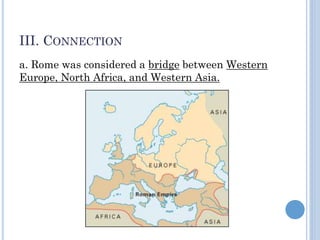
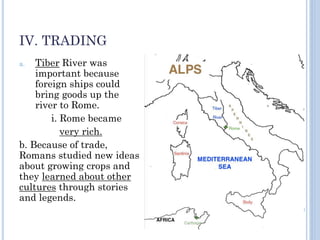
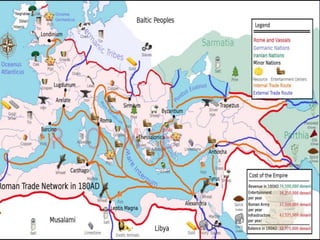
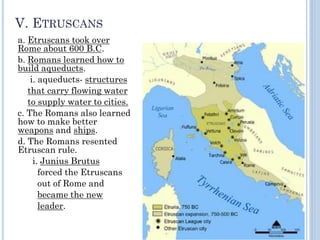
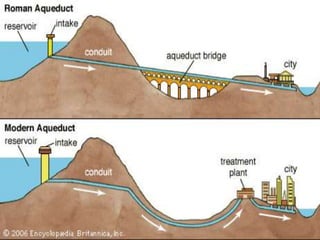
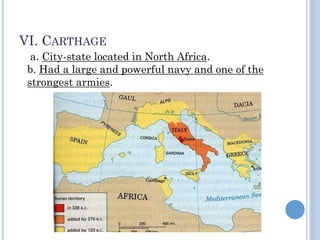
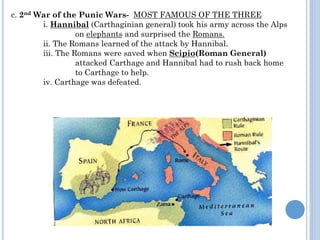
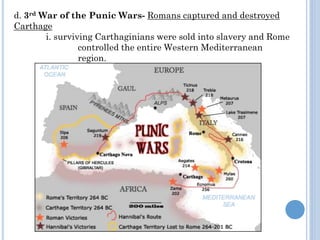
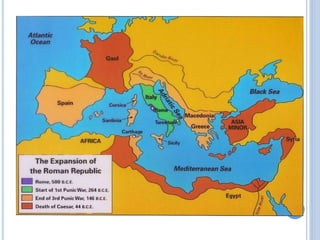
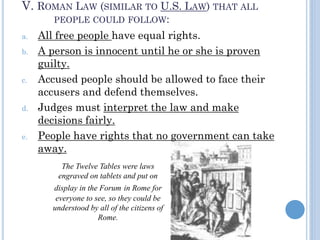
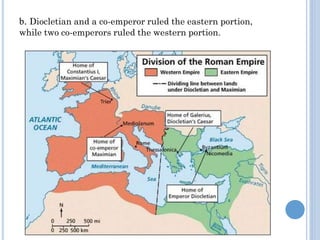
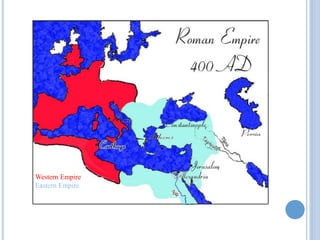
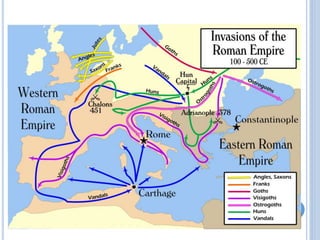
The document summarizes the origins and rise of ancient Rome from its founding as a city-state through the establishment of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It discusses Rome's early trade partnerships and conquest of neighboring regions like the Etruscans and Carthage. As Rome expanded across Western Europe, North Africa and Western Asia, it developed a republican government and granted citizenship and rights to conquered peoples. This period saw the rise of influential leaders like Julius Caesar and the emergence of Christianity. Internal conflicts and invasions by Germanic tribes eventually led to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD.