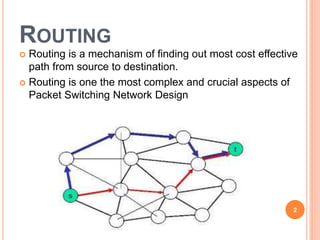
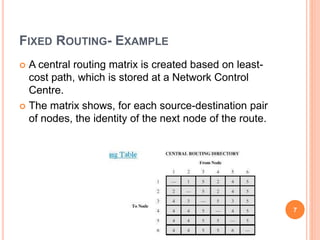
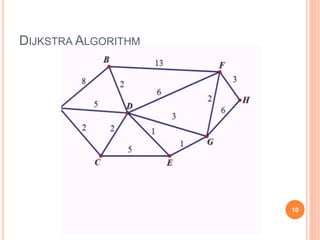
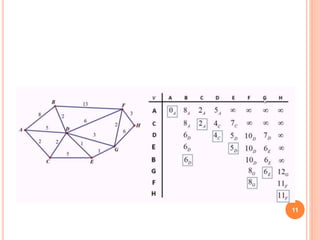
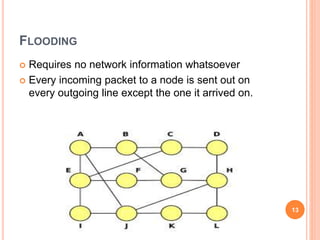
Routing is the mechanism for finding the most cost-effective path from source to destination in a packet switching network. There are several desirable properties for routing algorithms including correctness, robustness, stability, fairness, and efficiency. Common routing strategies include fixed/static routing, flooding, random routing, flow-based routing, and adaptive/dynamic routing. Fixed routing selects predetermined routes that may only change if the network topology changes, while flooding explores all possible routes by sending every incoming packet out every outgoing line except the one it arrived on.