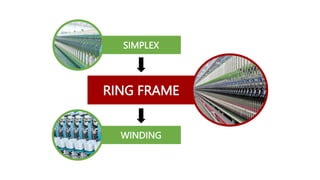
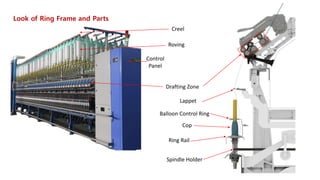
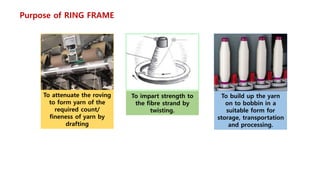
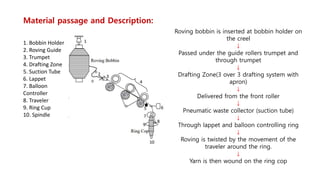
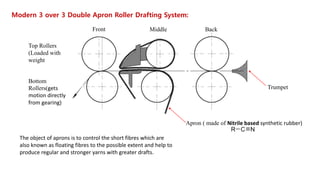
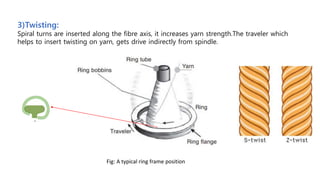
The document provides an overview of the ring frame machine, which transforms roving into spun yarn through processes including creeling, drafting, twisting, winding, building, and doffing. It details the machine's components, operational mechanics, and common faults, as well as outlines limitations such as traveler speed, delivery speed, yarn tension, and power consumption. Major functions of the machine include yarn formation with specific fineness and strength, while also addressing issues affecting yarn quality.