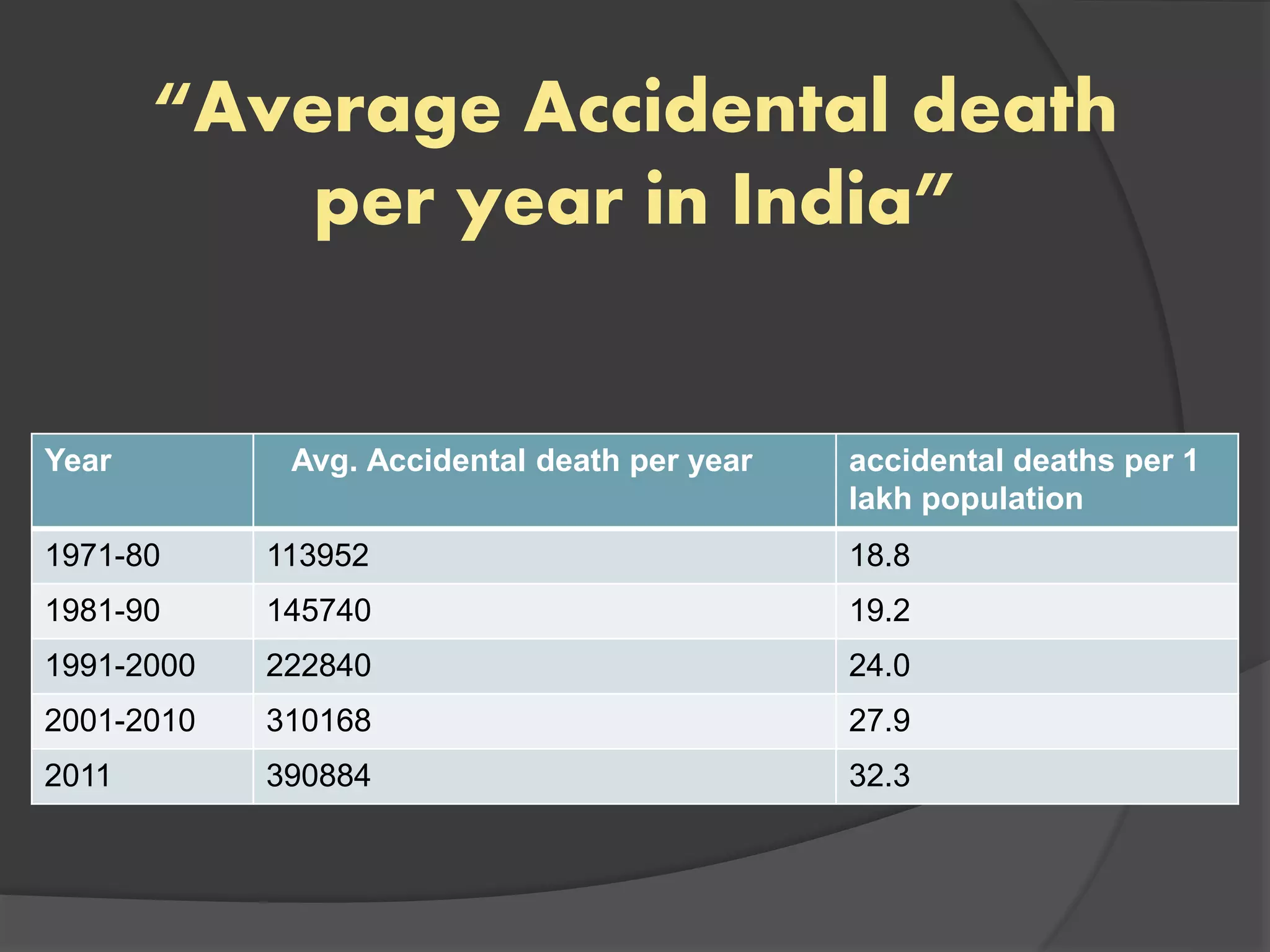
This document discusses road safety issues in India and proposes improvements. It notes that over 490,000 accidents occurred in India in 2011 resulting in 142,485 deaths. The majority of accidents are due to driver error, negligence of safety norms, and drunk driving. To address this, the document recommends increasing road safety priorities and funding, improving driver training programs, strengthening enforcement of traffic laws, upgrading road infrastructure, and implementing public awareness campaigns. The goal is to reduce accidents by changing policies and promoting best practices for road and driver safety across India.























![Reference
[1] Benegal et al. Alcohol and injury in emergency departments:summary of
the report from the WHO collaborative study on alcohol and injuries (in press).
by the WHO Collaborative Study Group on Alcohol and Injuries.
[2] Crompton RP et al. Crash risk of alcohol- impaired driving. In: Mayhew DR,
Dussault C, eds.Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Alcohol,
Drugs and Traffic
Safety, Montreal,4–9 August 2002. Montreal. Societe del’ assurance
automobile du Quebec, 2002:39–44.
[3] .Bahadur. A.P,Former Chief Engineer,MORT&H,NHAI presented at 6th IRF
Regional Conference-Road Safety Strategy in India.
[4] Chris Baguley Road Safety Policy and Programme (for India) Road User
Behaviour in developing Countries,
[5] Dr.Gangapathyay.S.,CRRI,India ,presented at 6th IRF Regional
Conference- Road Safety Strategy in India.
[6] Haddon, Suchman and Klein “Accident Research Methods and
approaches”, Harper and Row Publishers,New York.
[7]. Loomis .T.A, West. T.C. “The Influence of alcohol On Automobile Driving”
Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 19:1:30-46,March 1958
[8] Kjell Bjerver,B.M., Leonard Goldberg “Effect of Alcohol Ingestion on Driving
Ability” Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 19:1:30-46,March1958.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roadsafety-160416200303/75/Road-safety-and-Improvements-in-India-25-2048.jpg)

