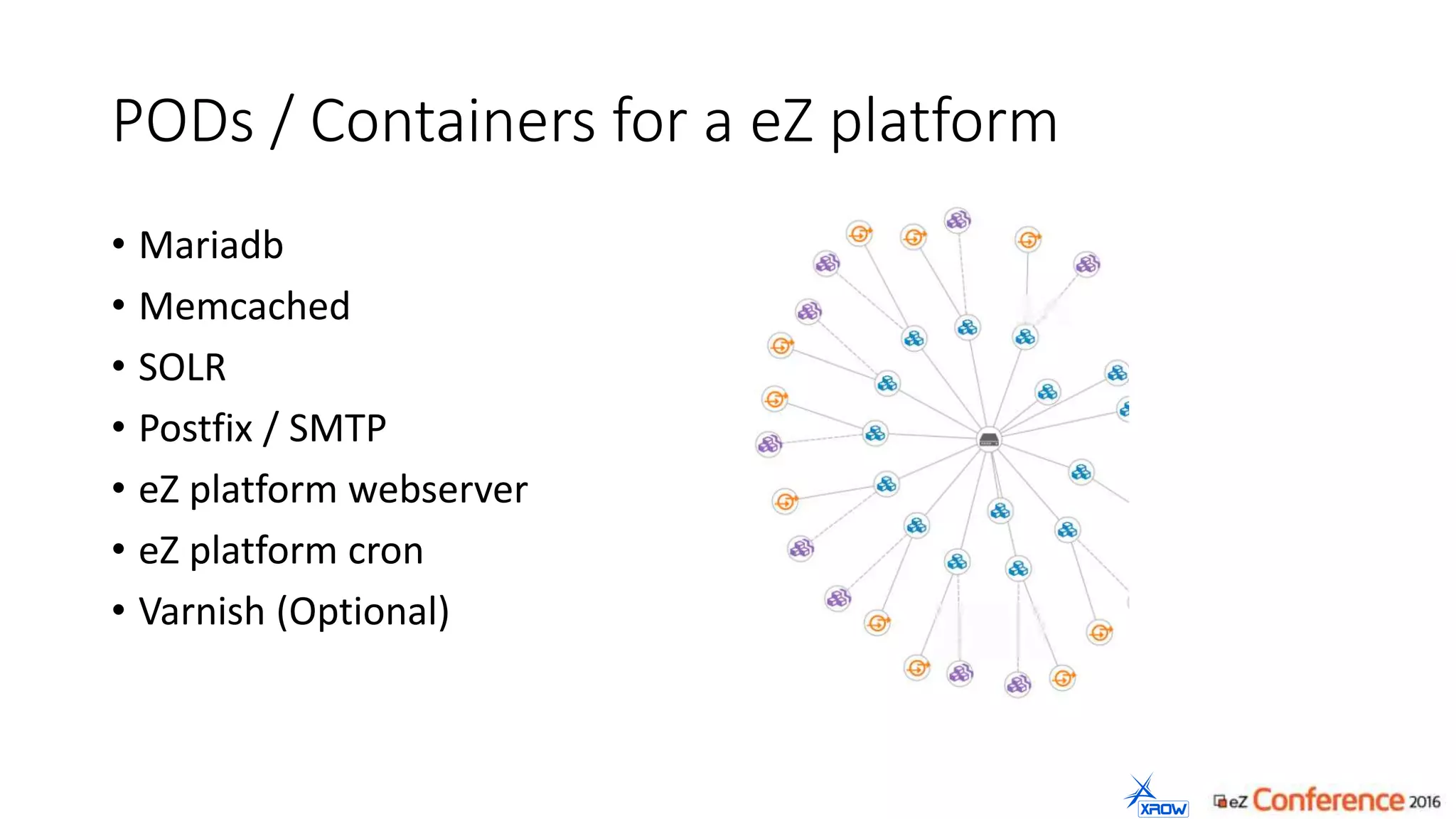
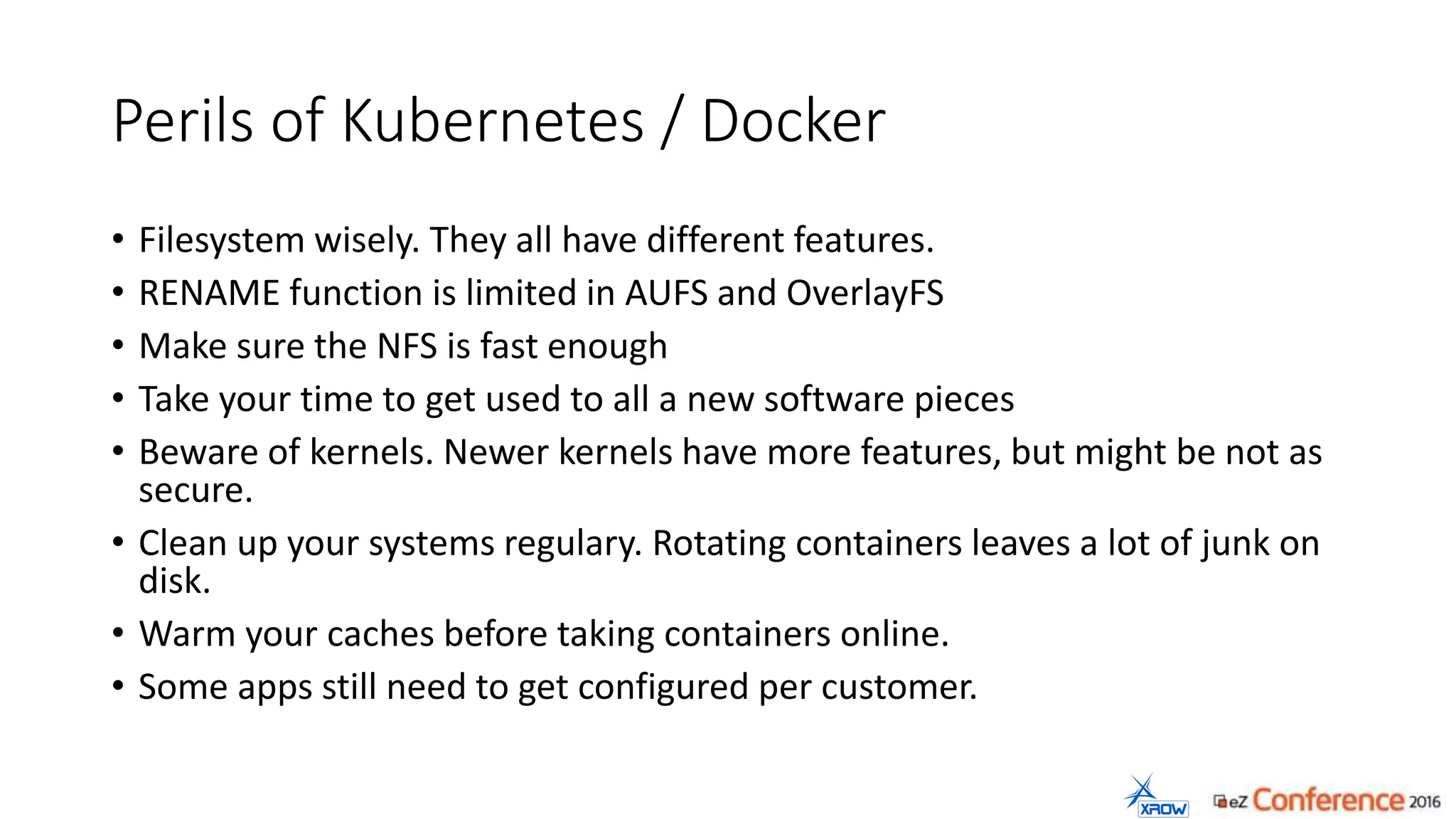
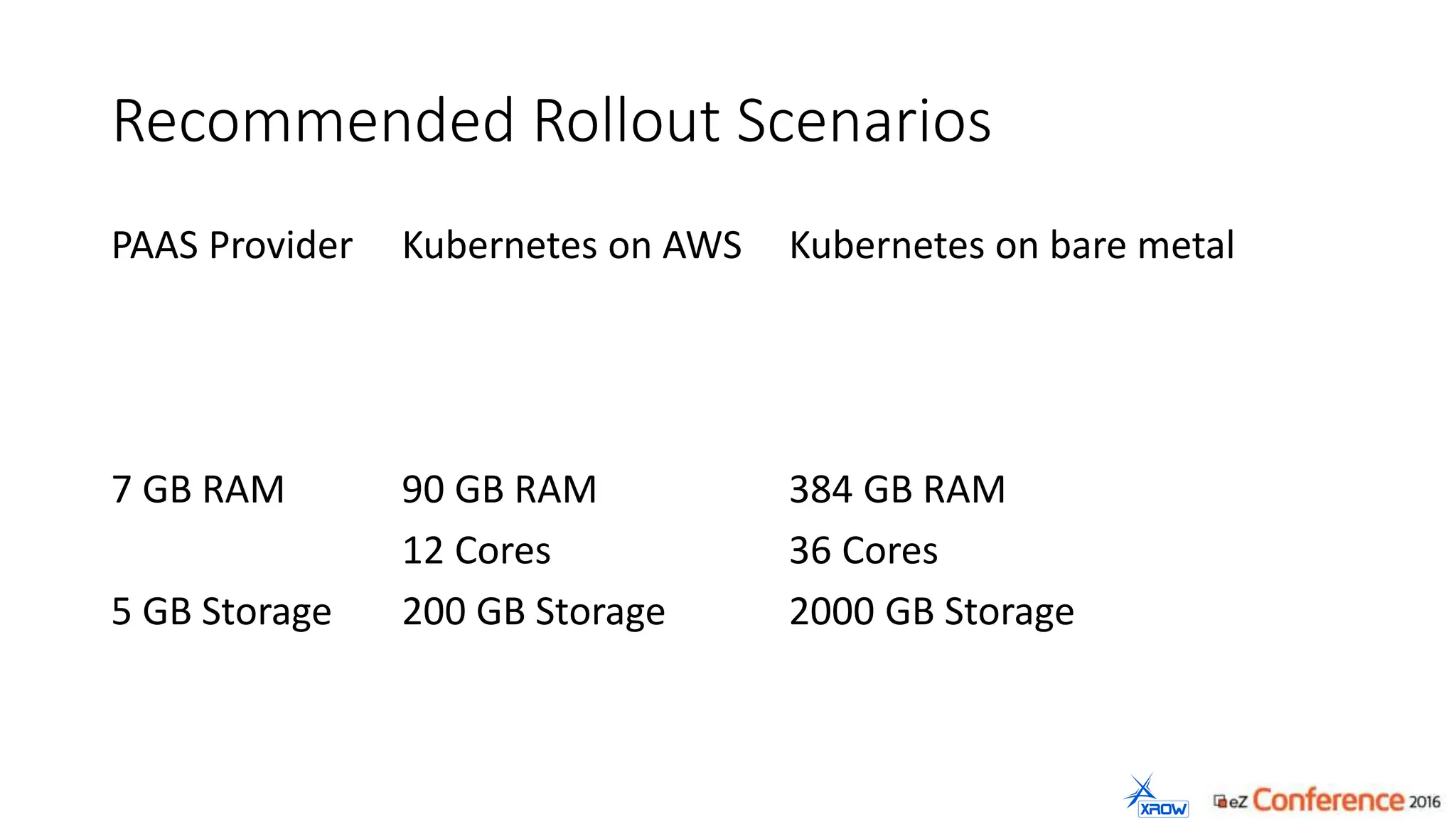
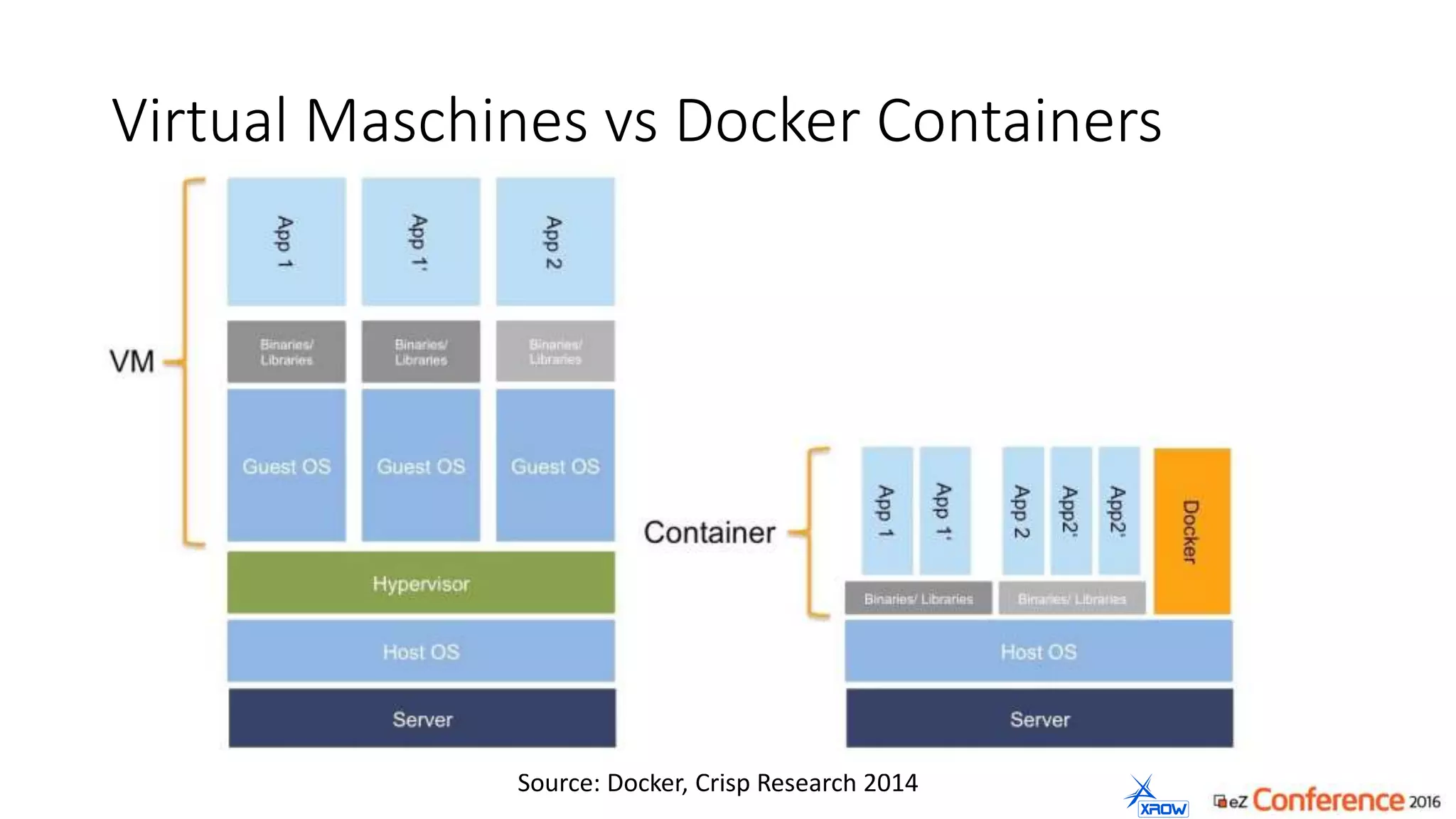
