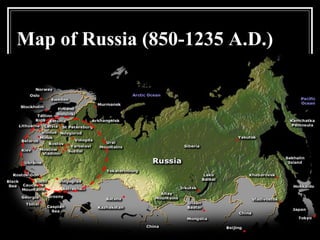
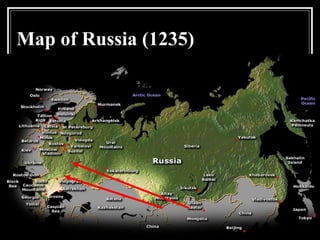
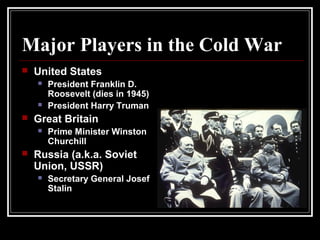
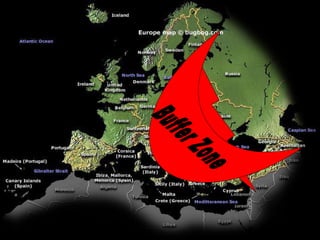
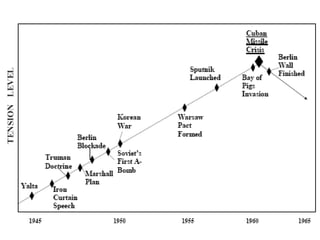
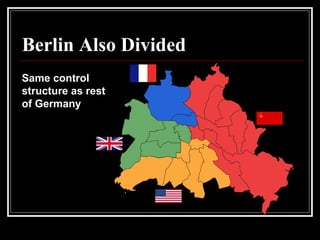
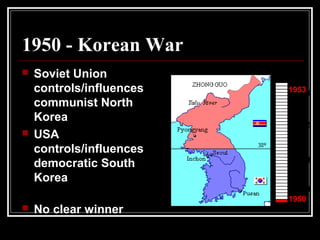
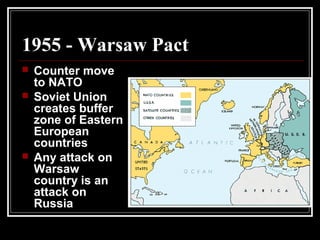
The document provides an overview of key events in Russian history from ancient times to the Cold War era. It discusses the establishment of Kievan Rus in the 9th century, the Mongol invasion in the 13th century, and the rise of the Romanov dynasty in the 17th century. It then summarizes major Cold War events between the Soviet Union and Western powers from 1945 to 1991, including the formation of NATO, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and space race developments.