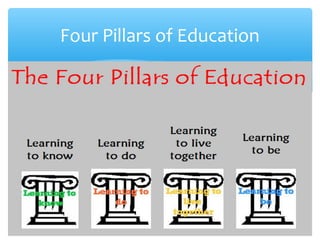
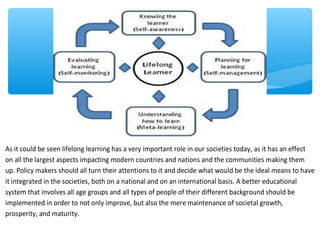
Lifelong learning is the concept that learning should continue throughout a person's life across formal and informal contexts. International organizations like UNESCO, the OECD, and the EU have promoted lifelong learning as important for both personal and economic reasons. Lifelong learning encompasses learning from childhood through old age through formal education as well as informal learning experiences. Key aspects of lifelong learning include learning to know, learning to do, learning to live together, and learning to be as outlined in the Delors report. Information literacy is also closely related to lifelong learning as it enables people to learn independently throughout their lives.