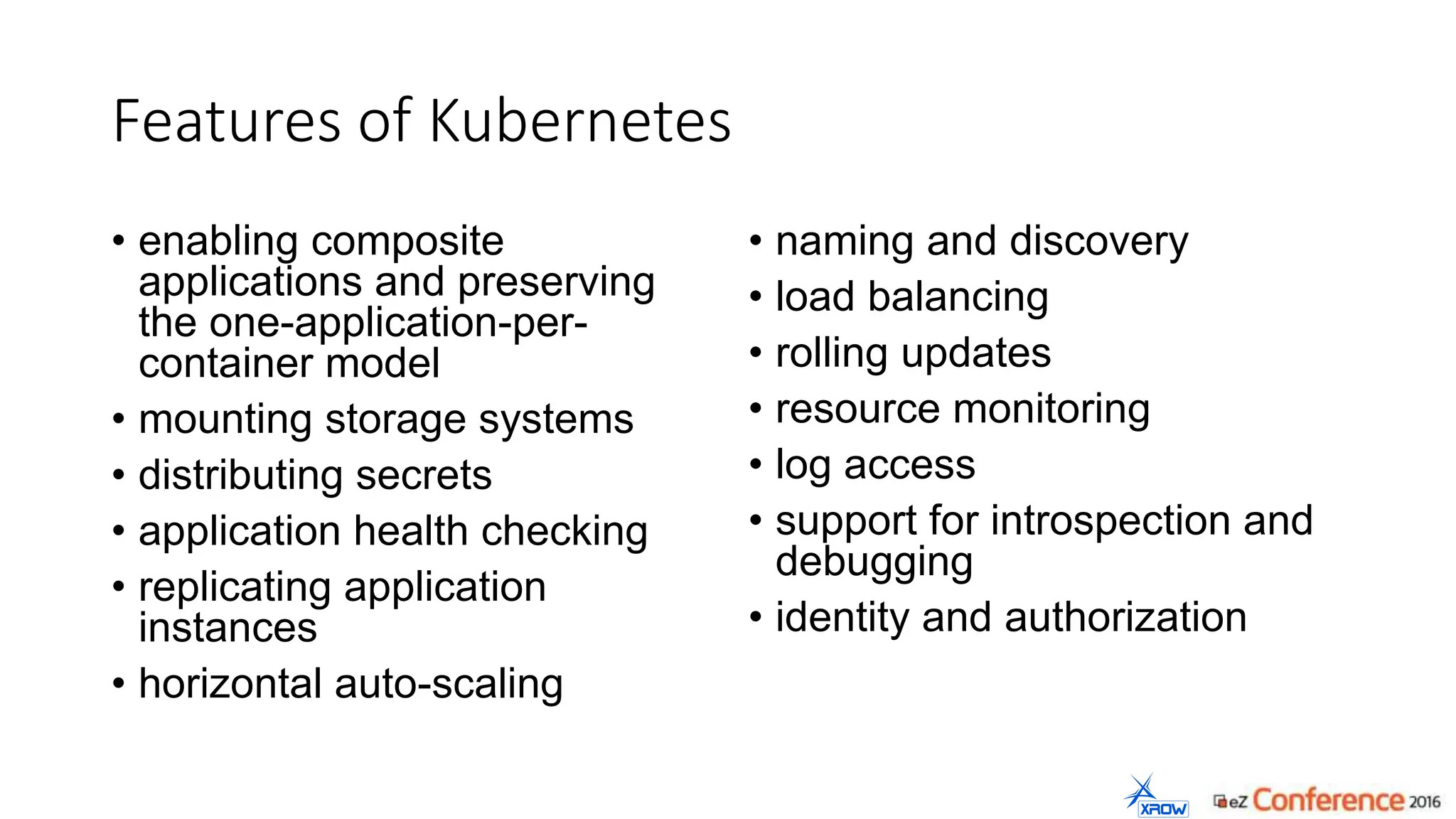
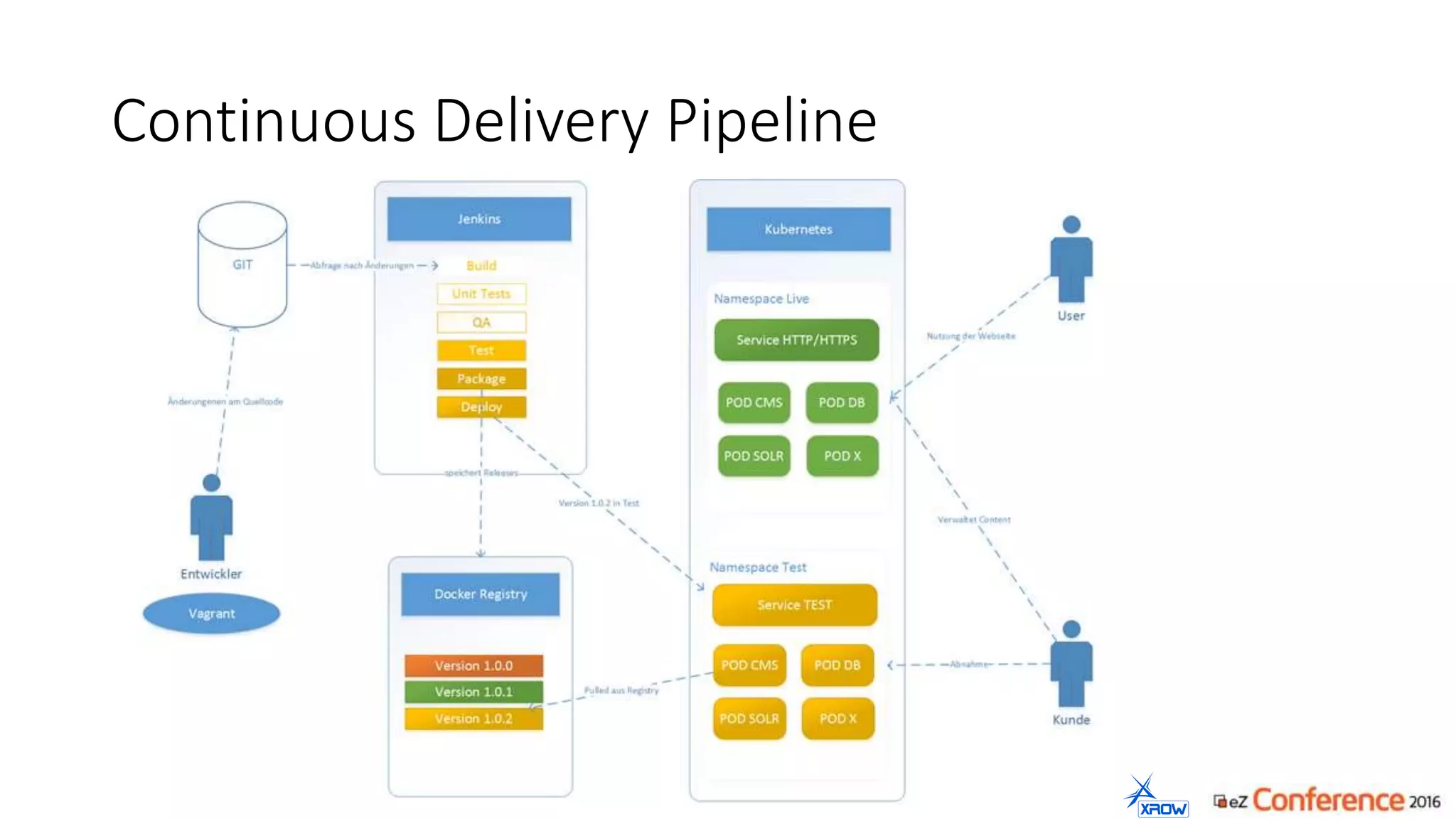
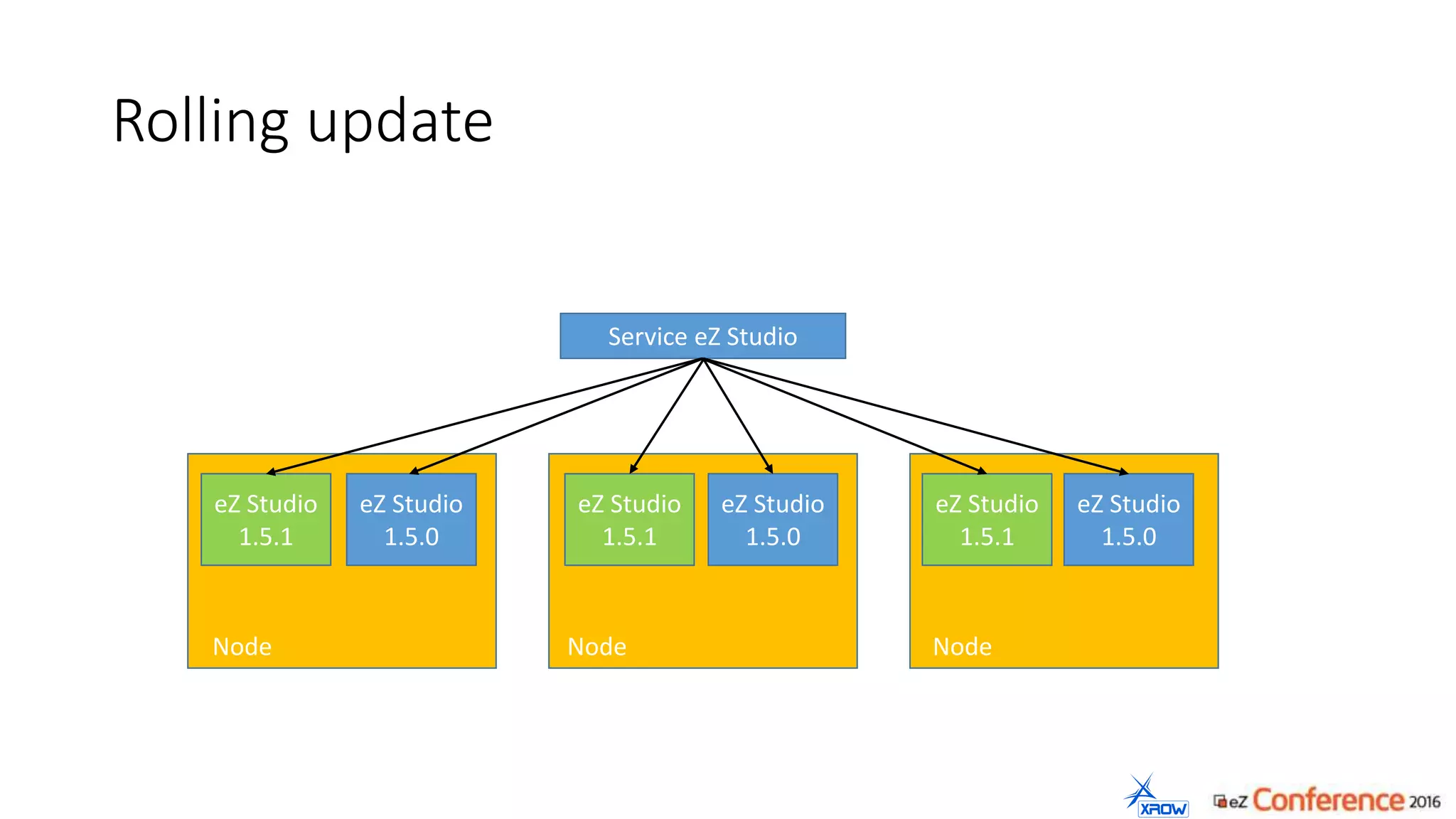
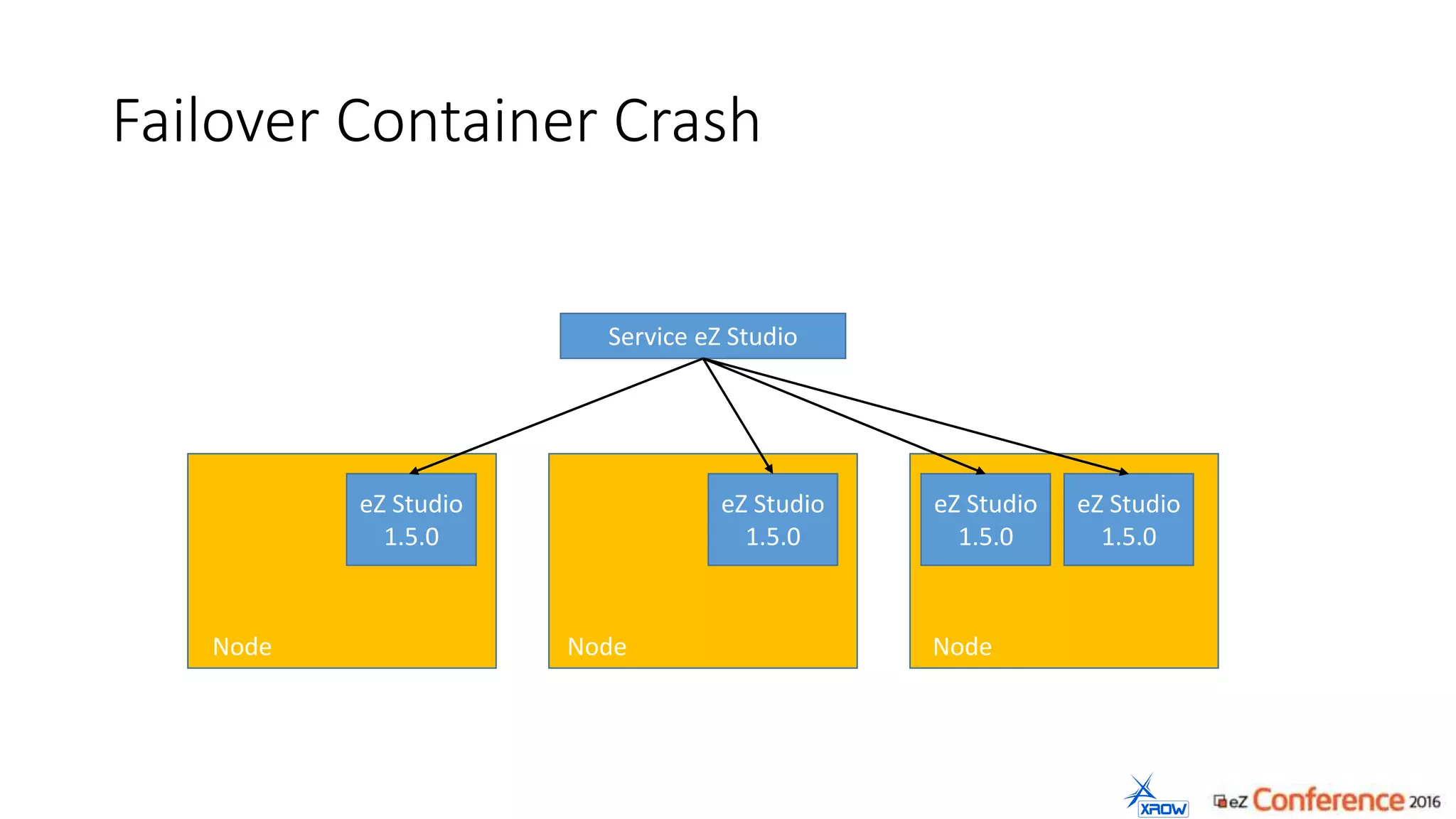
