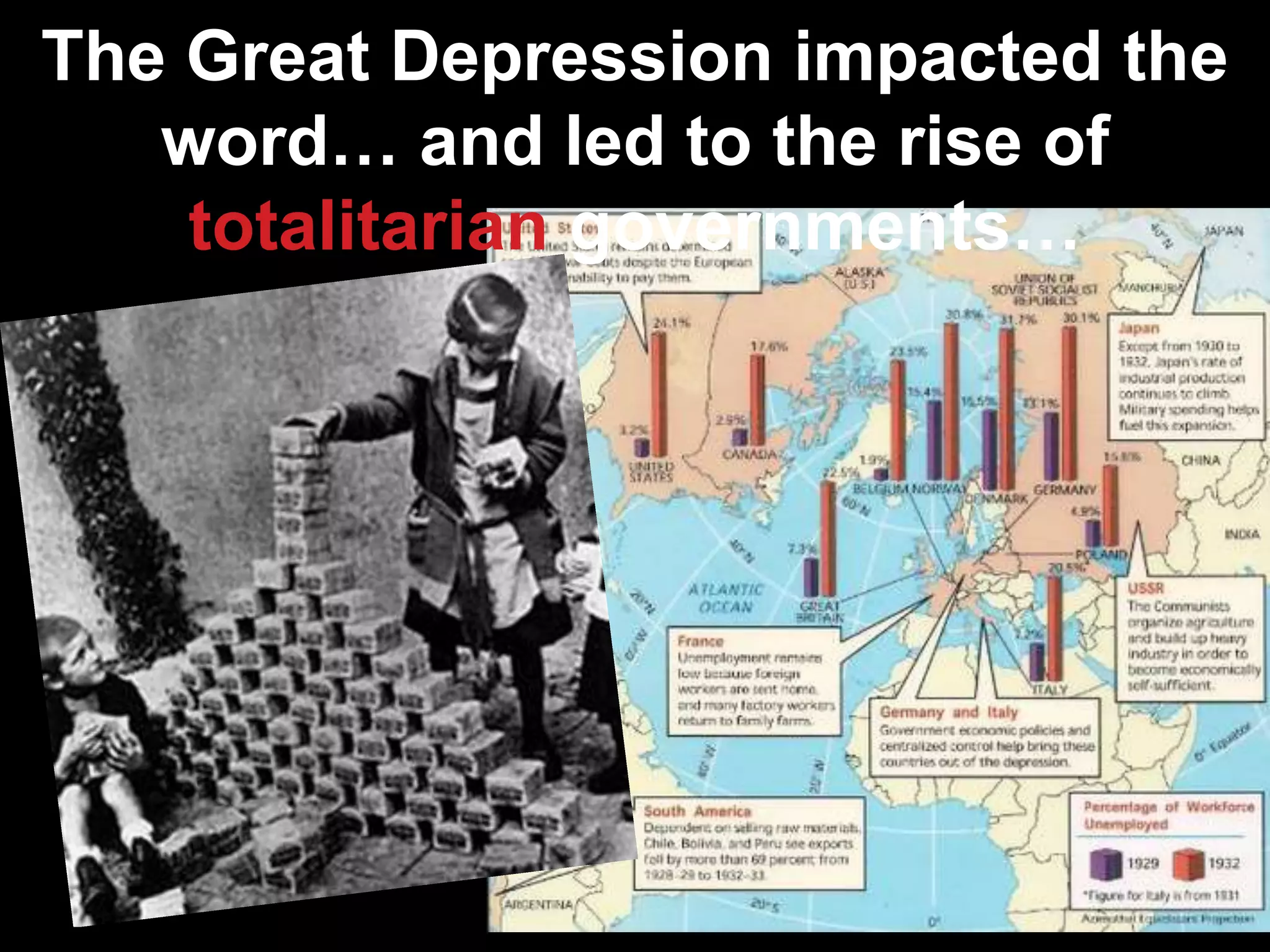
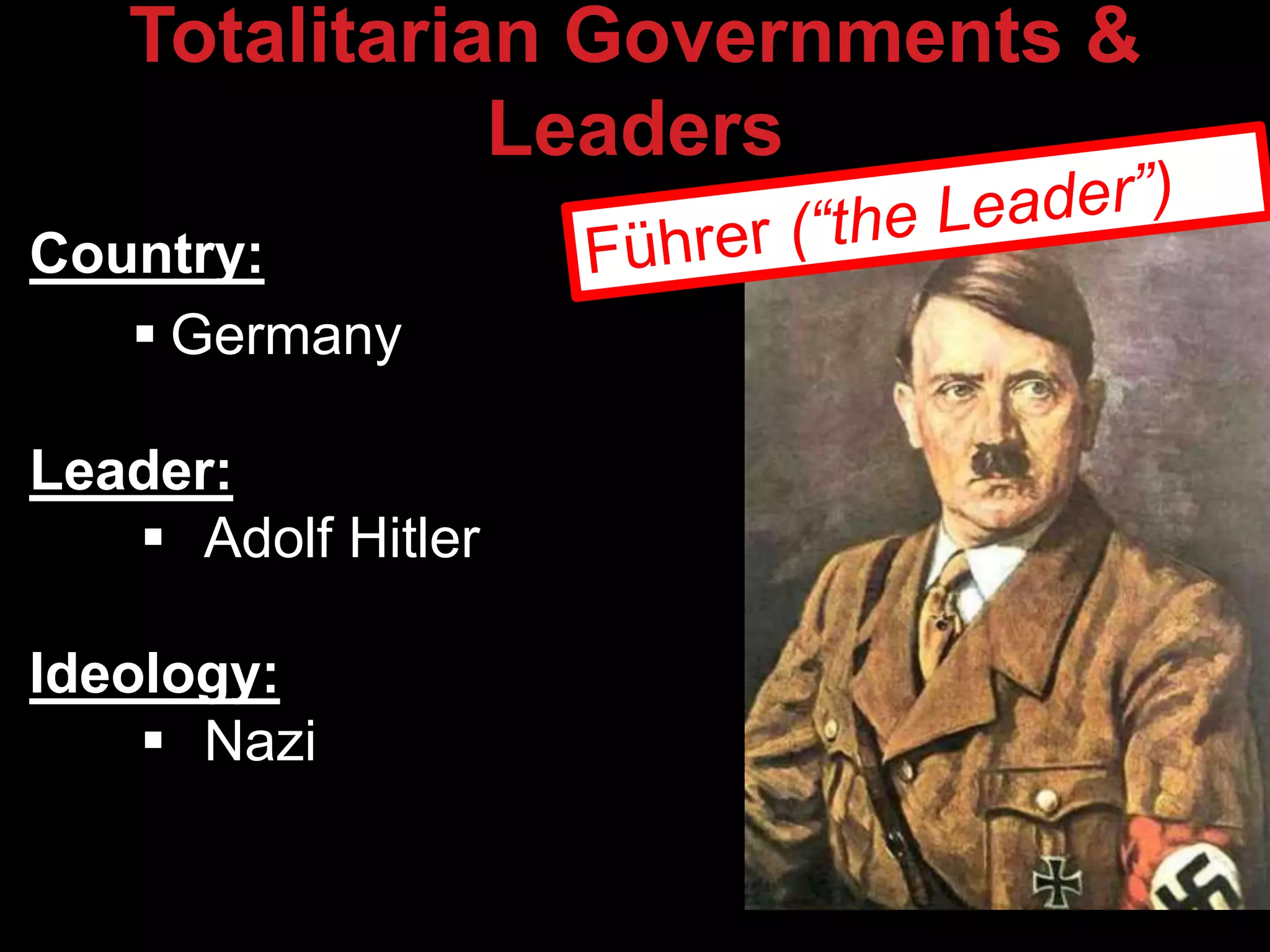
The document discusses the rise of totalitarian governments in Germany, Italy, Japan, and the Soviet Union in the 1930s-1940s and their aggressive actions which led countries like the UK and France to form an Allied alliance. It also discusses how the US initially pursued isolationism but began providing aid to the UK through Lend-Lease and faced growing threats from Japan in Asia, culminating in the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 which caused the US to enter World War 2 by declaring war on Japan.