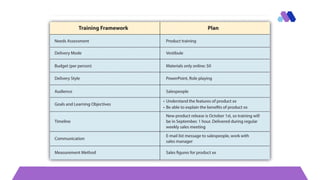
The document discusses the significance of training and development in human resource management, emphasizing its role in enhancing employee skills, improving job performance, and fostering organizational effectiveness. It outlines various training methods, objectives, and the design and evaluation of training programs, including assessments at organizational, occupational, and individual levels. Additionally, it highlights the importance of aligning training delivery methods with employee learning styles and organizational needs while considering factors such as budget and content development.