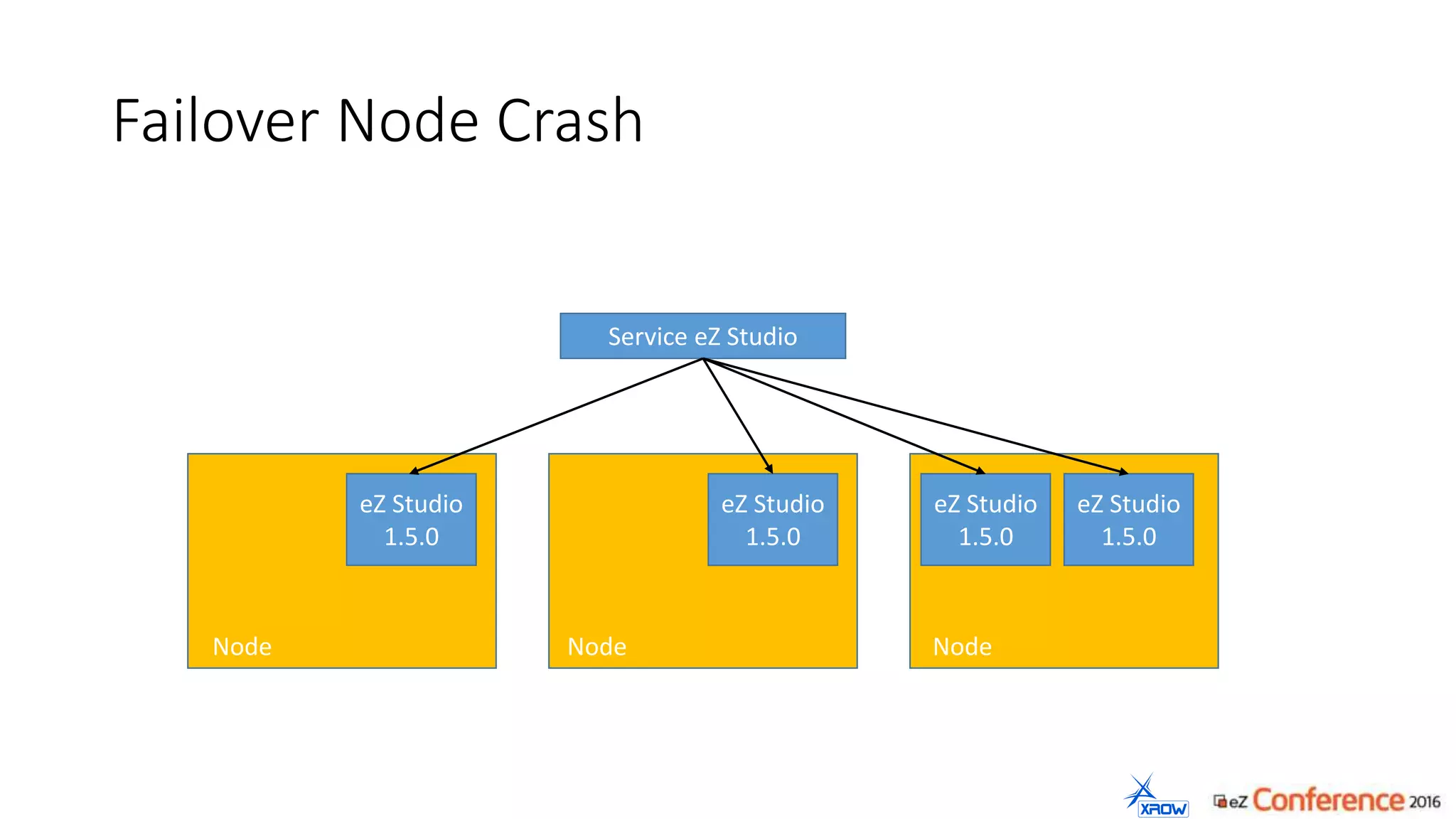
The document discusses the use of Kubernetes for managing Docker containers, emphasizing its advantages for both developers and administrators in terms of deployment and performance. It also outlines Kubernetes' features, including application scaling, load balancing, and resource monitoring. Additionally, it presents potential challenges with Kubernetes and Docker, and suggests recommended rollout scenarios based on resource specifications.









![Autodiscovery of services
$url = "https://10.254.0.1:443/api/v1/namespaces/project123-prod/services";
$json = json_decode(file_get_contents($url));
$ip = $this->services->items["mariadb"]->spec->clusterIP;
$container->setParameter("database_server", $ip );
• Read all services from the API
• Set the proper parameters in your symfony application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bjorndiedingrunningezplatformonkubernetes-161011145757/75/Running-eZ-Platform-on-Kubernetes-presented-by-Bjorn-Dieding-at-eZ-Conference-2016-19-2048.jpg)