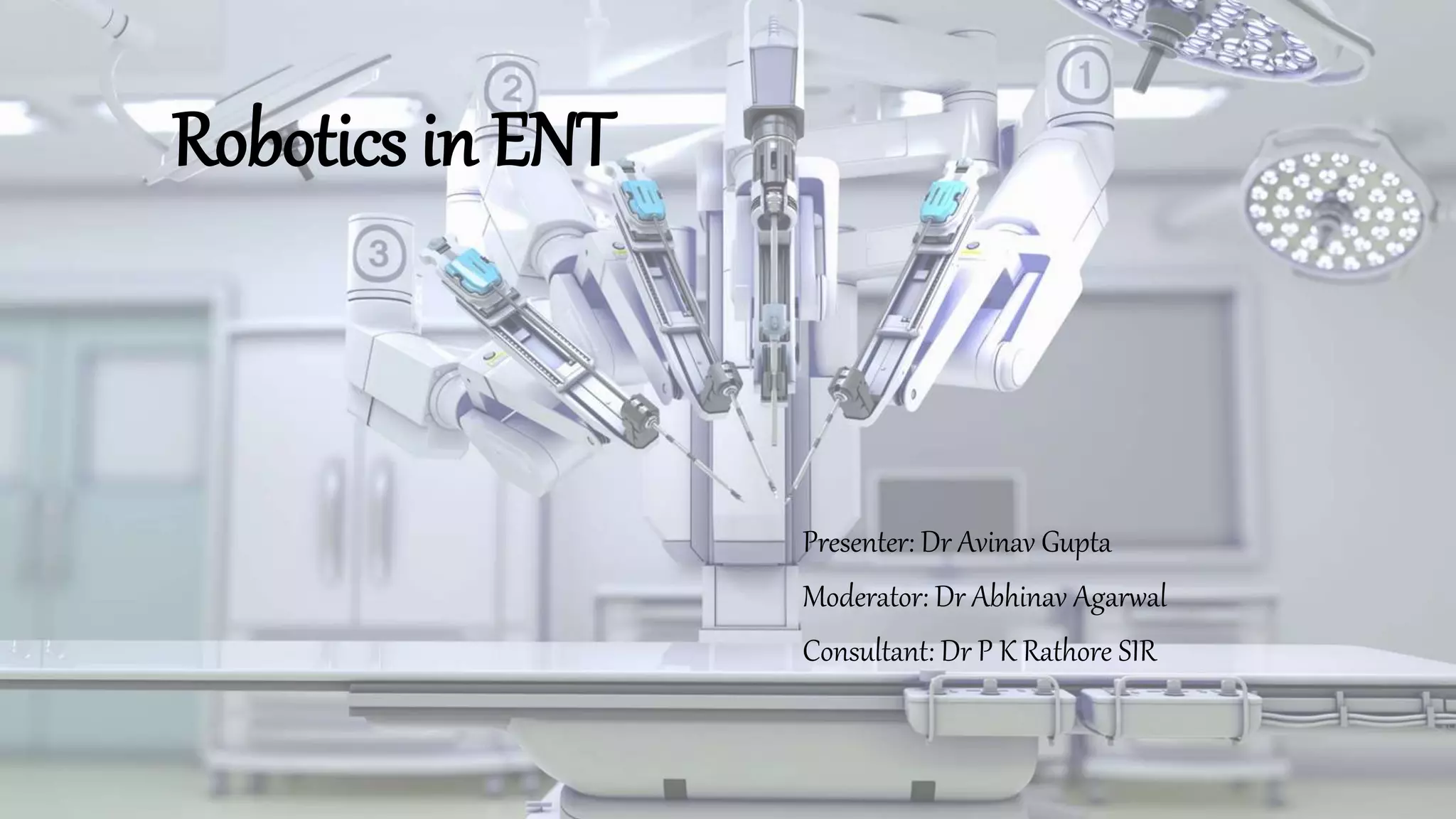
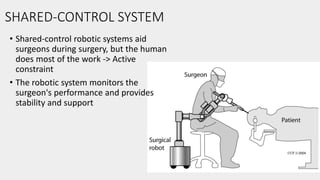
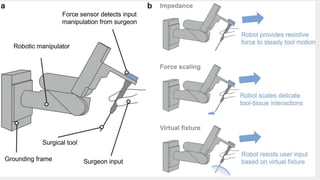
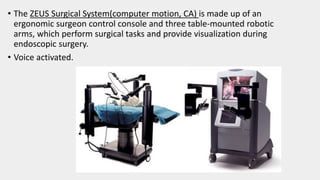
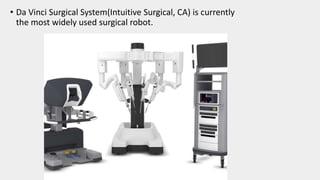
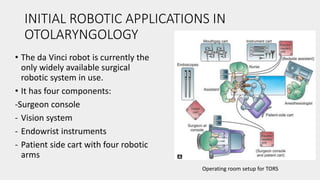
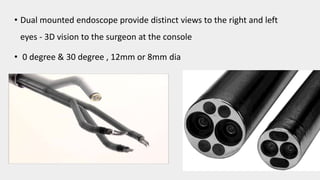
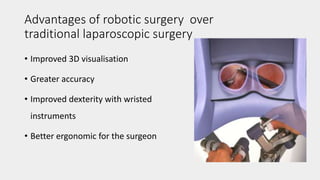
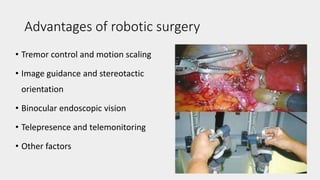
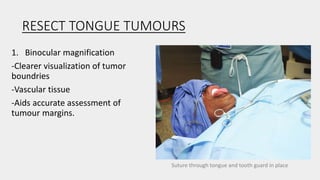
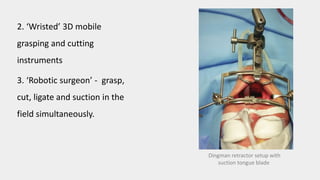
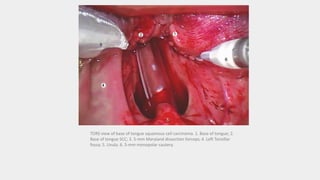
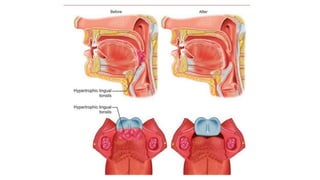
This document discusses the history and applications of robotics in ENT surgery. It begins with definitions of medical robots and an overview of their history. It then focuses on specific ENT applications including:
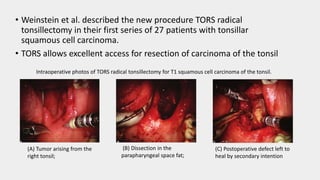
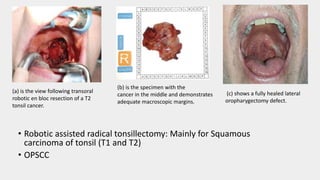
1) TORS (Transoral Robotic Surgery) for tumors of the tongue base, tonsils, and throat which offers improved visualization and dexterity.
2) Robotic surgery for obstructive sleep apnea by allowing minimally invasive resection of excess tongue base tissue.
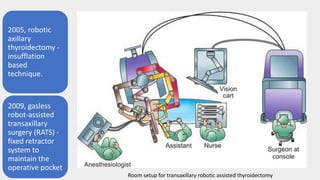
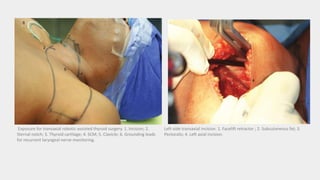
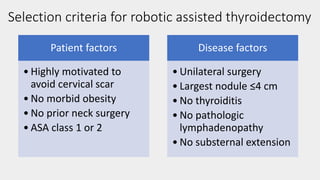
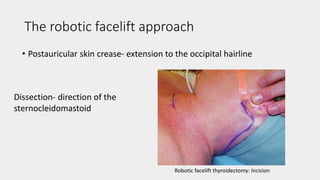
3) Robotic thyroidectomy techniques like RATS (Robotic Assisted Thyroidectomy) and robotic facelift thyroidectomy which allow smaller incisions.
4) Potential future applications in rhin