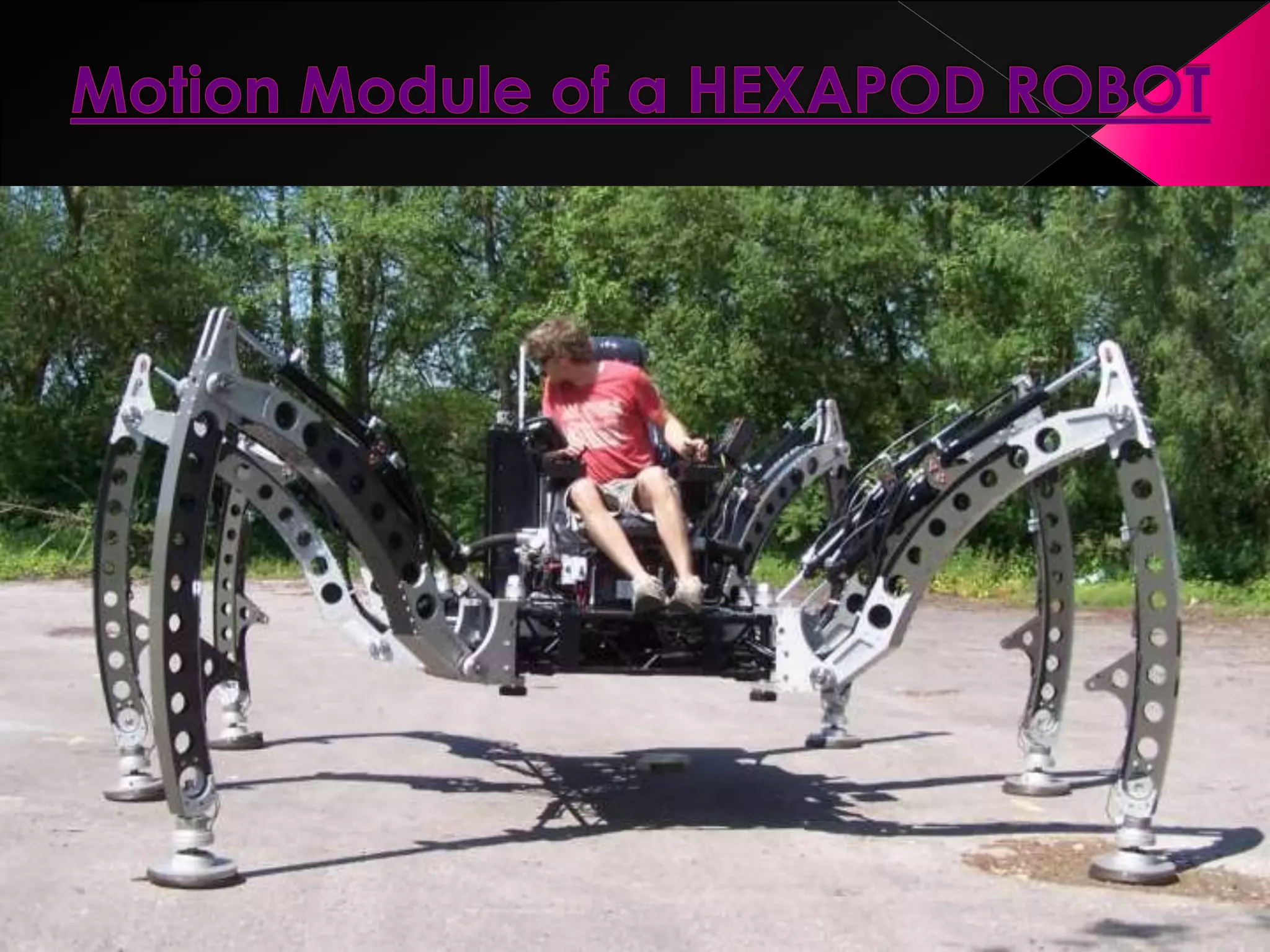
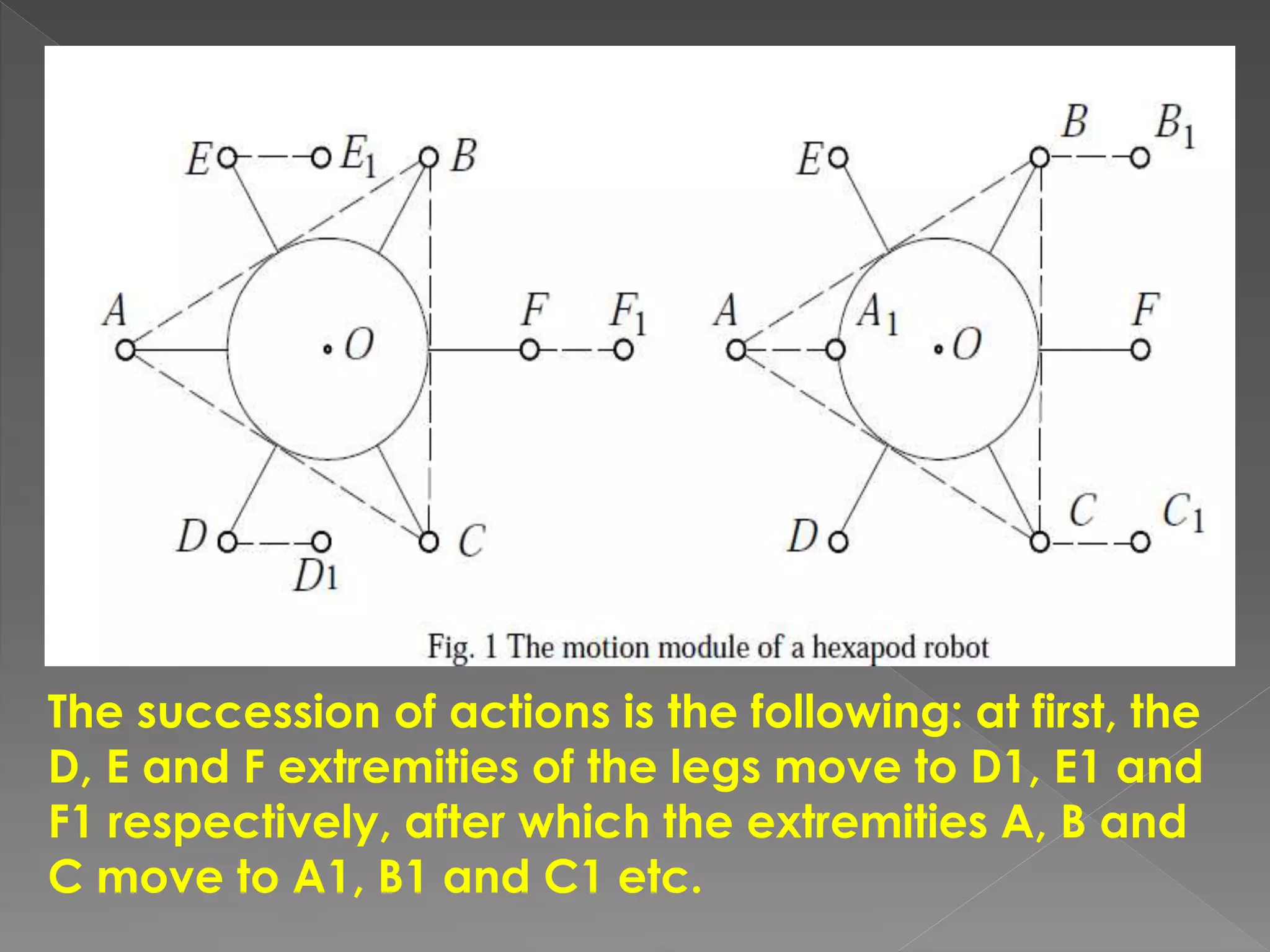
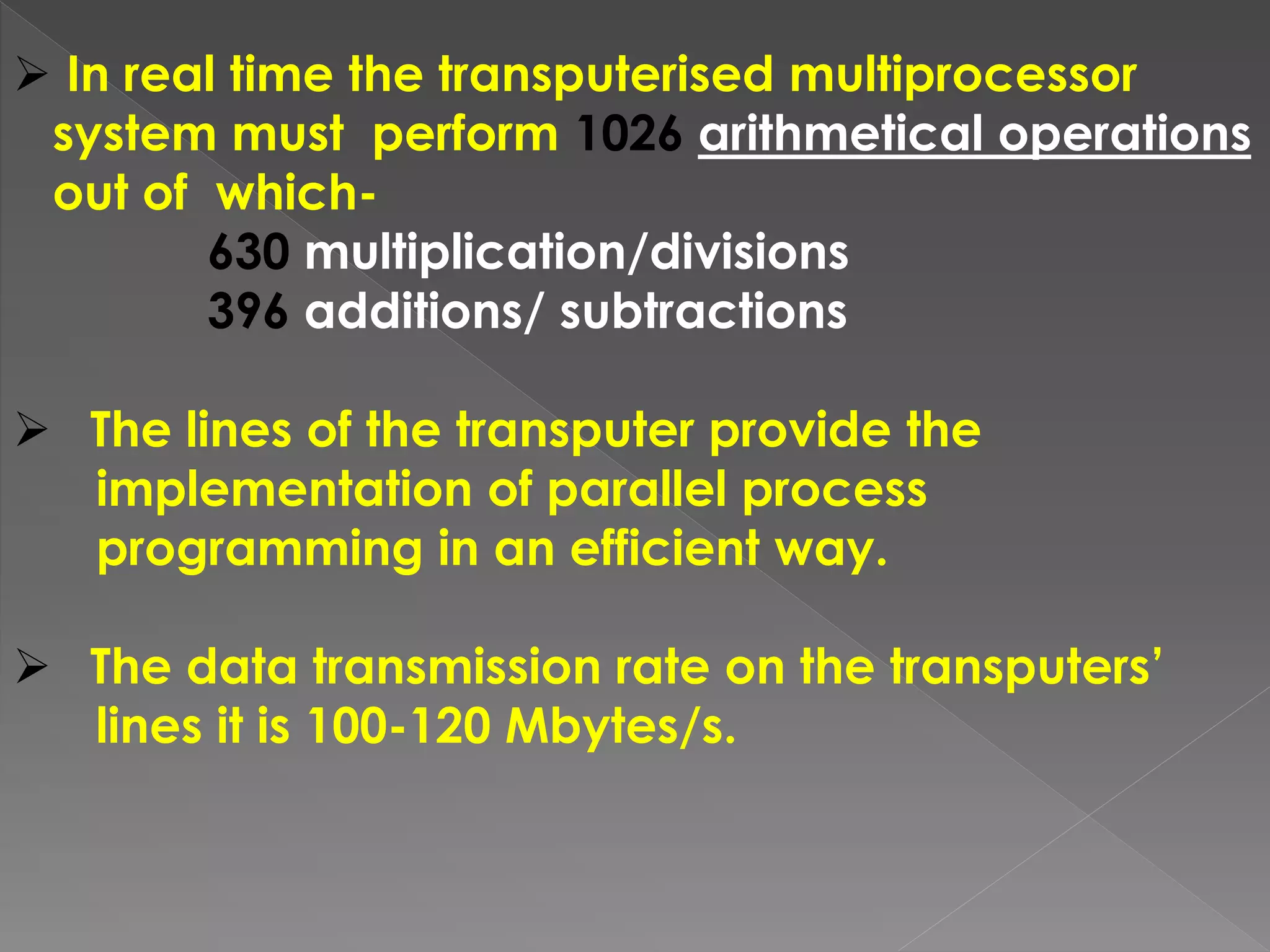
