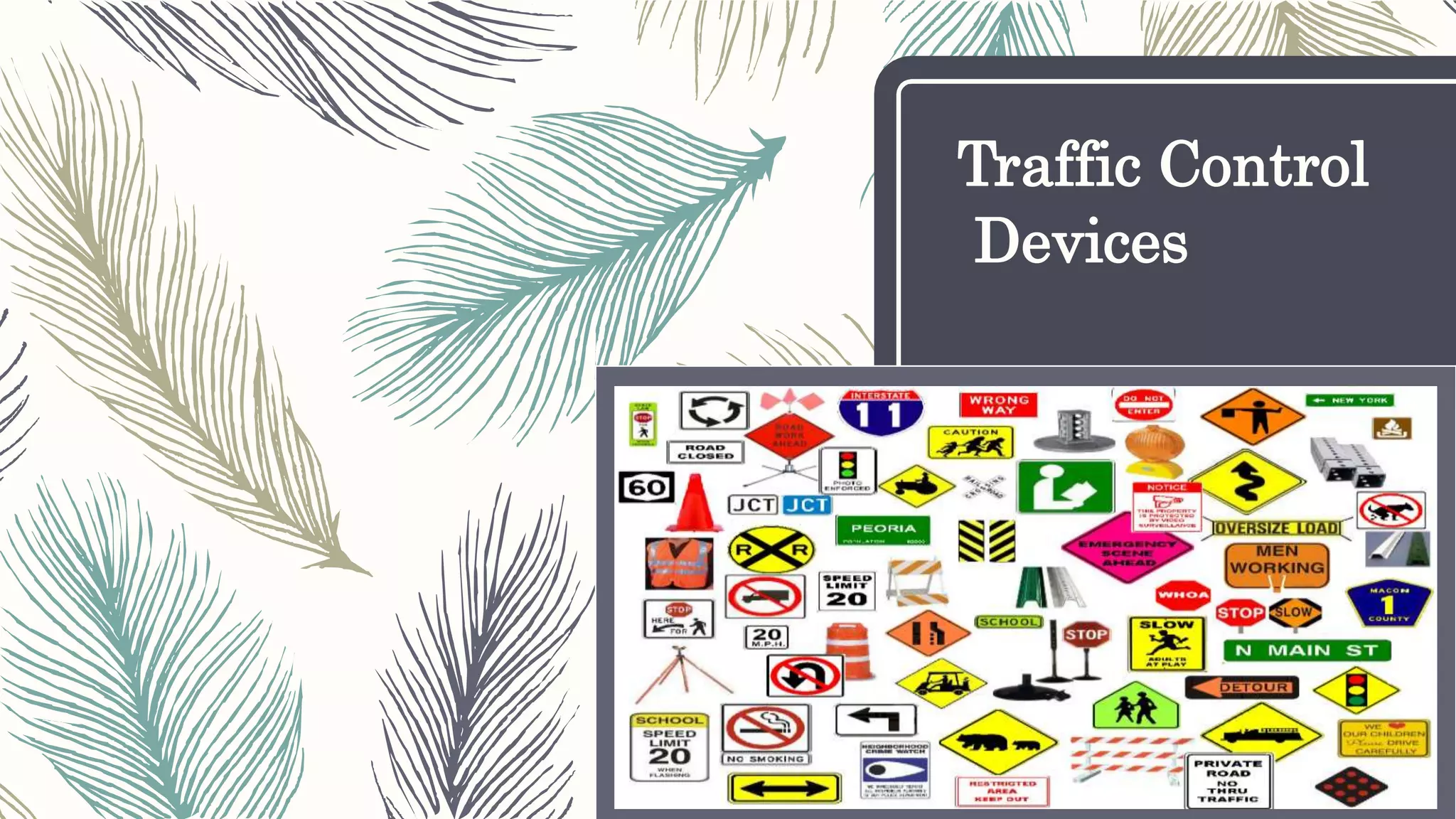
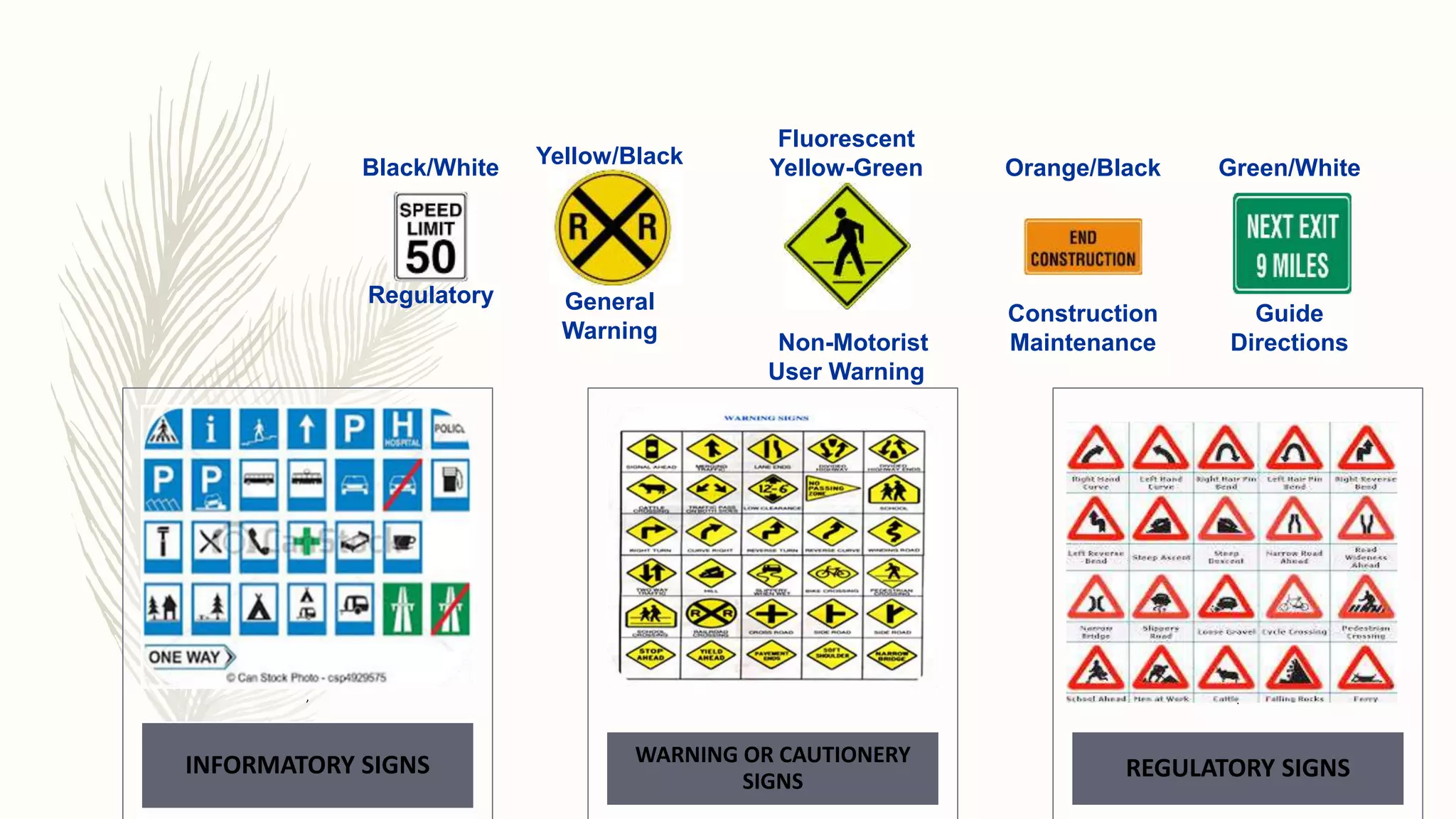
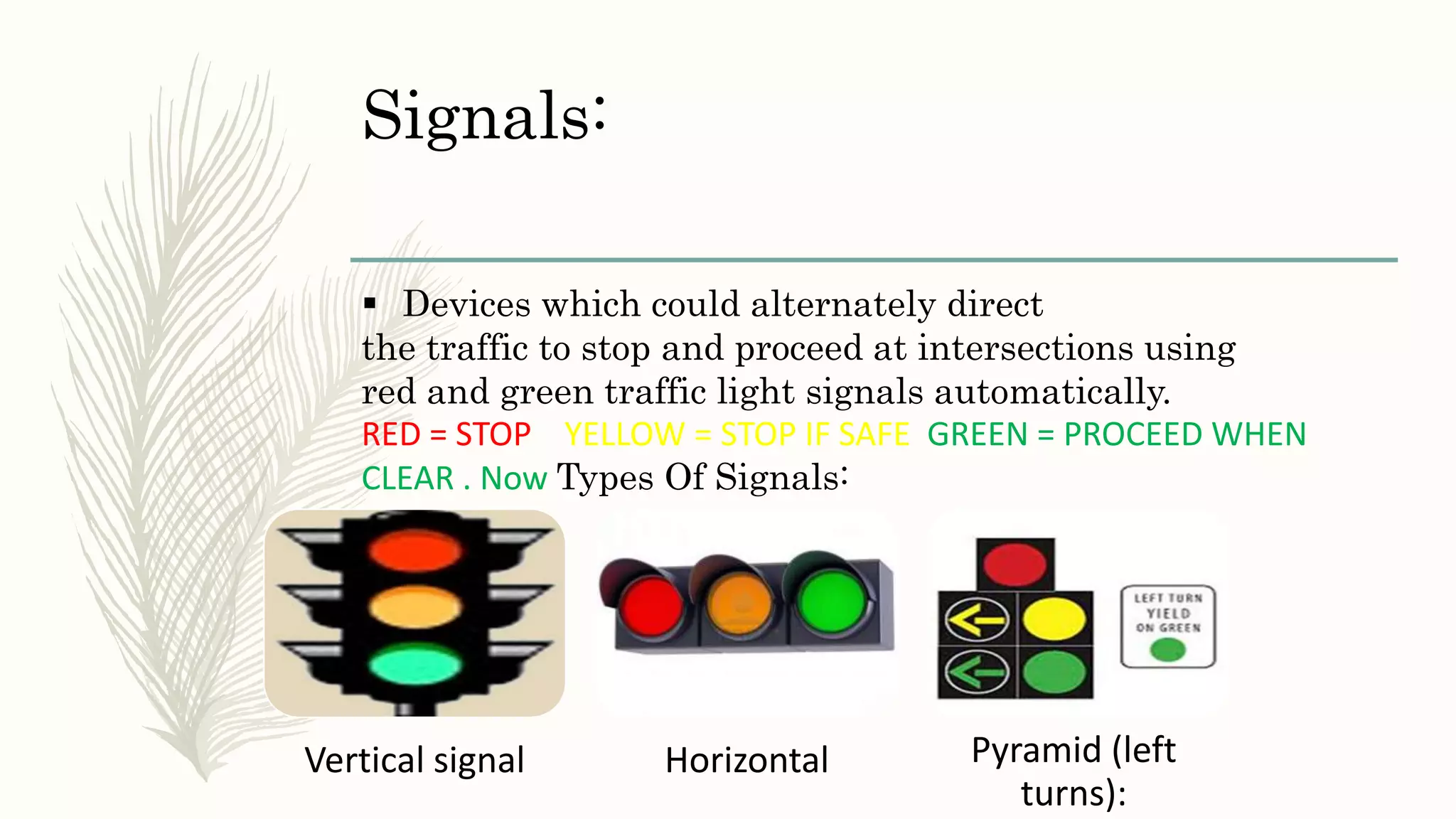
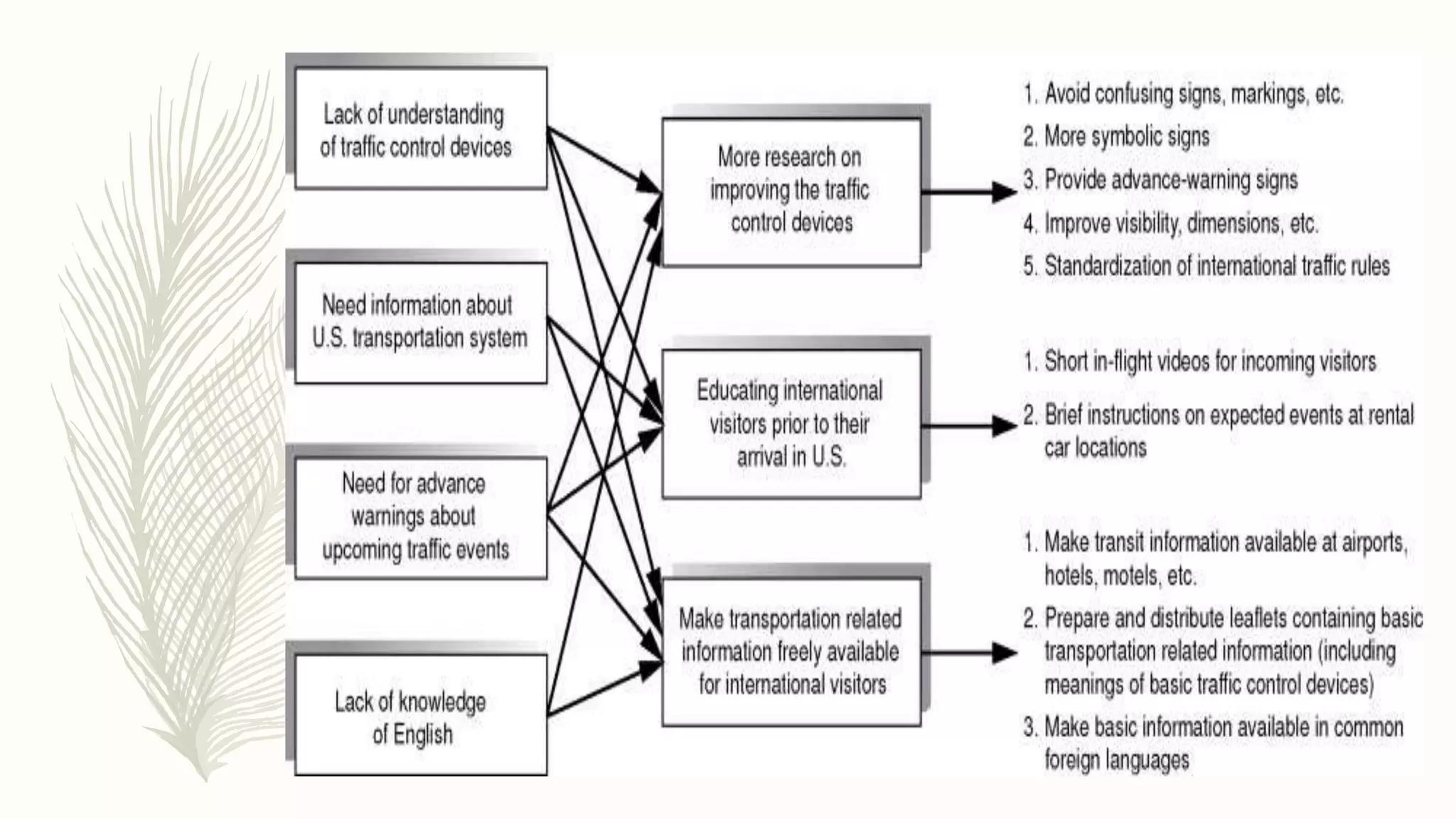
This document describes different types of traffic control devices used to regulate traffic flow and ensure safety. It outlines various sign types like regulatory, warning, and informational signs. It also discusses traffic signals, road markings like solid and dashed lines, arrows, and colors that impart instructions. Pavement markings are described for different road configurations. Traffic islands are defined as raised areas that physically guide vehicle movement. In summary, the document provides an overview of common traffic control devices and how they inform and direct drivers, pedestrians, and bicyclists.