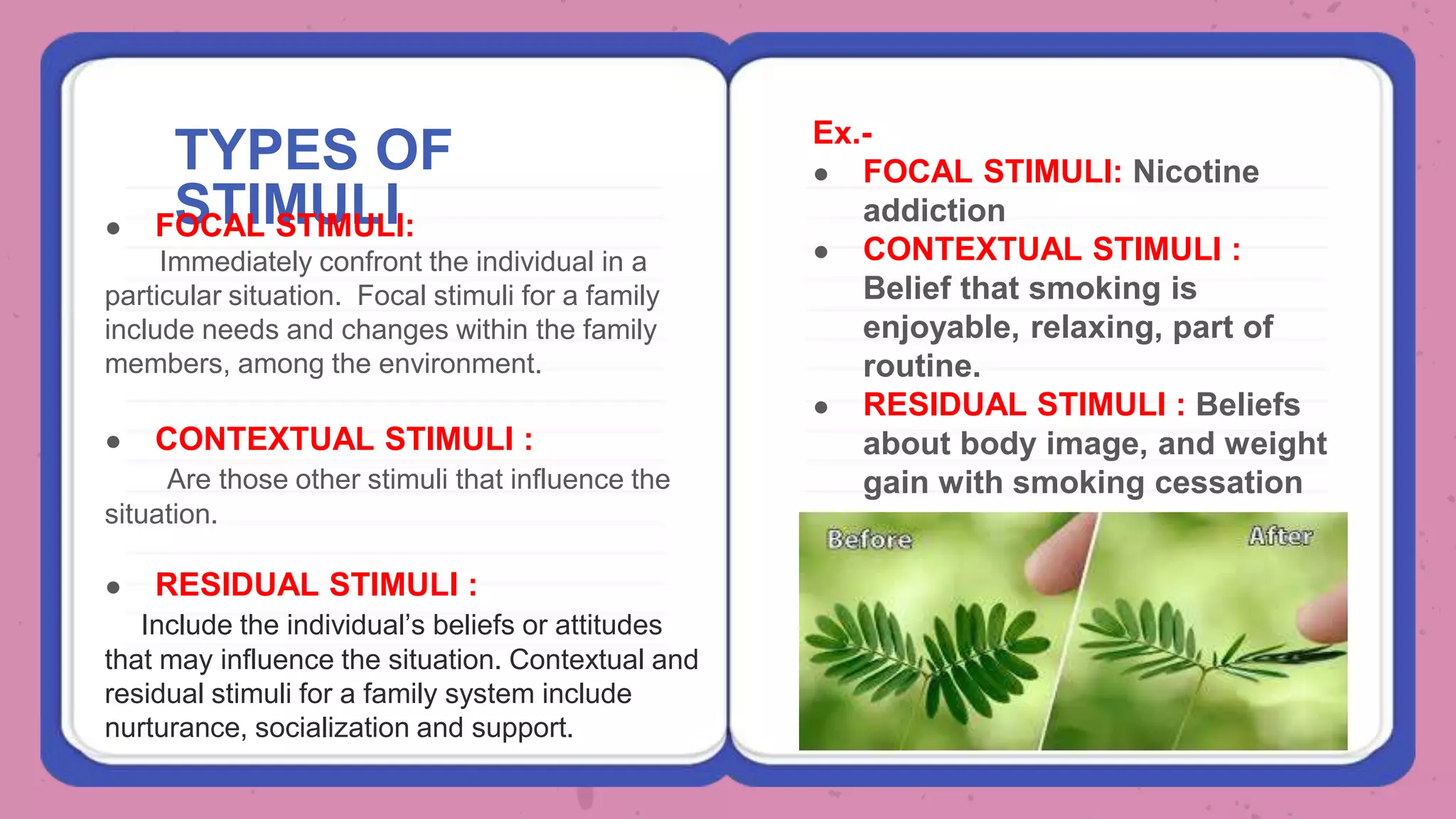
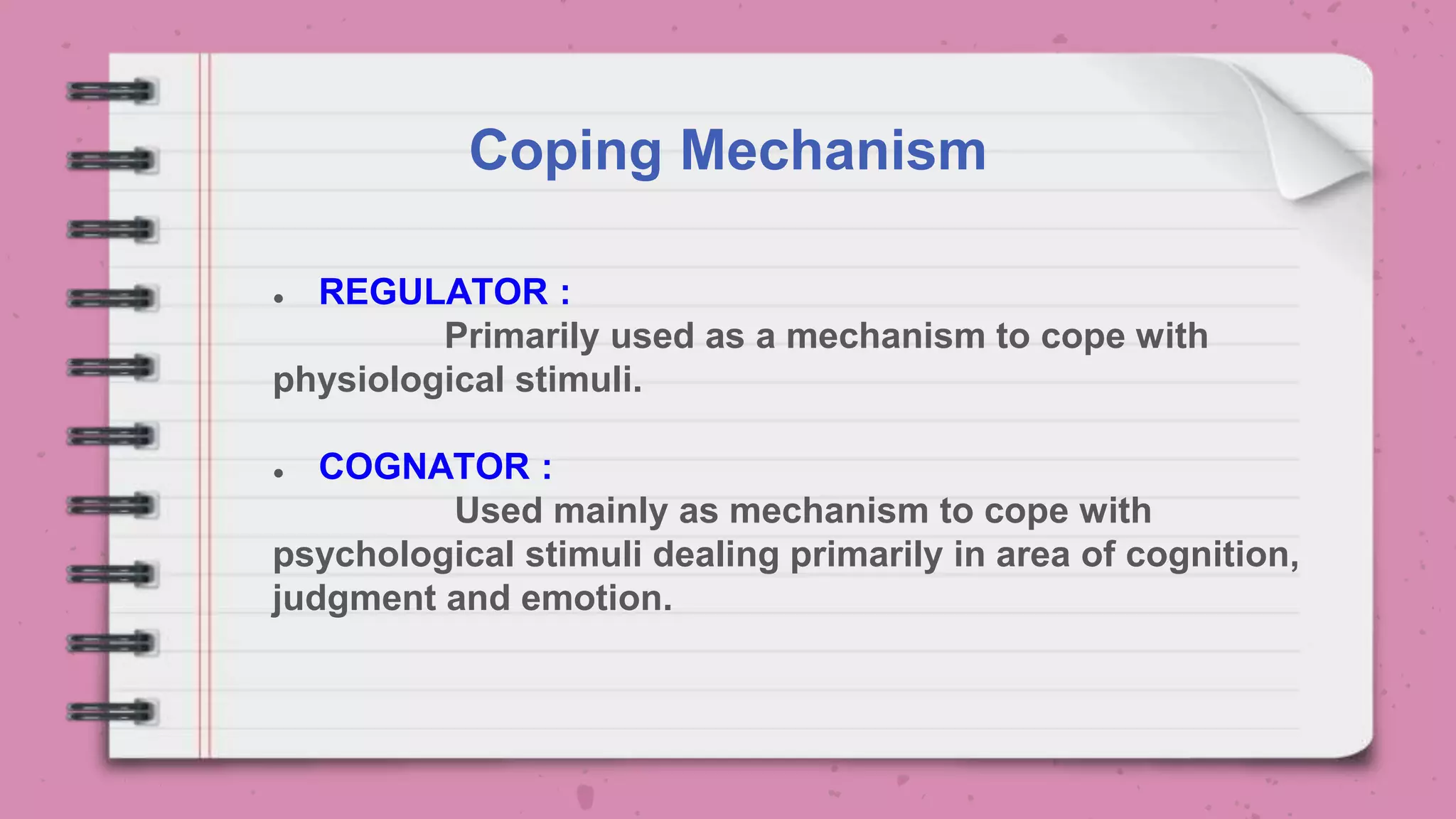
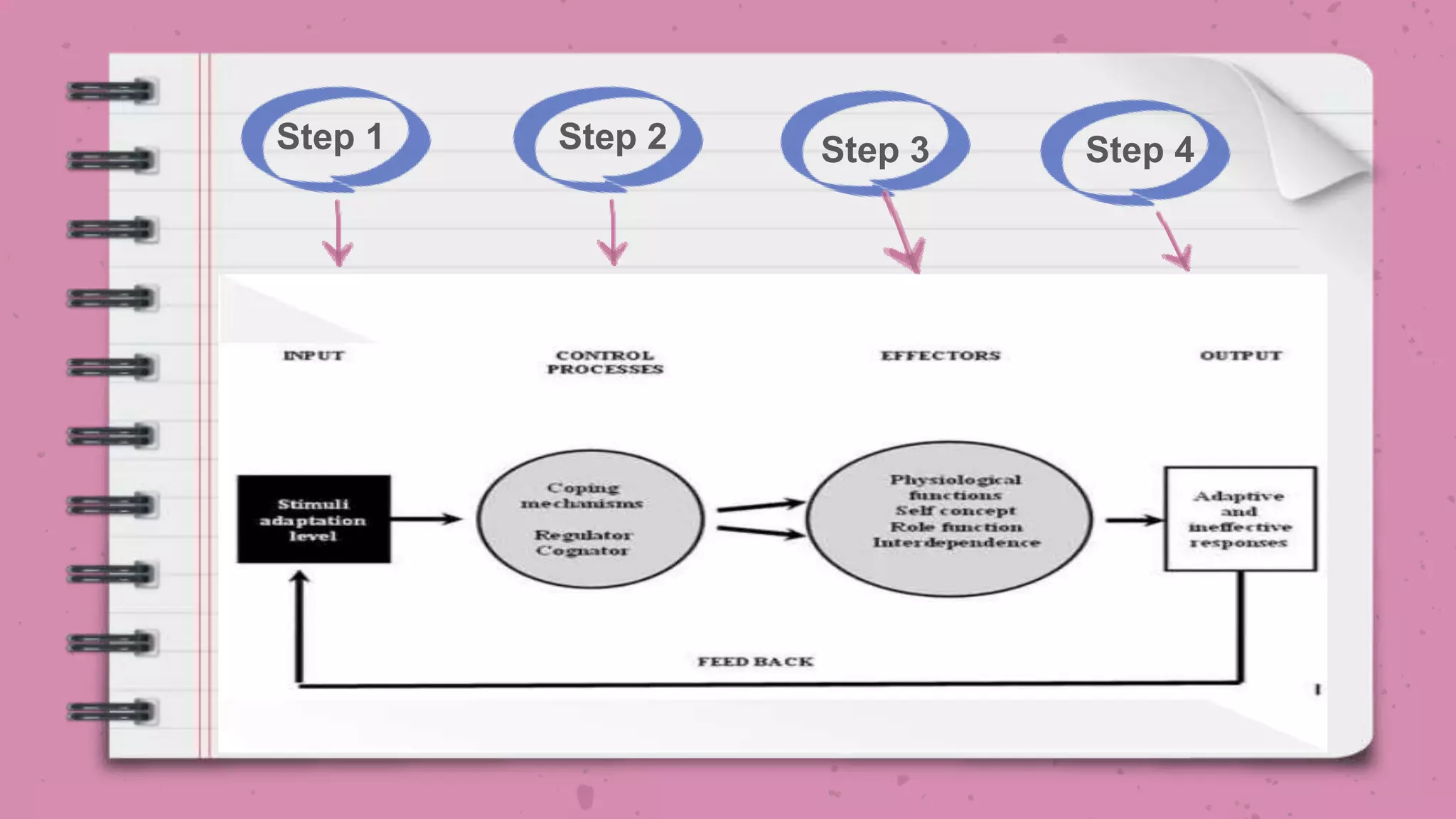
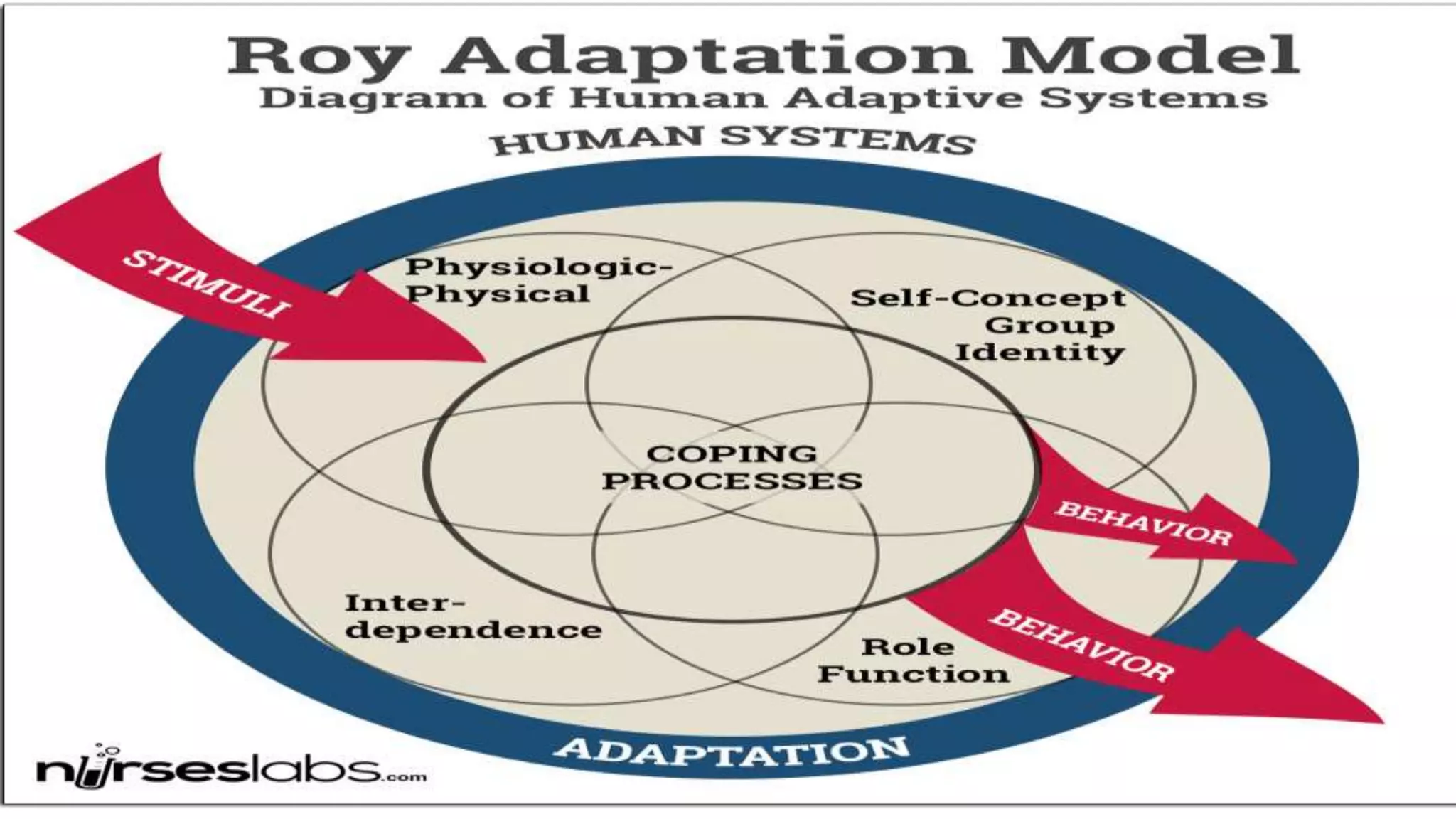
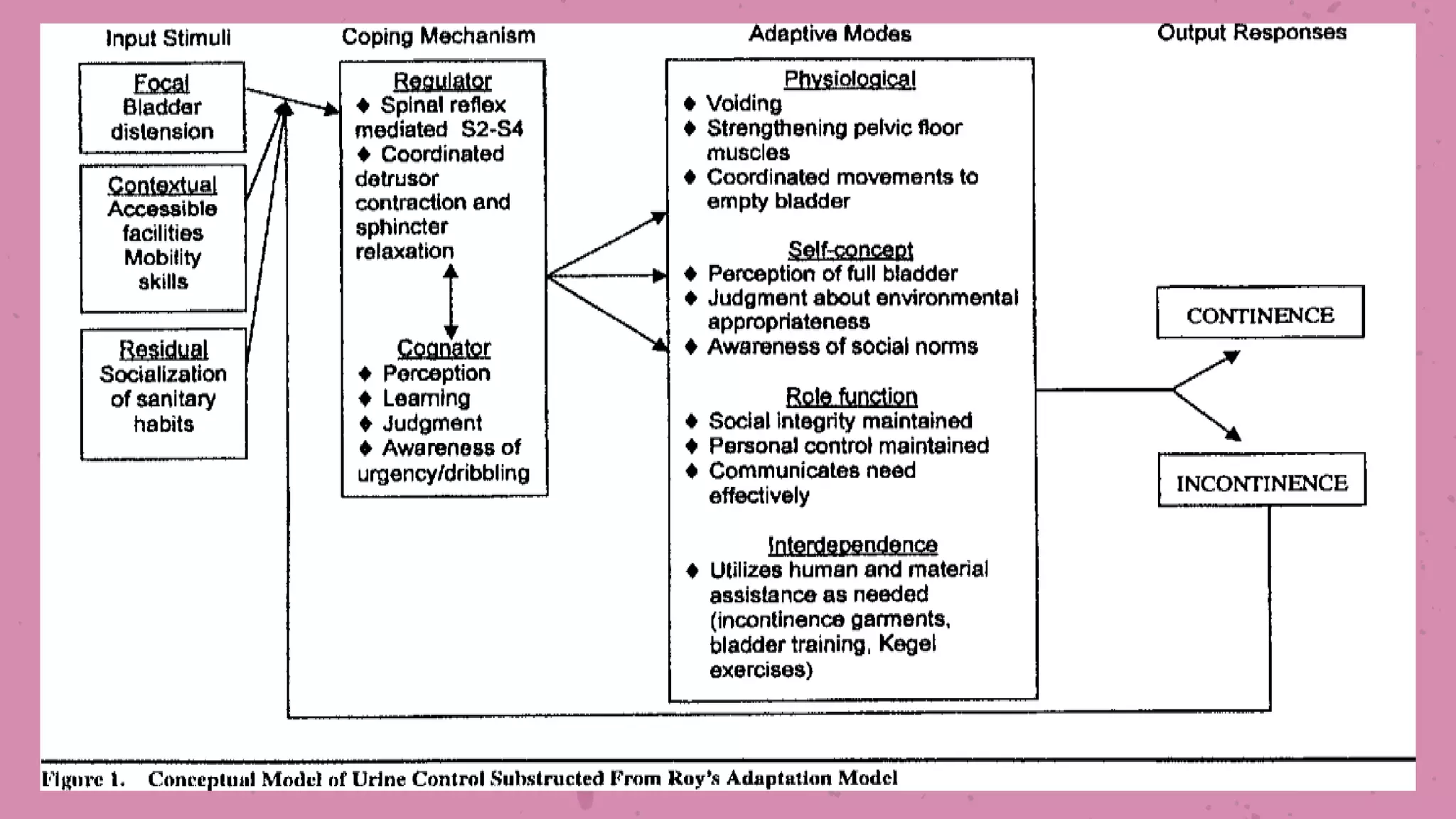
The document outlines Roy's Adaptation Model (RAM) developed by Callista Roy, detailing its evolution, assumptions, and applications in nursing practice and education. It emphasizes the role of nurses in helping individuals adapt to changes in health and environment through various coping mechanisms and types of stimuli. The RAM is presented as a framework for analyzing health and promoting well-being in individuals, families, and communities.