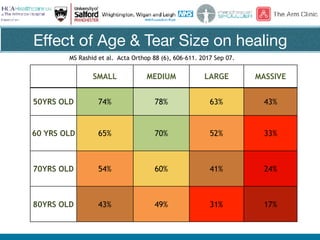
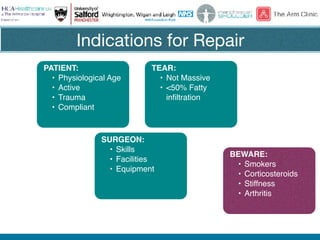
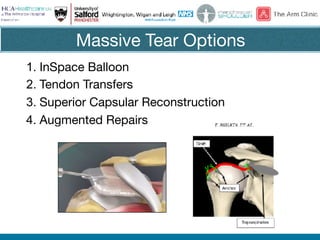
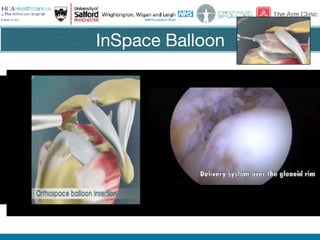
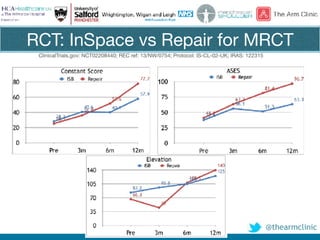
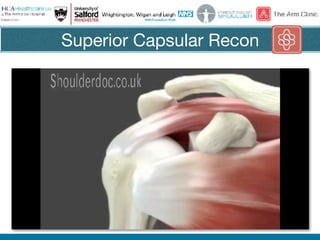
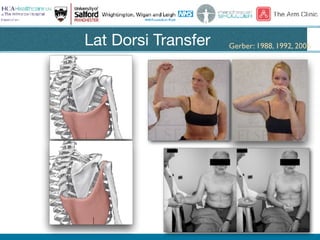
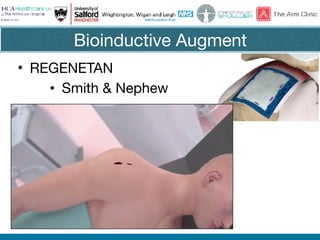
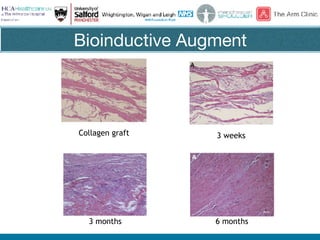
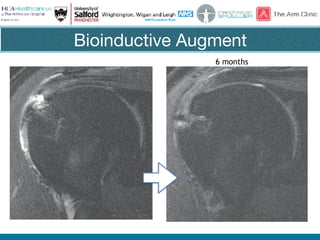
Rotator cuff tears do not always require surgical repair. The decision depends on factors like the patient's age and activity level as well as the size and chronicity of the tear. Smaller tears in younger, more active patients may heal with non-operative treatment or repair, while larger, chronic tears in older individuals often do not heal after repair. When repair is not indicated for massive, irreparable tears, options include tendon transfers, superior capsular reconstruction, augmented repairs, and InSpace balloon spacers. Ultrasound is useful for initial evaluation and post-operative monitoring but MRI may better assess tear size and tissue quality factors that predict repair outcomes.


![Natural History - AGE
• 54% Asymptomatic cuff tears over 60yrs [Sher. 1995]
» 28% - Full thickness (on MRI)
• 34% Apoptosis in Degenerate Supraspinatus
[Yuan & Murrell. 2002]
• Tendon Matrix Degeneration increases with Age
[Riley et al. 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotatorcufftearmanagement2019-190429065700/85/Rotator-cuff-tear-management-2019-4-320.jpg)


![Natural History - SYMPTOMS
• Asymptomatic tears become Symptomatic [Yamaguchi. 2001]
» 10 year follow-up of asymptomatic cuff
tears
» 50% developed symptomatic cuff tears
» 50% of tears increased in size
▪ Symptoms ⌿ Tear Size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotatorcufftearmanagement2019-190429065700/85/Rotator-cuff-tear-management-2019-7-320.jpg)