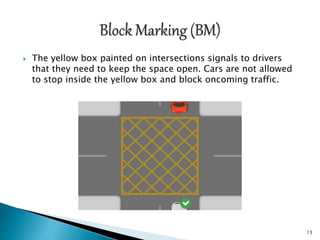
The document outlines various types of pavement markings used for traffic management, including longitudinal, transverse, hazard, block, and directional markings. Each type serves specific purposes, such as separating traffic lanes, indicating passing zones, and guiding vehicles at intersections and pedestrian crossings. The proper use and maintenance of these markings are essential for road safety and compliance with traffic regulations.