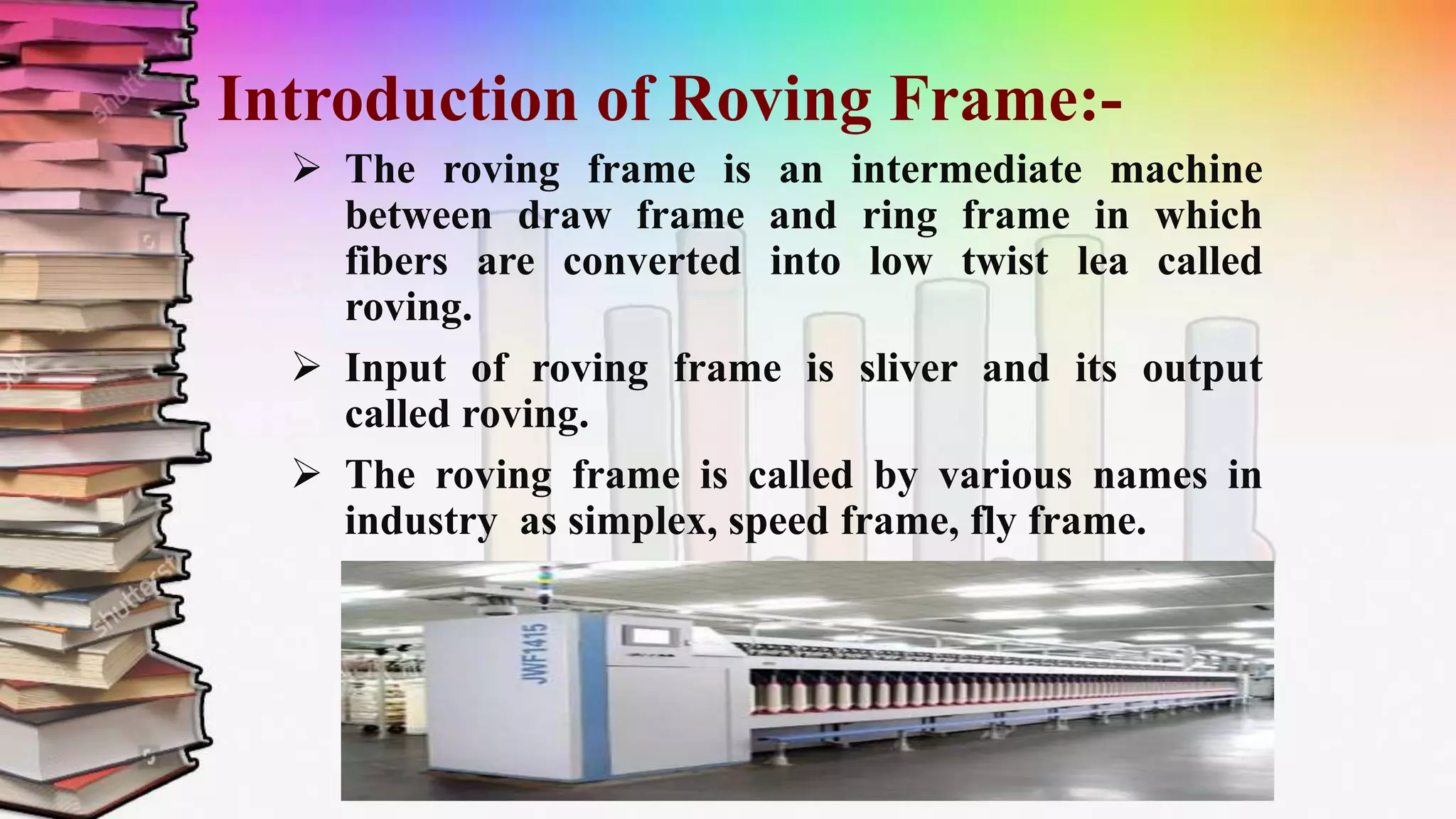
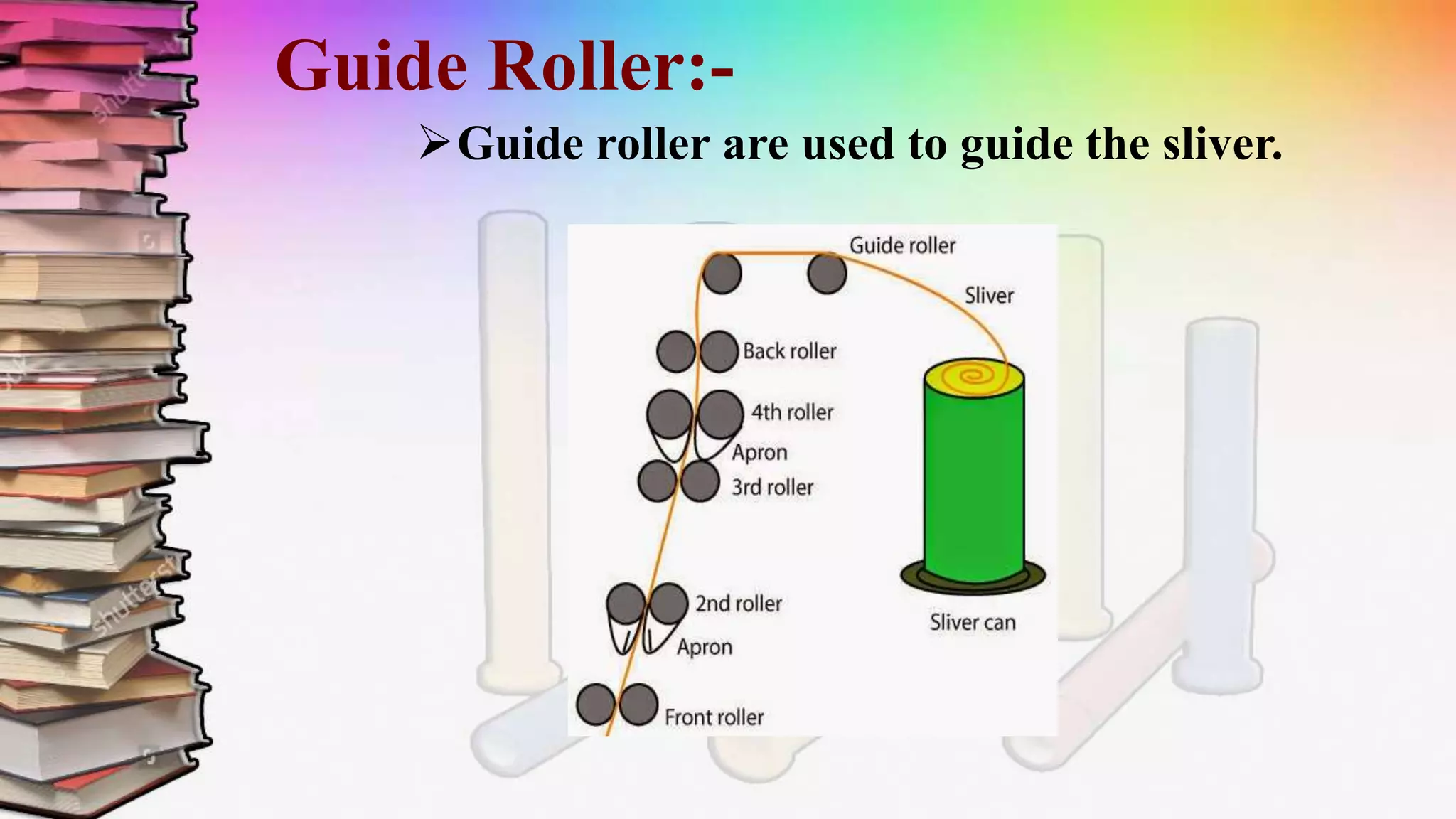
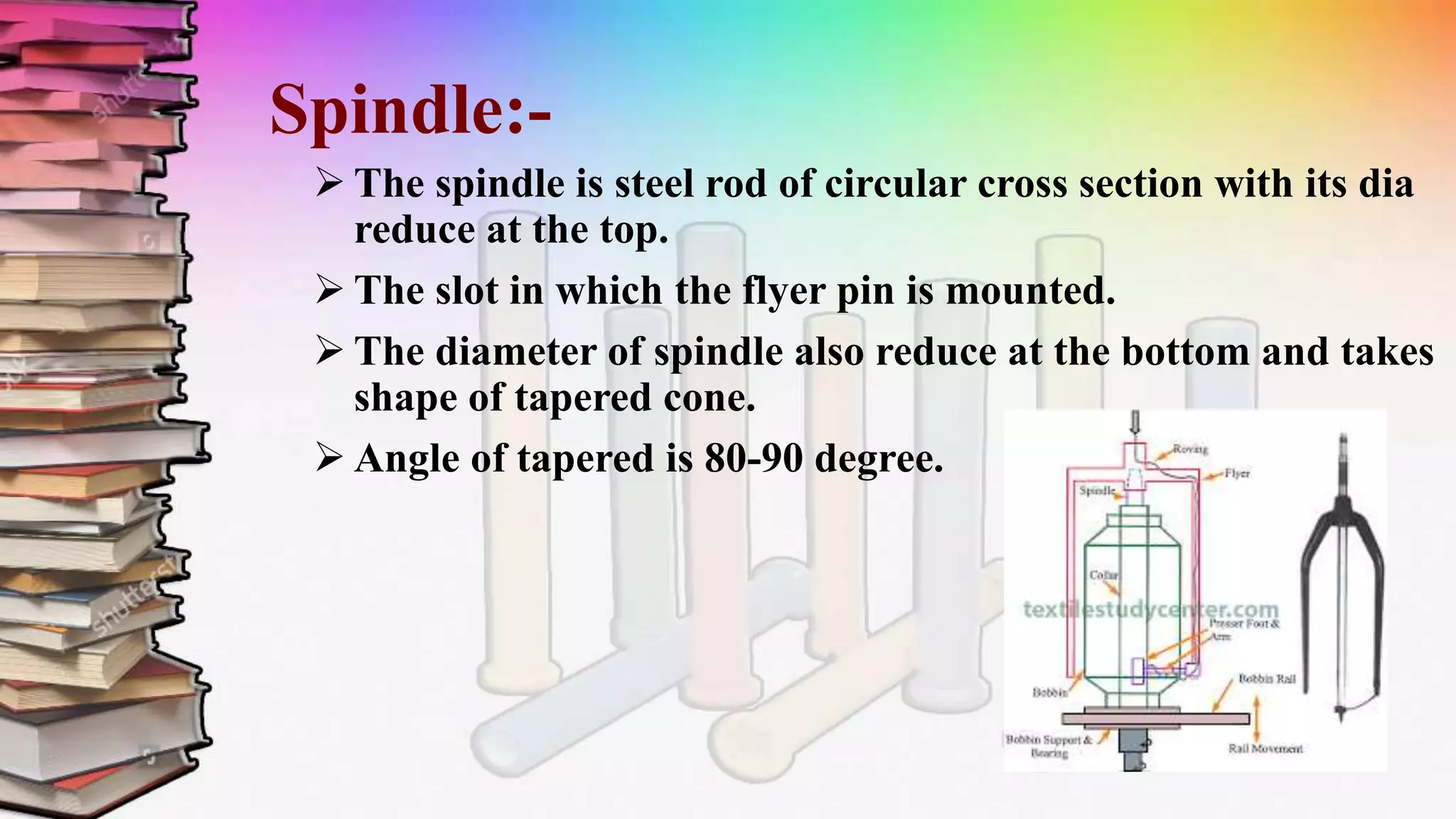
