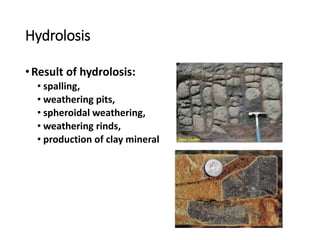
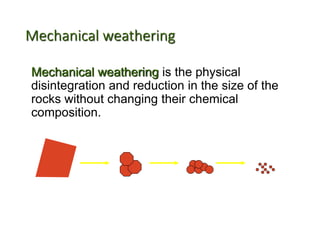
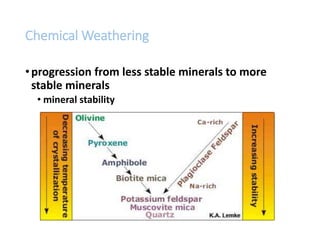
The document discusses weathering, which is the breakdown of rock material into smaller fragments and involves three main types: mechanical, chemical, and biological weathering. Mechanical weathering occurs without changing the chemical composition of rocks, while chemical weathering involves reactions that lead to new minerals and soluble salts. Biological weathering is driven by the activities of organisms that facilitate rock breakdown through various processes such as root wedging, burrowing, and acid production from decaying materials.

























![Hydrolysis
• The reaction of any substance with water.
• Water molecules dissociate to form hydrogen (H-)
and hydroxyl (OH-) ions.
• Hydrogen ion attacks and replaces other ions.
• Silicates are decomposed primarily by this process.
• 2KAlSi3O8 + 2(H+ + HCO3
-) + H2O Al2Si2O5(OH)4
+2K+ + 2HCO3
- + 4SiO2
• Potassium Feldspar + carbonic acid + water
kaolinite (residual clay) + [potassium ion + bicarbonate
ion + silica (in solution)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weatheringpaleozoic-191031190522/85/Rock-Weathering-28-320.jpg)