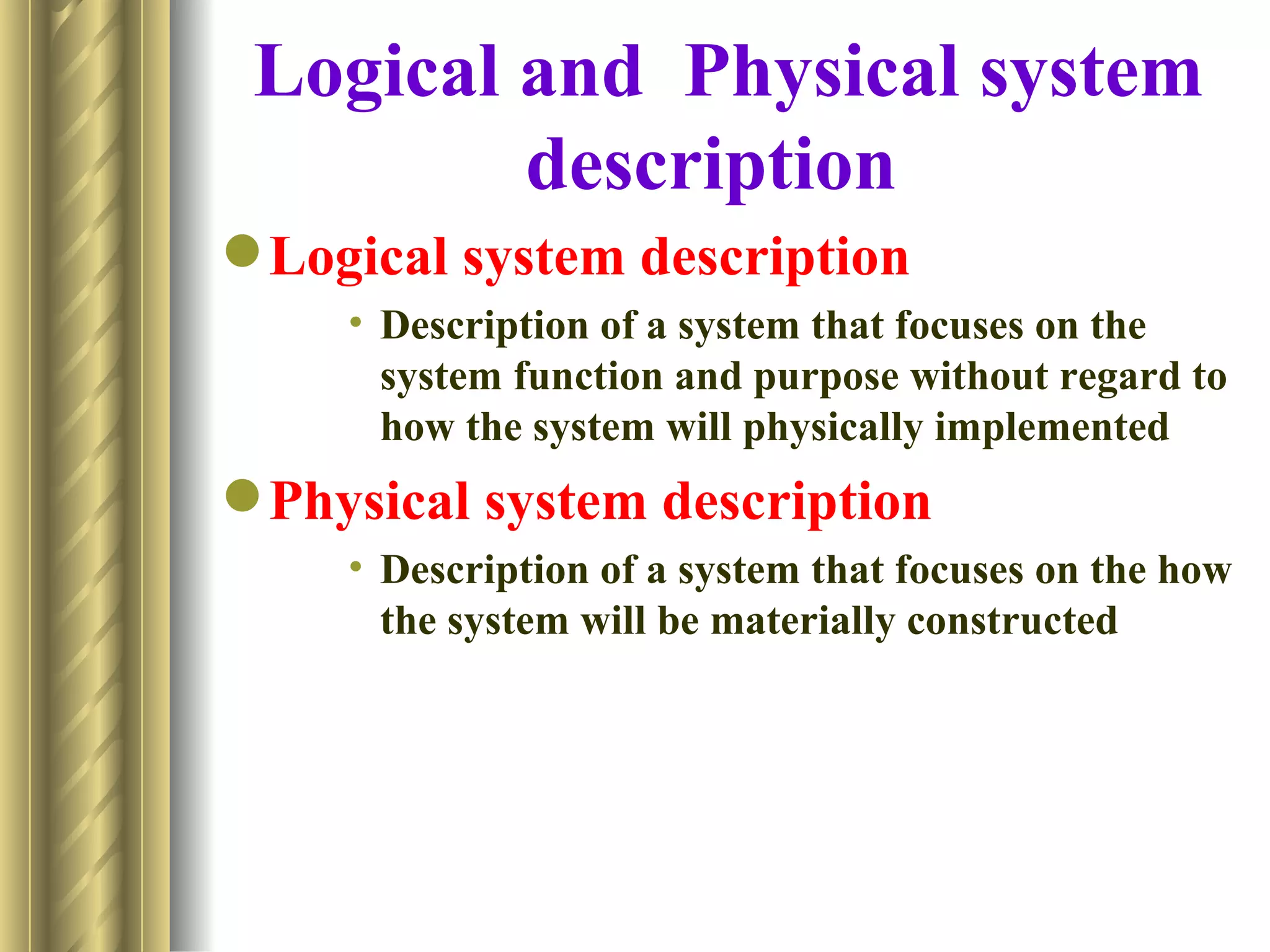
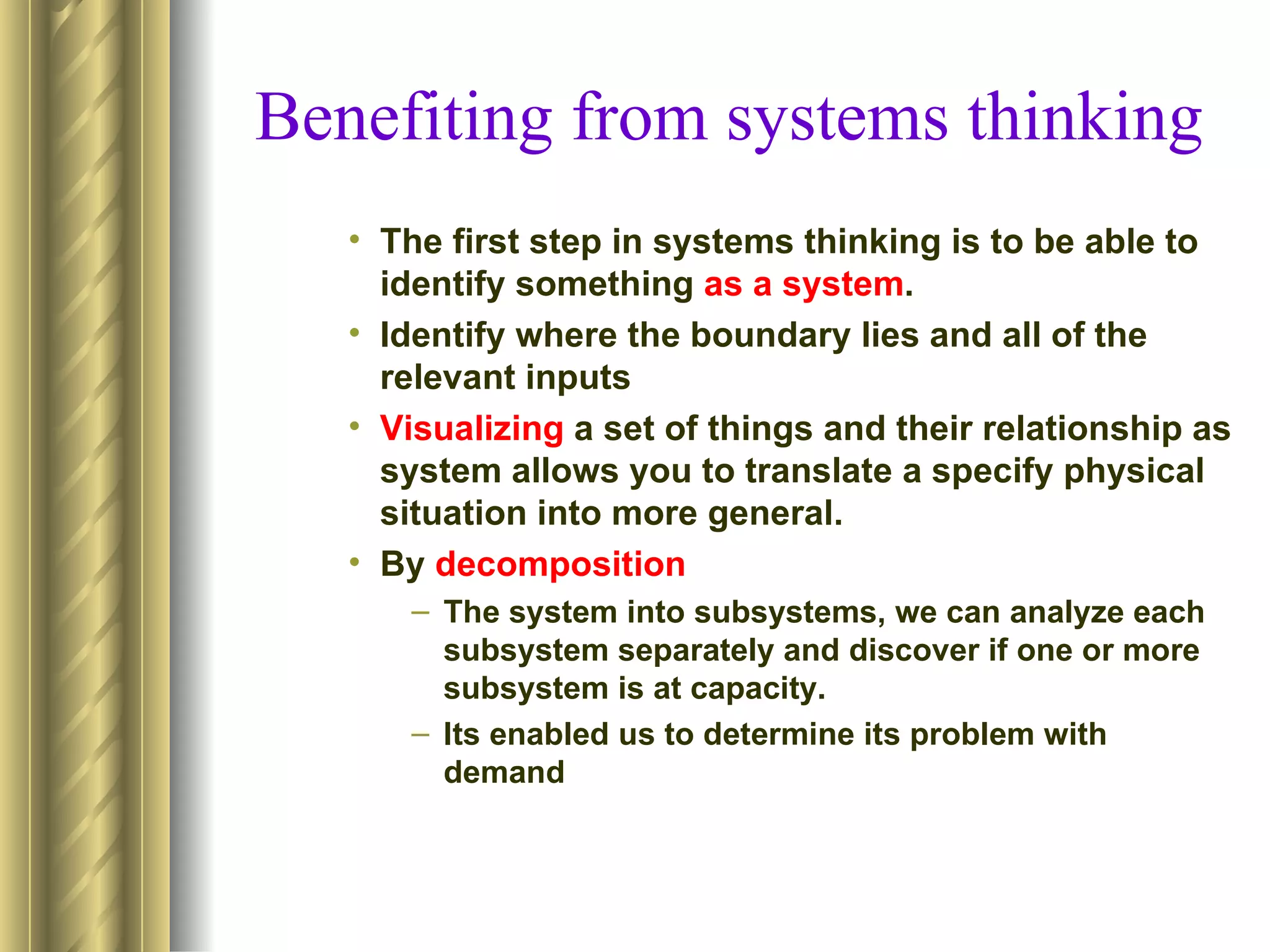
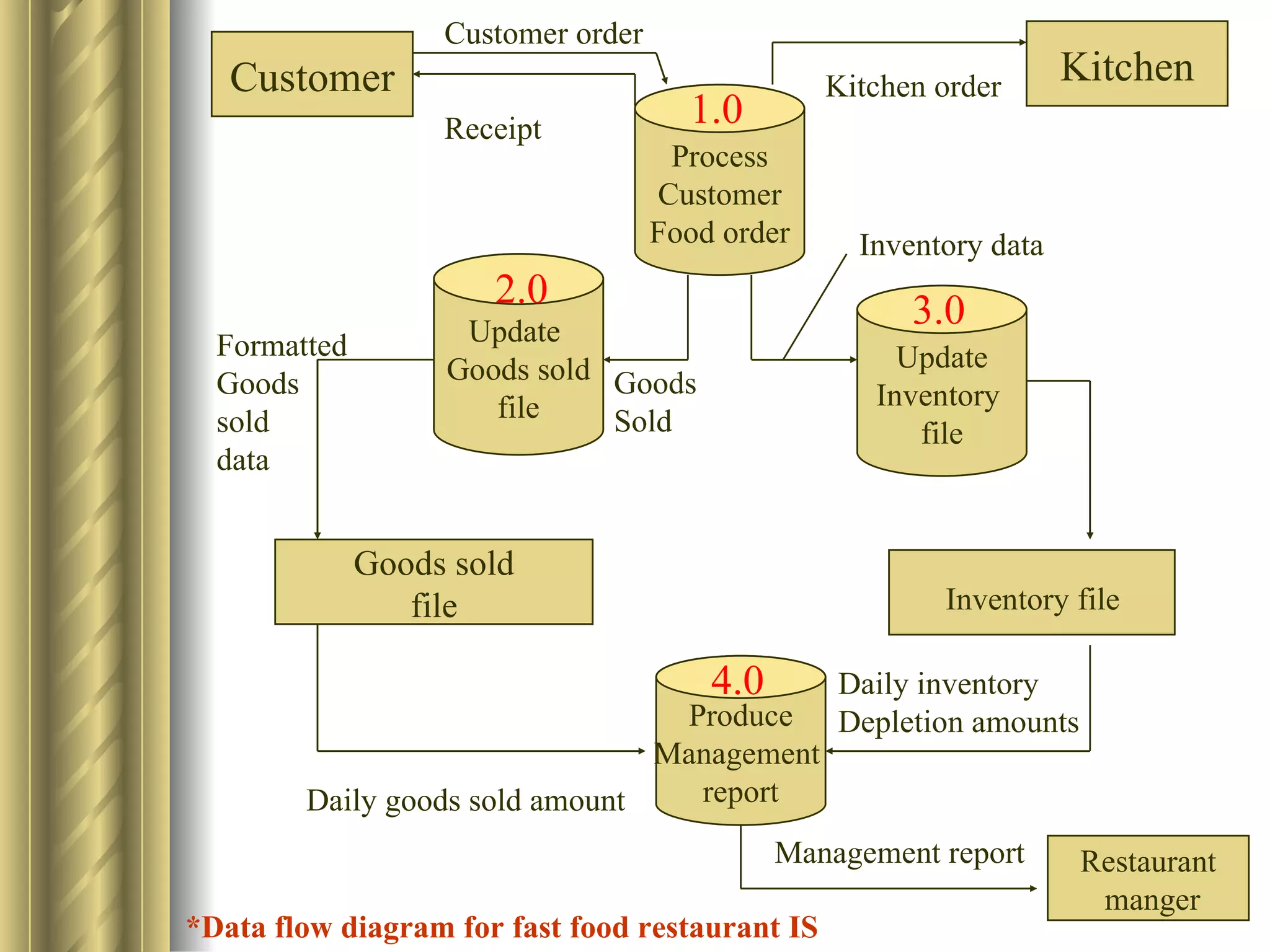
The document discusses the analytical, technical, management, and interpersonal skills needed for systems analysts, describing how each set of skills relates to different phases of the Systems Development Life Cycle. It focuses on analytical skills like systems thinking, organizational knowledge, problem identification, and problem solving. The document also provides examples of how to apply systems concepts to understand organizations as systems.