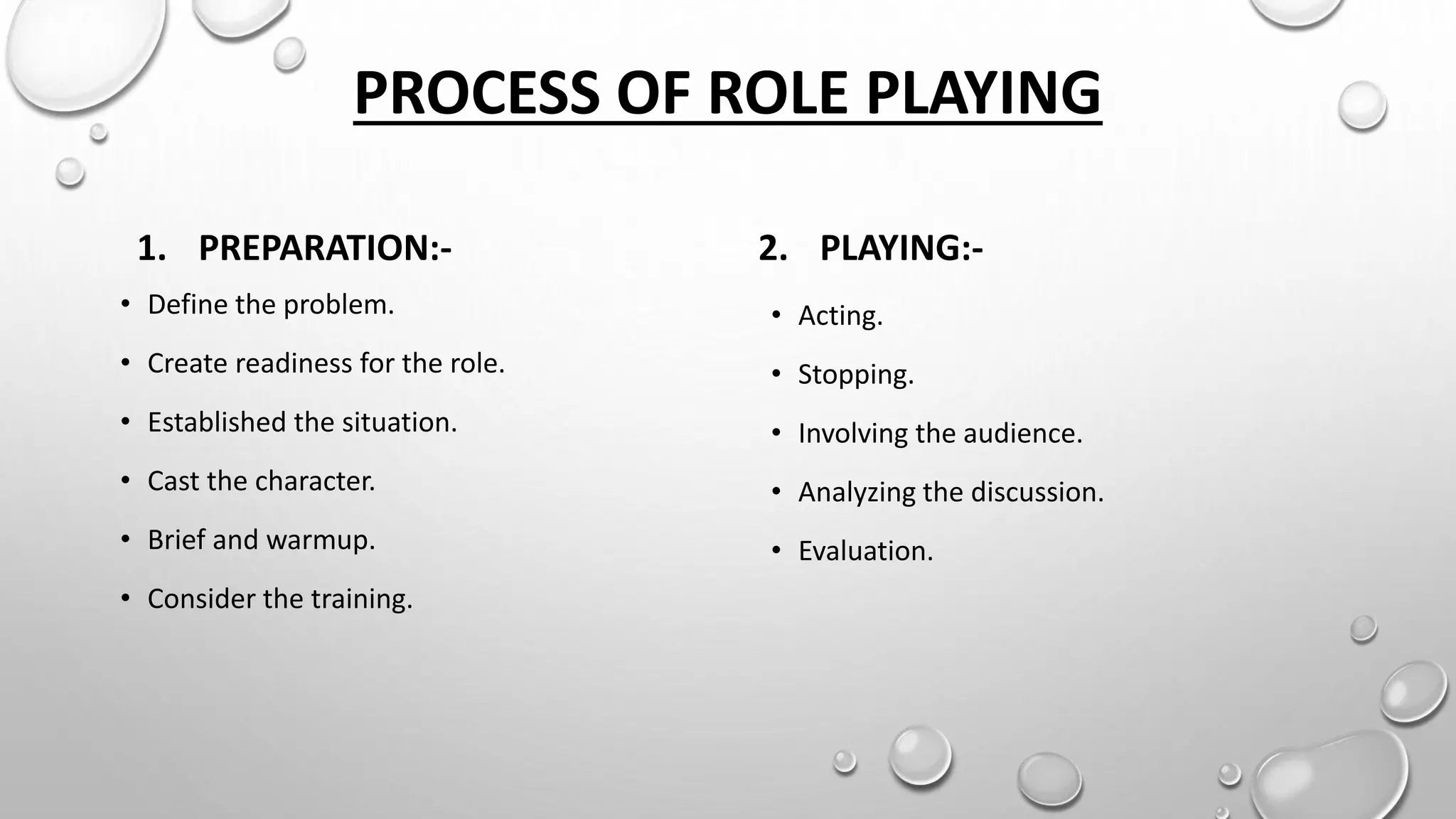
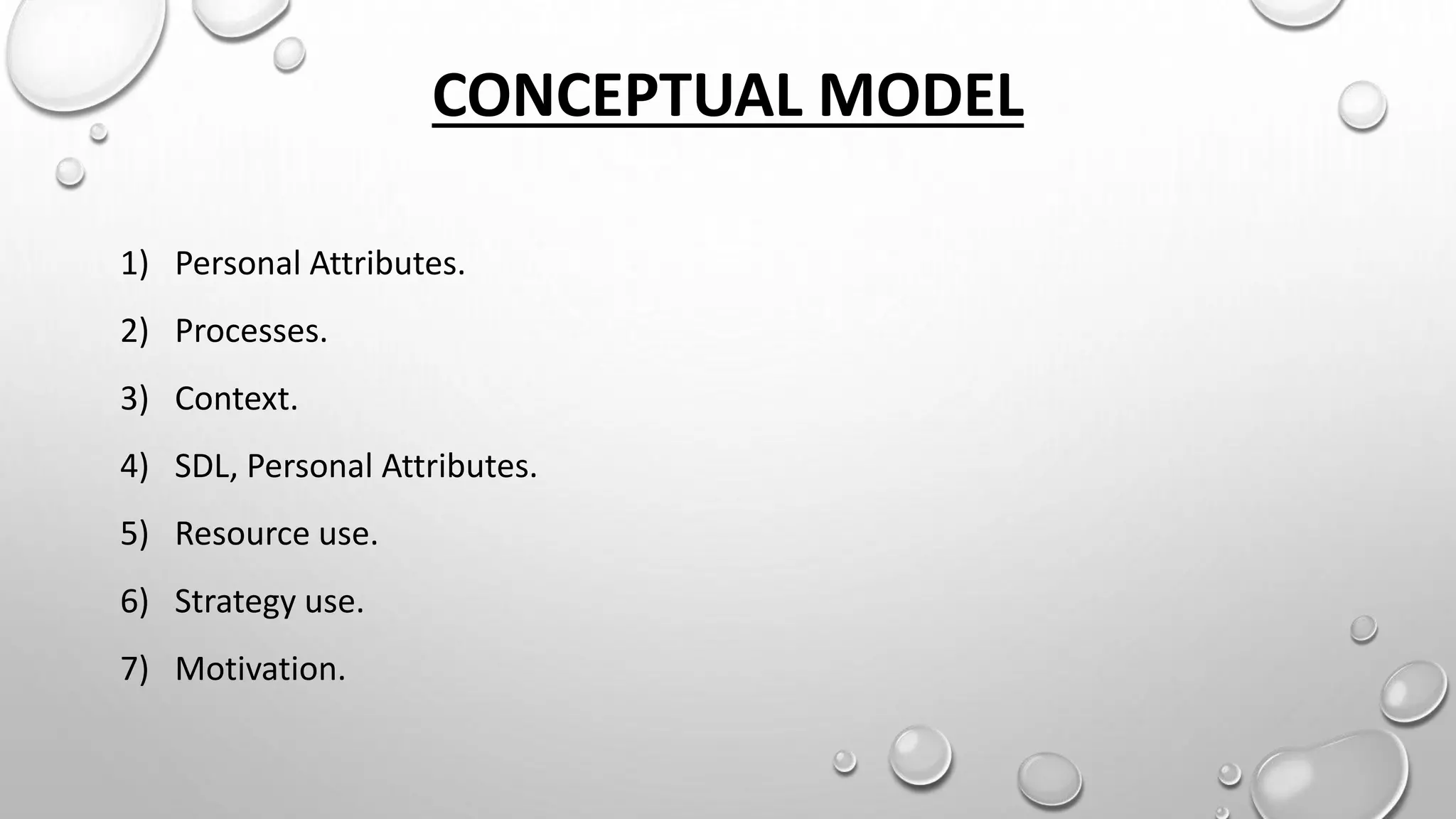
This document discusses role play, programmed instruction, and self-directed learning. It provides definitions and objectives of role play, the history and principles of programmed instruction, and the key principles and skills required for self-directed learning. Role play is defined as assuming roles to act out problems and develop skills. Programmed instruction breaks learning down into small steps and uses reinforcement. Self-directed learning involves learners taking initiative for their own learning through goal setting, resources, and evaluation.