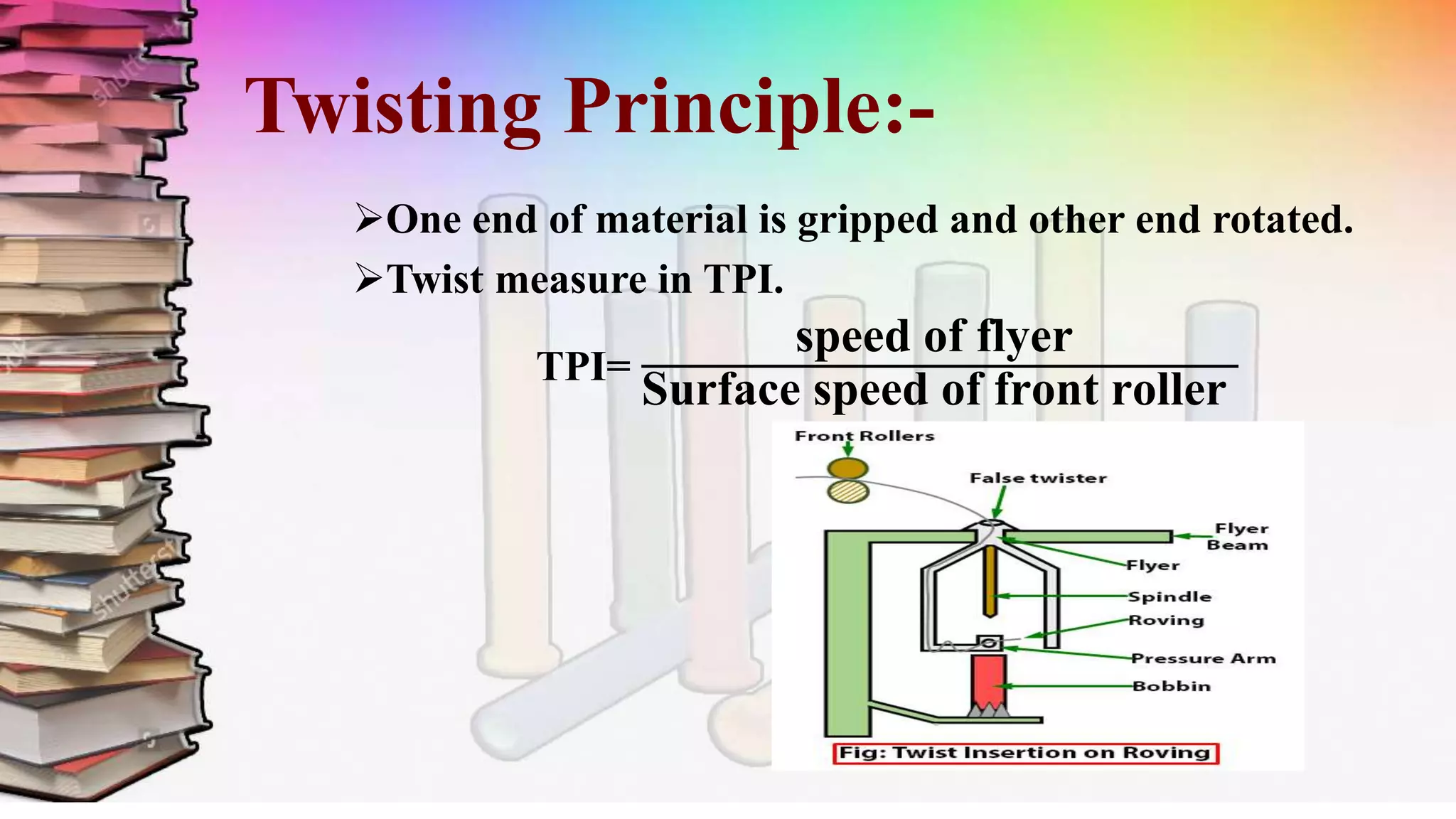
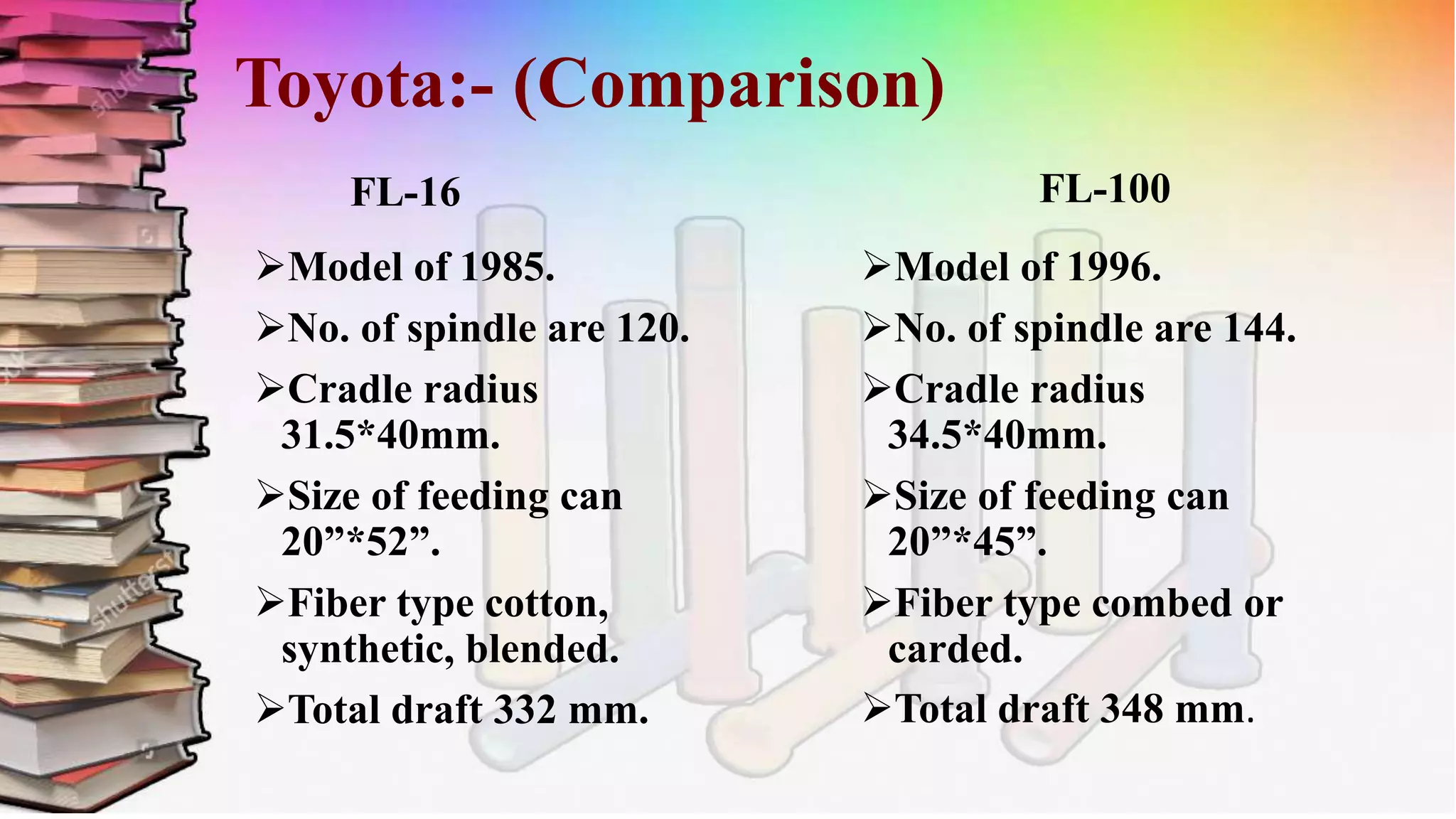
This document discusses a study on roving frames conducted by four students. It begins by introducing the roving frame, which drafts sliver into low-twist roving between the draw frame and ring frame. It then covers the objectives, operations, advantages and parts of the roving frame. The principles of drafting, twisting and winding on the roving frame are explained. Finally, different manufacturers and models of roving frames are compared.