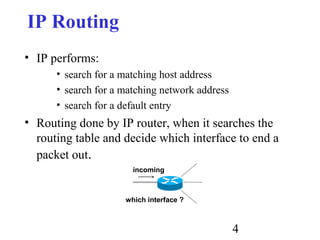
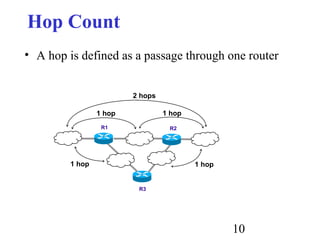
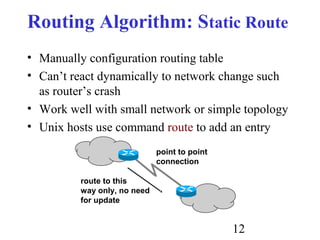
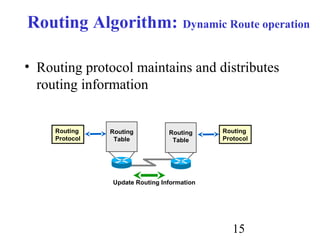
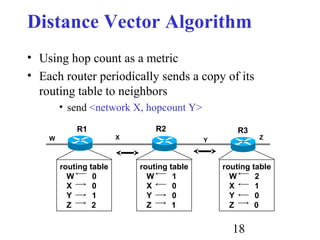
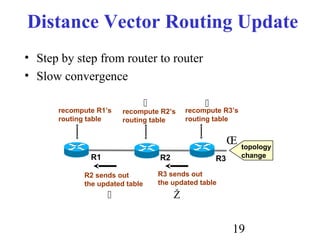
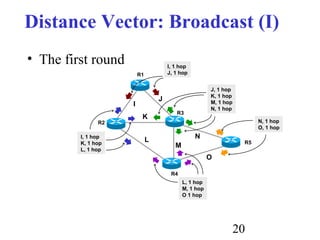
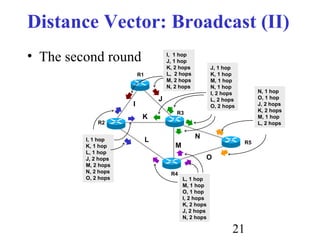
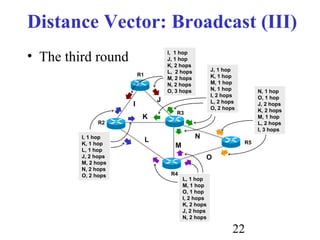
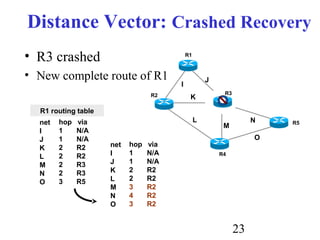
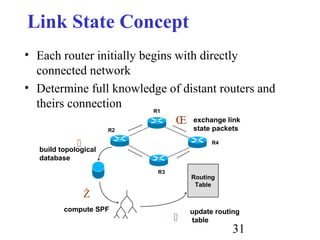
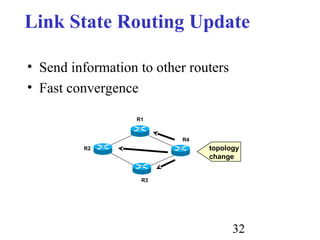
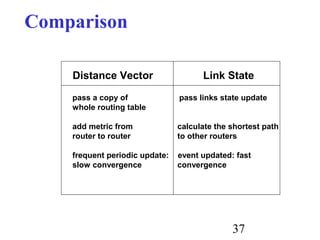
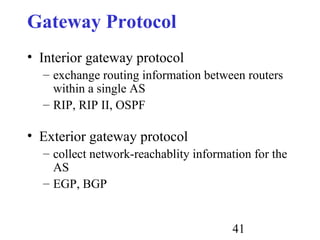
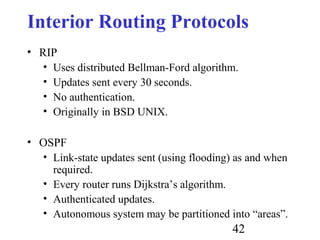
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. There are several key components involved in routing, including routing algorithms, routing tables, and routing protocols. Common routing algorithms include distance vector algorithms like RIP, which use periodic updates between routers to share routing information, and link state algorithms like OSPF, which flood link state information to all routers to enable shortest path calculations. The Internet uses a hierarchical routing model with intra-domain routing protocols like OSPF and inter-domain routing with BGP.