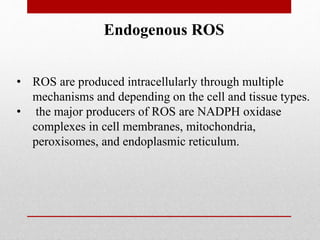
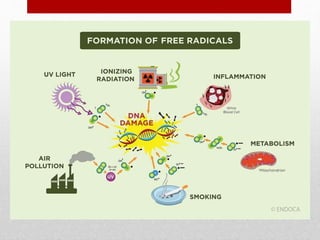
The document discusses oxidative stress and redox regulation. It defines oxidative stress as an imbalance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in cells. Reactive oxygen species are formed through normal metabolism but also during environmental stress. They can damage biomolecules and lead to diseases. Antioxidants help neutralize reactive oxygen species and may help prevent certain diseases. Redox regulation involves electron transfer processes like oxidation, which is the loss of electrons, and reduction, which is the gain of electrons. An example of redox regulation is the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, which is involved in cell survival signaling and can be activated under oxidative stress conditions through redox modification.