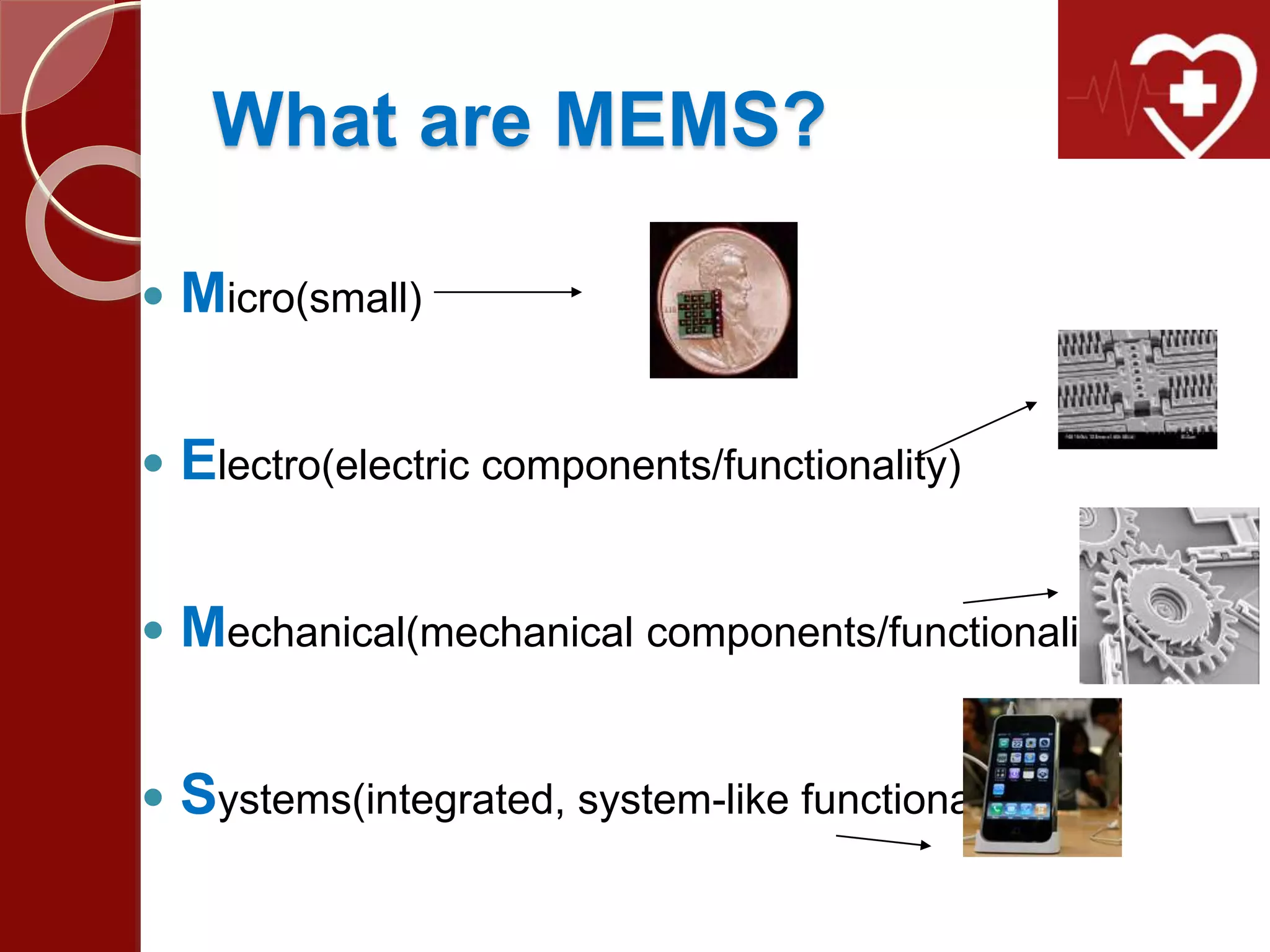
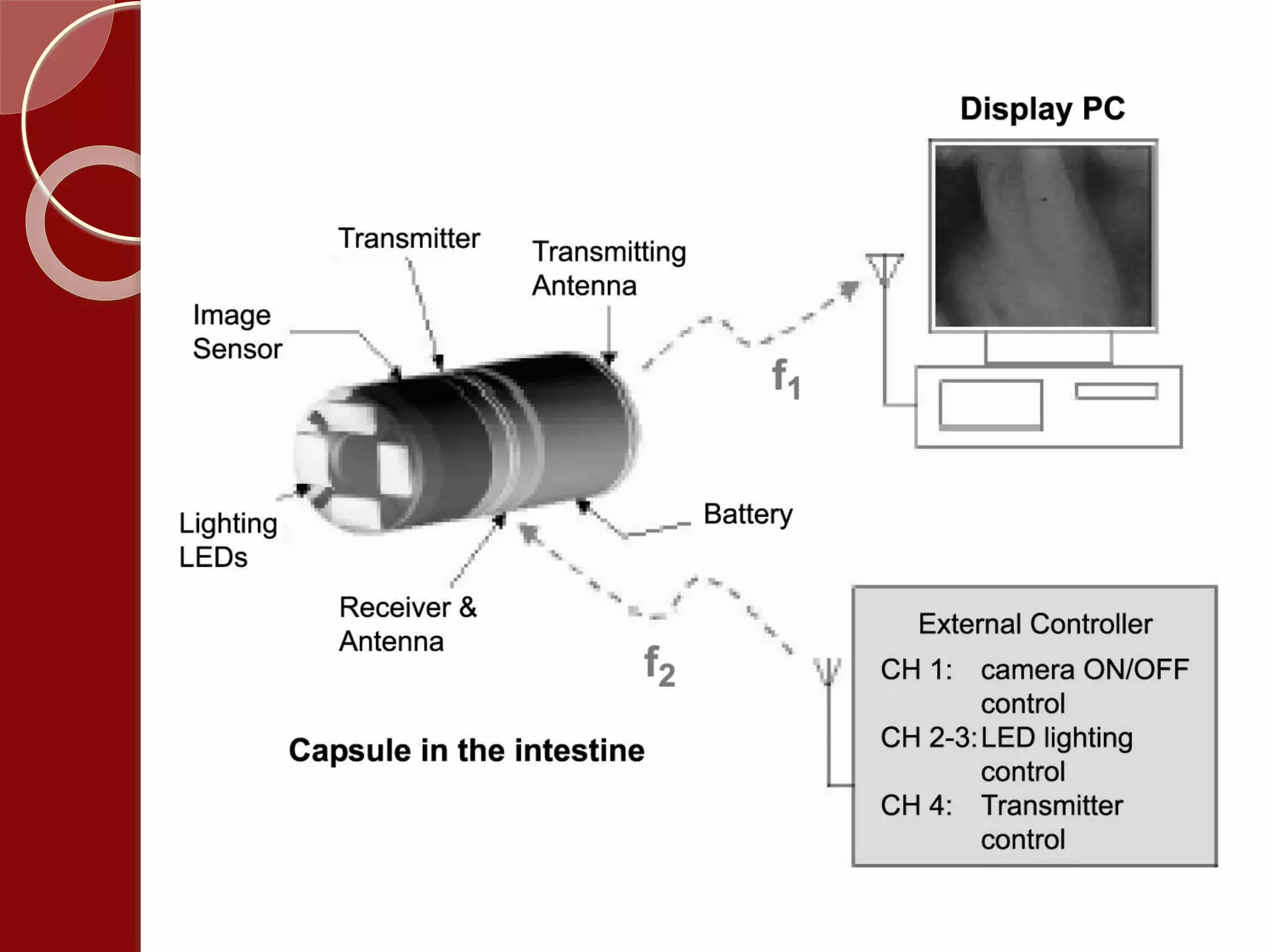
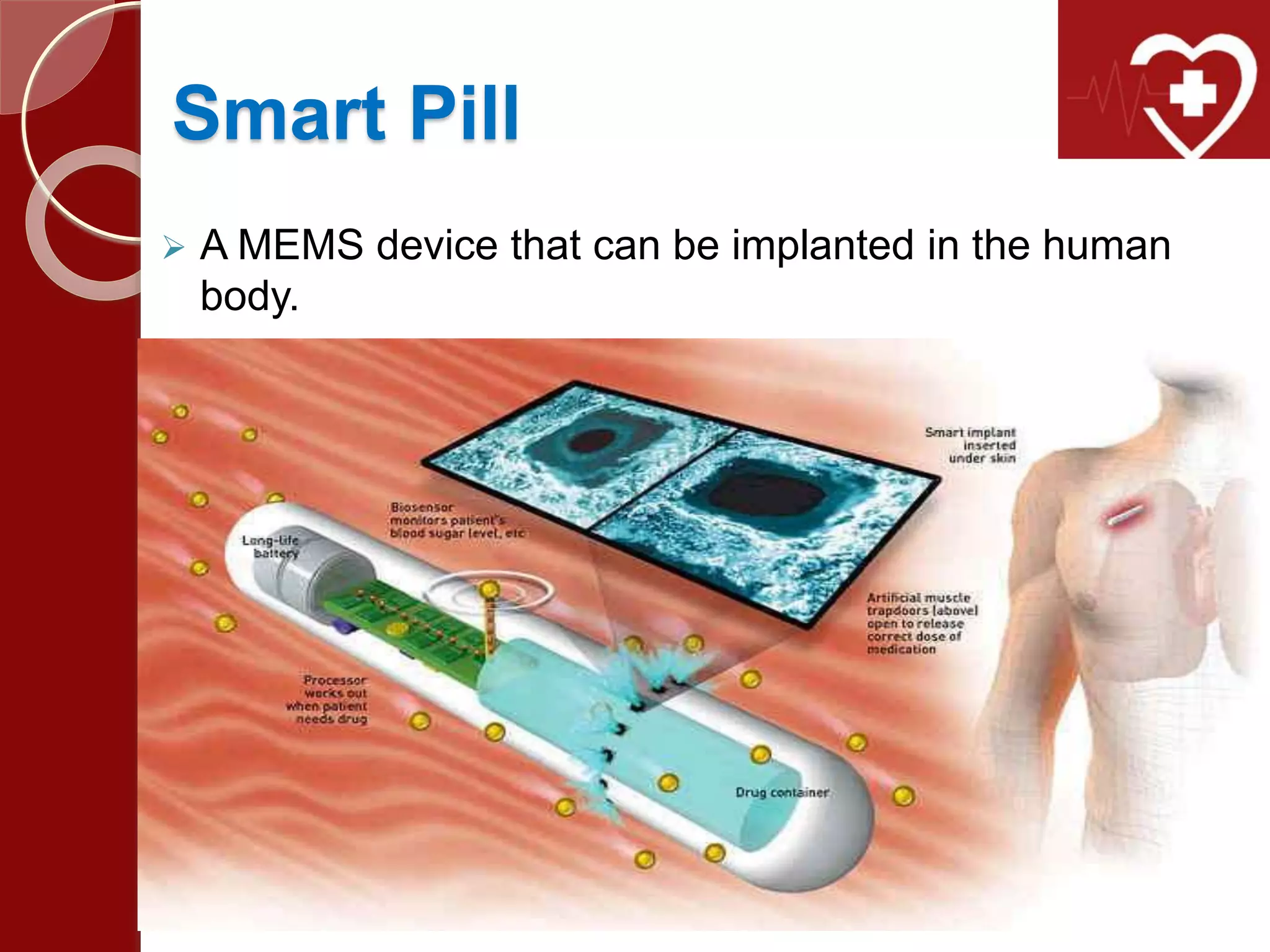
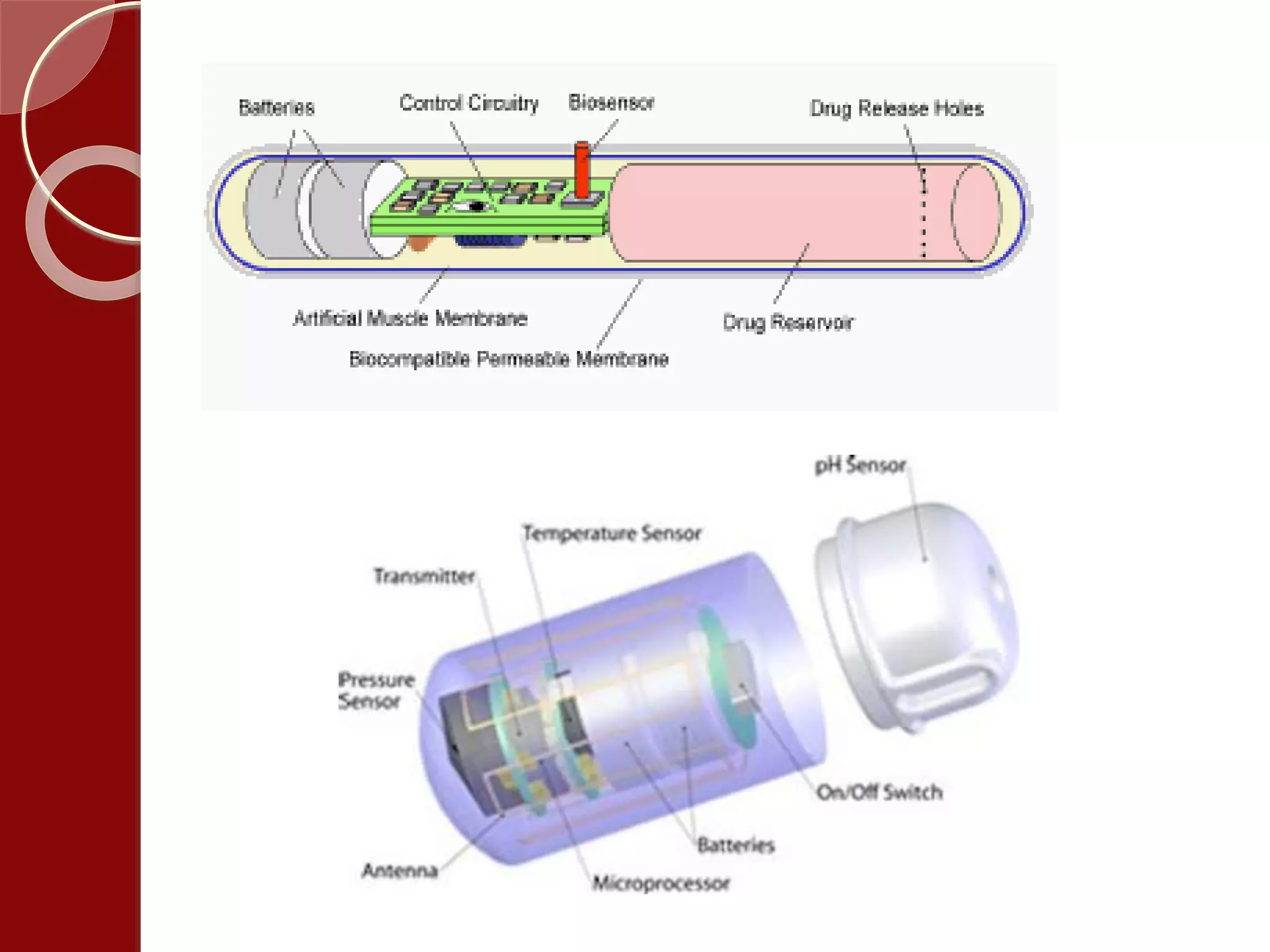
MEMS combines microscale mechanical and electrical components to create integrated systems. In medical applications, MEMS enables new endoscopy devices like a "lab on a pill" with a camera and sensors to view the entire small intestine without sedation. MEMS also allows for smart pills that can automatically deliver drugs on demand when implanted in the body. MEMS technology is expanding what is possible in both sensing environments and controlling systems by merging small sensors and actuators with information processing.