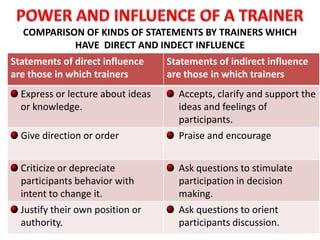
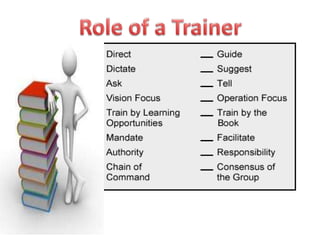
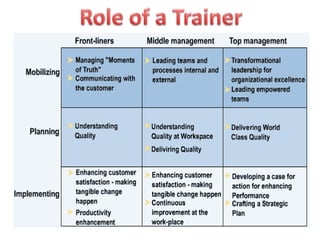
The document outlines the major competencies required of trainers which include presentation skills, business skills, and content development skills. It then discusses technical competencies such as understanding adult learning, career development theories, and computer competence. Business competencies involve budgeting, understanding organization behavior, and organization development theories. Interpersonal competencies include coaching, feedback, group processes, and relationship building. Intellectual competencies are data reduction, information search, and visioning. The document also compares direct and indirect influences of trainer statements and outlines the unique roles of a trainer.