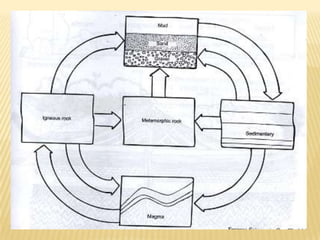
There are three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, either underground as intrusive igneous rocks or on the surface as extrusive igneous rocks. Sedimentary rocks form from the compaction and cementation of sediments. Metamorphic rocks were originally igneous or sedimentary rocks that were changed by heat and pressure in the Earth. Examples are provided for each rock type.