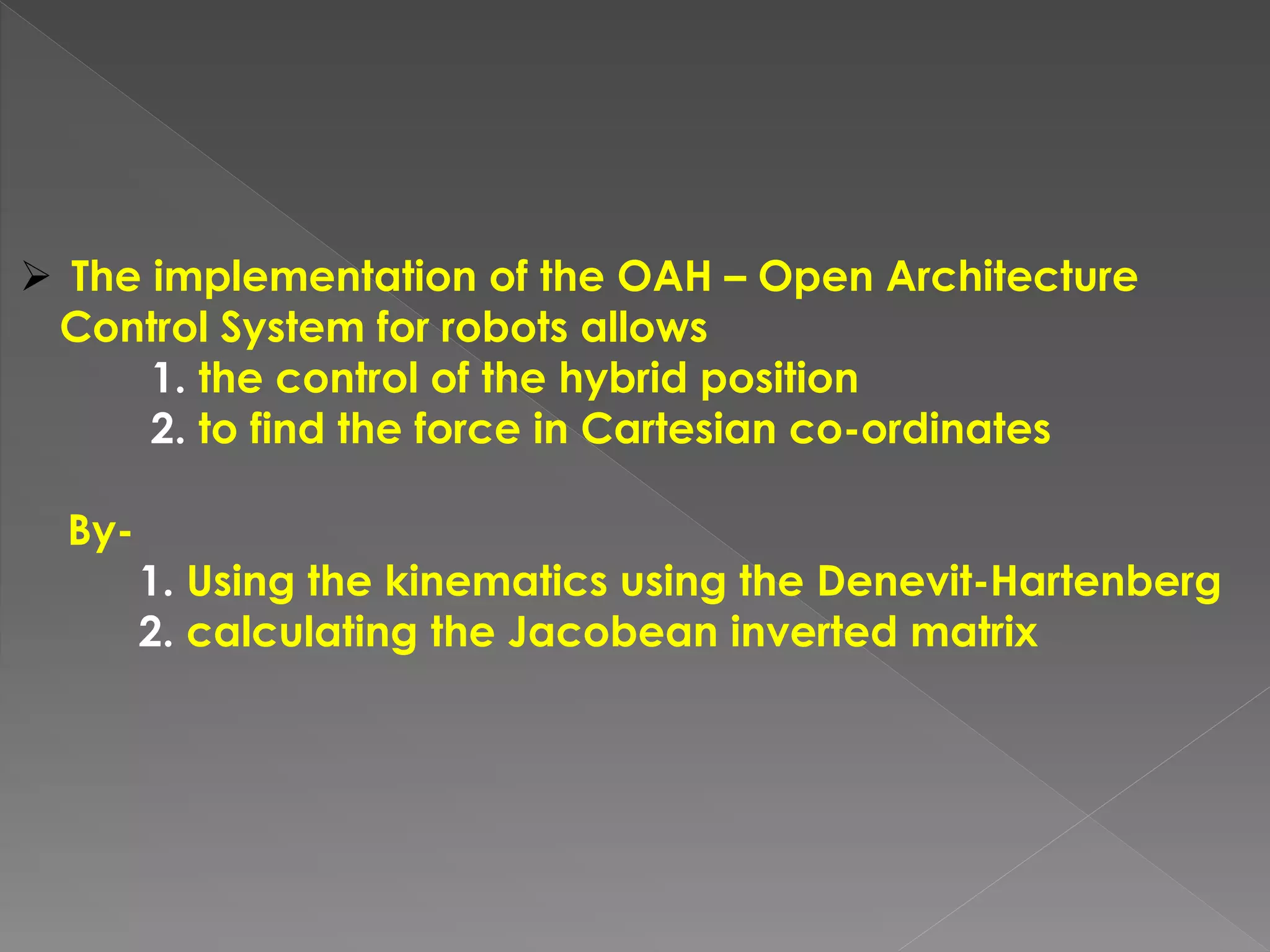
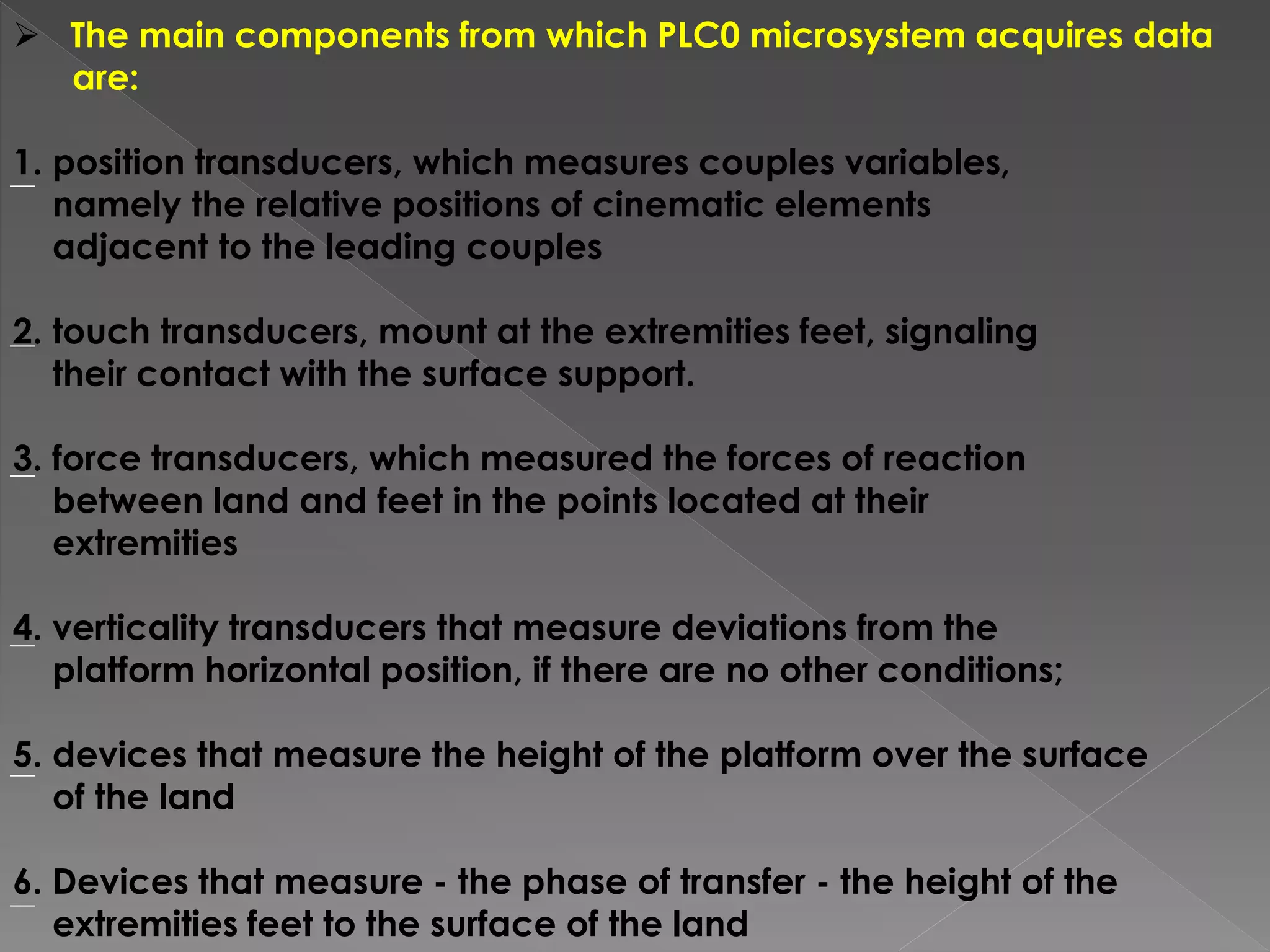
