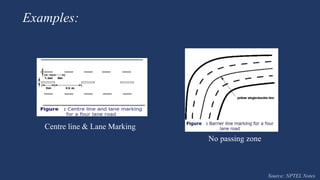
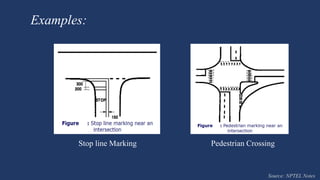
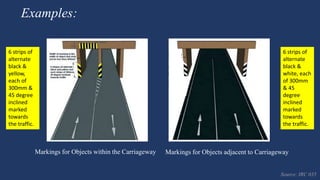
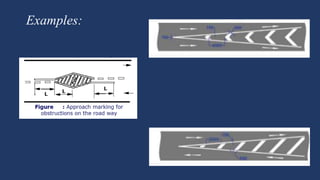
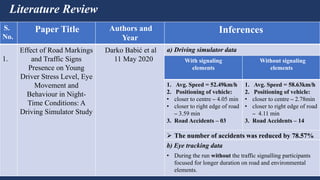
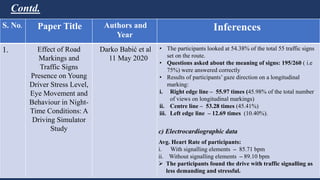
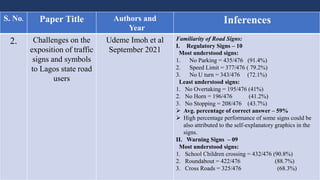
The document summarizes traffic signs and road markings. It describes different types of traffic signs like regulatory, warning, and informative signs. It also discusses various types of road markings like longitudinal markings, transverse markings, object markings, and word messages. It then reviews two research papers about the effects of traffic signs and familiarity of drivers with signs and markings in Lagos, Nigeria. The studies found that signs reduced accidents but familiarity with markings was low, around 30%.