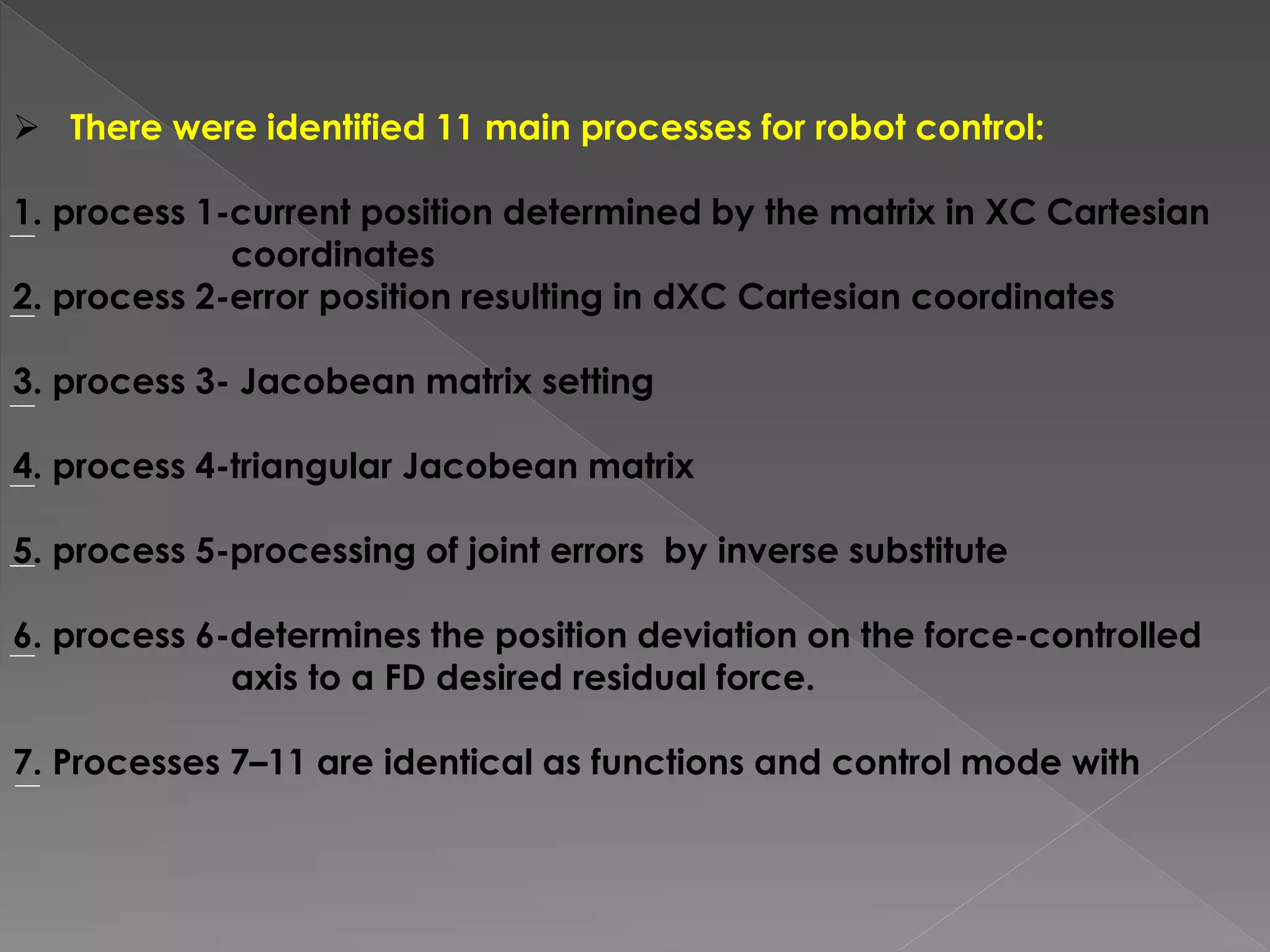
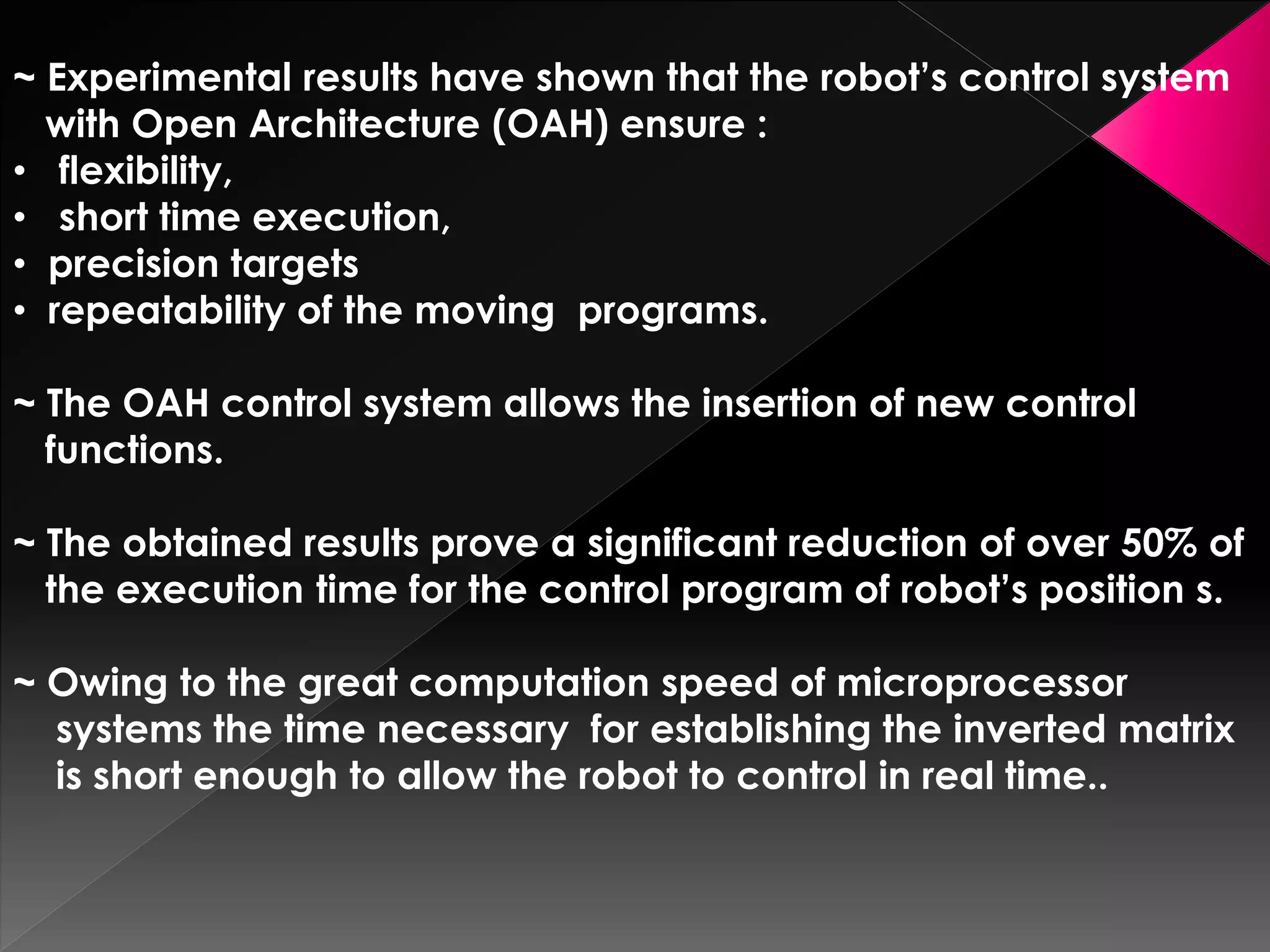
This document discusses a multi-microprocessor system for controlling the position and force of a walking robot in real time. It presents the implementation of an open architecture system that uses forward and inverse kinematics to control the robot's position in Cartesian coordinates. Experimental results showed that the open architecture control system ensured flexibility, short execution time, precision targeting and repeatability of movement programs compared to a single microprocessor system.